Models, Programs and Executable UML
- 1. Models, Programs and Executable UML Presented at the First International Workshop on Combined Object-Oriented Modeling and Programming Ed Seidewitz
- 2. Models and Programs What is a model? A model is a set of statements in a modeling language about some system under study or domain. * What is a program? A program is a specification for a computation to be a executed on a computer. * See Ed Seidewitz, “What Models Mean”, IEEE Software, September/October 2003 for more.
- 3. Contentions All programs are models. Executable UML models are programs. Executable UML models are useful.
- 4. 1. All programs are models A program is a model of the specified computation, abstracting away from the details of how the computation is actually executed on a computer. A programming language is a modeling language for creating models of execution. Customer customer = customers.get(customerId); if (customer != null ) { int totalBalance = 0; for (Account account: customer.accounts) { totalBalance += account.balance; } } … and a value called “totalBalance”… … that is iteratively computed to be the sum of the customer’s account balances. There is a customer identified by “customerId”… Java
- 5. OO programs are also domain models public class Bank { private String bankId; private Set<Customer> customers; private Set<Account> accounts; ... } public class Customer { private String customerId; private Set<Account> accounts; ... } public class Account { private String accountId; private int balance = 0; private Set<Customer> accountOwners; ... } Classes are intended to reflect domain concepts. Fields reflect properties of those concepts… … or relationships with other concepts.
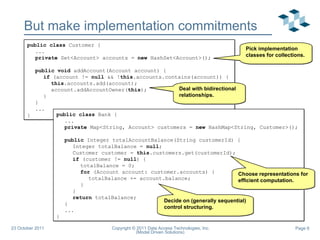
- 6. But make implementation commitments public class Customer { ... private Set<Account> accounts = new HashSet<Account>(); public void addAccount(Account account) { if (account != null && ! this .accounts.contains(account)) { this .accounts.add(account); account.addAccountOwner( this ); } } ... } public class Bank { ... private Map<String, Account> customers = new HashMap<String, Customer>(); public Integer totalAccountBalance(String customerId) { Integer totalBalance = null ; Customer customer = this .customers.get(customerId); if (customer != null ) { totalBalance = 0; for (Account account: customer.accounts) { totalBalance += account.balance; } } return totalBalance; } ... } Pick implementation classes for collections. Deal with bidirectional relationships. Choose representations for efficient computation. Decide on (generally sequential) control structuring.
- 7. 2. Executable UML models are programs UML began as a notation for models of programs. But UML 2 has constructs that allow the specification of Turing-complete computation models. Foundational UML (fUML) provides precise execution semantics. Action Language for fUML (Alf) provides a textual notation. customer = Customer -> select c (c.customerId == customerId); totalBalance = customer.accounts.balance -> reduce '+'; … and a value called “totalBalance” that is sum of the customer’s account balances. There is a customer identified by “customerId”… Alf
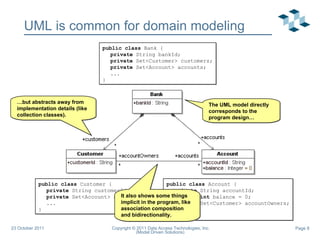
- 8. UML is common for domain modeling public class Bank { private String bankId; private Set<Customer> customers; private Set<Account> accounts; ... } public class Customer { private String customerId; private Set<Account> accounts; ... } public class Account { private String accountId; private int balance = 0; private Set<Customer> accountOwners; ... } The UML model directly corresponds to the program design… … but abstracts away from implementation details (like collection classes). It also shows some things implicit in the program, like association composition and bidirectionality.
- 9. But diagrams are just notation class Bank { public bankId: String; public customers: compose Customer[*]; public accounts: compose Account[*]; } assoc AccountOwnership { public accountOwners: Customer[*]; public accounts: Account[*]; } class Account { public accountId: String; public balance: Integer = 0; } class Customer { public customerId: String; } A UML class model has semantics independent of its mapping to any other language… … which can be notated textually as well as graphically. UML isn’t “just pictures”!
- 10. Computation can be modeled, too class Bank { public bankId: String; public customers: compose Customer[*]; public accounts: compose Account[*]; public totalAccountBalance( in customerId: String): Integer[0..1] { customer = this.customers -> select c (c.customerId == customerId); return customer.accounts.balance -> reduce '+'; } ... } The underlying semantics are based on data-flow, not an implicit von Neumann architecture. These actions are inherently concurrent. … with far fewer implementation commitments.
- 11. 3. Executable UML models are useful Executable UML models… … can be tested, because they are programs … don’t need to be “recoded”, they can be “compiled” … abstract computation, not machine architecture
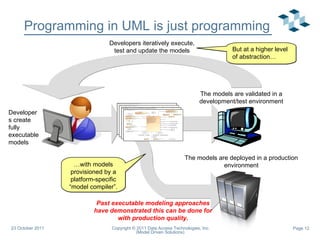
- 12. Programming in UML is just programming … with models provisioned by a platform-specific “model compiler”. But at a higher level of abstraction… Past executable modeling approaches have demonstrated this can be done for with production quality. The models are validated in a development/test environment The models are deployed in a production environment Developers create fully executable models Developers iteratively execute, test and update the models
- 13. Resources Foundational UML (fUML) Specification http://www.omg.org/spec/FUML Reference Implementation Project http://www.modeldriven.org/fuml Action Language for fUML (Alf) Specification http://www.omg.org/spec/ALF Reference implementation repository http://lib.modeldriven.org/MDLibrary/trunk/Applications/Alf-Reference-Implementation /doc – Latest specification document (currently v1.0 Beta) /dist – Parser for latest language version Alf implementation in Eclipse Papyrus UML tool https://bugs.eclipse.org/bugs/show_bug.cgi?id=329865 Contact: [email_address] , http://twitter.com/seidewitz






![But diagrams are just notation class Bank { public bankId: String; public customers: compose Customer[*]; public accounts: compose Account[*]; } assoc AccountOwnership { public accountOwners: Customer[*]; public accounts: Account[*]; } class Account { public accountId: String; public balance: Integer = 0; } class Customer { public customerId: String; } A UML class model has semantics independent of its mapping to any other language… … which can be notated textually as well as graphically. UML isn’t “just pictures”!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xumlpresentation111023modelsprogramsandxuml-111026005033-phpapp01/85/Models-Programs-and-Executable-UML-9-320.jpg)
![Computation can be modeled, too class Bank { public bankId: String; public customers: compose Customer[*]; public accounts: compose Account[*]; public totalAccountBalance( in customerId: String): Integer[0..1] { customer = this.customers -> select c (c.customerId == customerId); return customer.accounts.balance -> reduce '+'; } ... } The underlying semantics are based on data-flow, not an implicit von Neumann architecture. These actions are inherently concurrent. … with far fewer implementation commitments.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xumlpresentation111023modelsprogramsandxuml-111026005033-phpapp01/85/Models-Programs-and-Executable-UML-10-320.jpg)
![Resources Foundational UML (fUML) Specification http://www.omg.org/spec/FUML Reference Implementation Project http://www.modeldriven.org/fuml Action Language for fUML (Alf) Specification http://www.omg.org/spec/ALF Reference implementation repository http://lib.modeldriven.org/MDLibrary/trunk/Applications/Alf-Reference-Implementation /doc – Latest specification document (currently v1.0 Beta) /dist – Parser for latest language version Alf implementation in Eclipse Papyrus UML tool https://bugs.eclipse.org/bugs/show_bug.cgi?id=329865 Contact: [email_address] , http://twitter.com/seidewitz](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xumlpresentation111023modelsprogramsandxuml-111026005033-phpapp01/85/Models-Programs-and-Executable-UML-13-320.jpg)