WORKING OF SEM: SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
- 1. MOUSAM CHOUDHURY Amity Institute of Nanotechnology Amity University, Noida . SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
- 2. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY - A BASIC MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY EQUIPMENT FOR POLYMER COMPOSITES AND NANOCOMPOSITES
- 3. Electron microscope divided into the following Basic components :- 1- Illumination system. 2- Imaging system. 3- Specimen stage. 4- Vacuum pump system. 5- Image recording system.
- 4. x-rays composition backscattered e's microstructure secondary e's microstructure elastically scattered e's crystallographic structure inelastically scattered e's composition transmitted e's microstructure SIGNALS IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
- 5. TYPES OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPY FOR POLYMER COMPOSITES • SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (SEM) • TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM)
- 7. SEM - Scanning Electron Microscopy • tiny electron beam scanned across surface of specimen • backscattered or secondary electrons detected • signal output to synchronized display
- 10. Effects of increasing voltage in electron gun: •Resolution increased ( decreased) •Penetration increases •Specimen charging increases (insulators) •Specimen damage increases •Image contrast decreases = h/(2melectronqVo + q2Vo2/c2))1/2 VOLTAGE IN ELECTRON GUN:
- 11. FIELD EMISSION ELECTRON SOURCE: High electric field at very sharp tip causes electrons to "tunnel" maybe
- 12. FIELD EMISSION ELECTRON SOURCE:
- 13. ELECTRIC FIELD High electric field at very sharp tip causes electrons to "tunnel" cool tip ——> smaller E in beam improved coherence many electrons from small tip ——> finer probe size, higher current densities (100X >) problems - high vacuum
- 14. Electrons focused by Lorentz force from electromagnetic field F = qv x B effectively same as optical lenses Lenses are ring-shaped • coils generate magnetic field • electrons pass thru hollow center • lens focal length is continuously variable • apertures control, limit beam LENSES
- 15. Conducting - • little or no preparation • attach to mounting stub for insertion into SEM instrument • may need to provide Conductive path with Ag paint Non-conducting (E.g., Polymers and Plastics)- usually coat with conductive very thin layer (Au, C, Cr) SPECIMEN
- 16. Can examine • fracture surfaces • electronic devices • fibers • coatings • particles etc. TYPES OF SPECIMENS (SOLID/ PARTICLE/ etc)
- 17. •Actually one at a time is preferred •However, four to five can be placed on the stub •The Specimen Holder can be tilted, translated •Specimen size limited by size of sample chamber i.e. the area of the stub No. of Samples
- 18. THAT IS HOW AN IMAGE IS FORMED AND CALLED A MICROGRAPH TYPES OF ELECTRONS FROM SPECIMEN What comes from specimen? Backscattered electrons Secondary electrons Fluorescent X-rays high energy compositional contrast low energy topographic contrastcomposition - EDS Brightness of regions in image increases as atomic number increases (less penetration gives more backscattered electrons)
- 19. BSEs SEs E/Eo 1 Main Electrons accounted for a Micrograph, coming out from specimen • Backscattered electrons • Secondary electrons ELECTRON ENERGY DISTRIBUTION
- 20. Electron Energy up to 30-50 keV annular around incident beam repel secondary electrons with — biased mesh images are more sensitive to •chemical composition (electron yield depends on atomic number) •line of sight necessary BACKSCATTERED ELECTRON DETECTOR - SOLID STATE DETECTOR
- 21. SECONDARY ELECTRON DETECTOR - SCINTILLATION DETECTOR + bias mesh needed in front of detector to attract low energy electrons line of sight unnecessary
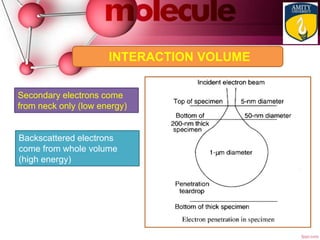
- 22. INTERACTION VOLUME Backscattered electrons come from whole volume (high energy) Secondary electrons come from neck only (low energy)
- 23. Fracture Surface in iron SECONDARY ELECTRONS BACKSCATTERED ELECTRONS CHOOSE CORRECT DETECTOR- TOPOGRAPHY EXAMPLE
- 24. Comes from any kind of interaction with electron beam Topography Composition o Elements o Phases Grain (crystal) orientation Charging affects contrast TYPES OF STUDY USING SEM
- 25. MAGNIFICATION – DETERMINED BY DISTANCE
- 26. RESOLUTION – DETERMINED BY PROBE SIZE
- 27. RESOLUTION – PROBE DIAMETER & PROBE SIZE
- 28. d = depth of field = required spatial resolution a = convergence angle d region of image in focus tana 0.5 0.5d d For small angles, tana = a d a Can control depth of field (d) with convergence angle (a) DEPTH OF FIELD
- 29. DEPTH OF FIELD WD Rap tana Rap WD
- 30. Thank you