Abapprogrammingoverview 090715081305-phpapp02
- 1. ABAP Programming Overview
- 2. ABAP Course Outline Chapter 1 : Introduction to ABAP Chapter 2 : List Processing in ABAP Chapter 3 : Open SQL & Internal Table Chapter 4 : Event-driven Programming & Selection Screen Chapter 5 : Modularization & Catch Statement Chapter 6 : Message, Debugging, File Transfer and Type Group
- 3. ABAP Chapter 1 Introduction to SAP Architecture ABAP Overview Data Object in ABAP
- 4. SAP System : 3 Tier Client/Server DB Server SAP Application Server SAP GUI Presentation Server SAP GUI SAP GUI
- 5. SAP SYSTEM (3 Tier Architecture) Presentation Layer (Windows based) Application Layer (Windows Server/UNIX) Database Server Database Layer (Windows Server/UNIX) M SAP Instance Oracle Informix DB2 MS SQL Server MaxDB G Dispatcher Request Queue D D B V S E SAP Buffer (Shared Mem) SAP GUI SAP GUI
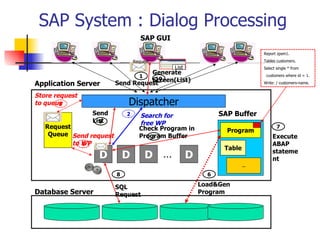
- 7. SAP System : Dialog Processing Database Server Application Server Dispatcher Request Queue D D D D … SAP Buffer Program Table … 1 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 Report zpsm1. Tables customers. Select single * from customers where id = 1. Write: / customers-name. Execute ABAP statement Check Program in Program Buffer 7 Load&Gen Program SQL Request Send List Generate Screen(List) Send Request Request List 2 Search for free WP Store request to queue Send request to WP SAP GUI
- 8. Dialog Work Process Architecture TaskHandler DYNPRO Processor ABAP Processor Local Memory Memory Space DB Interface List buffer Database Server Dialog Work Process Result Set Memory
- 10. ABAP Overview DATA ... WRITE ... IF ... MOVE … WHILE... *Comment... SEARCH ... SELECT ... LOOP AT ... DO ...
- 11. ABAP A dvanced B usiness A pplication P rogramming
- 12. ABAP Feature Declaring data with various types and structure Operational elements for data manipulation Control elements for controlling the program flow Event elements for reacting to external events
- 13. ABAP Operating/Database system-independent programming ABAP contains a subset of SQL called Open SQL for comfortable database access for various database
- 14. ABAP Programming ABAP Report Dialog Programming(Transaction)
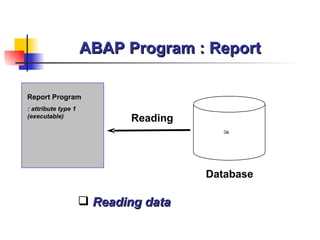
- 15. ABAP Program : Report Report Program : attribute type 1 (executable) Reading Database Reading data
- 16. Types of ABAP Report 1. Report Listing 2. Drill-down Report 3. Control-break Report 4. ALV Report 1 3 4
- 17. ABAP Program : Dialog Program Dialog Program : attribute type M (Module Pool) Reading Database Reading and changing data Writing
- 18. Dialog Program : Transaction
- 19. ABAP Programming
- 20. How to create ABAP program Transaction Code : SE38
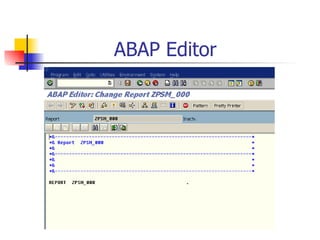
- 23. ABAP Editor
- 24. The Structure of the Language Each statement must end with a period DATA tmp TYPE I. WRITE ‘Hello World’. WRITE ‘OK’.
- 25. Literal DATA tmp TYPE I. WRITE ‘Hello World’. WRITE ’10’. MOVE 9 TO tmp. Text Literal Numeric Literal Text Literal
- 26. Chained Statements Successive statements that have the same string segment can be combined to form a single chained statement To do so, you specify the identical starting segment once and conclude it with a colon (:), the remaining segments are then listed, separated by commas (,) and concluded with a period (.) At runtime, a chained statement is treated like an equivalent sequence of individual ABAP statements
- 27. Chained Statements WRITE ‘Hello World’. WRITE ‘OK’. = WRITE: ‘Hello World’, ‘OK’. DATA tmp1 TYPE I. DATA tmp2 TYPE C. = DATA: tmp1 TYPE I, tmp2 TYPE C.
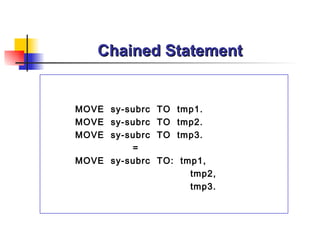
- 28. Chained Statement MOVE sy-subrc TO tmp1. MOVE sy-subrc TO tmp2. MOVE sy-subrc TO tmp3. = MOVE sy-subrc TO: tmp1, tmp2, tmp3.
- 29. Chained Statement PERFORM cal_1 USING a1 a2. PERFORM cal_1 USING a3 a4. = PERFORM cal_1 USING: a1 a2, a3 a4.
- 30. Comments * This is full line comment WRITE ‘Hello World’. “ Write data (partial line comment) WRITE ‘Test’.
- 31. ABAP Command : Case Sensitivity ABAP command is not case sensitive WRITE ‘Hello World’. WriTe ‘Hello World’. wRiTE ‘Hello World’.
- 32. Data Objects in ABAP
- 33. Data Objects in ABAP Memory Space Structure Table Structure Internal Table Variable Constants <Field-symbols>
- 34. Variable
- 35. Variable Variables can be declared at any point in a program Variables can be up to 30 characters in length REPORT ZTEST. DATA firstname TYPE STRING. firstname = ‘John’.
- 36. Predefined ABAP Data Types Type Description Initial Value C D F I N P T X String xstring Character Date Floating Point Integer Numeric Text Packed Decimal Time Hexadecimal Variable-length Variable-length Hexadecimal Space ‘ 00000000’ 0.0 0 ‘ 0’ 0 ‘ 000000’ ’ 00’ Space Blank string Length 1 – 65535 8 characters 8 bytes 4 bytes 1 – 65535 1 – 16 bytes 6 characters 1 – 65535 Variable Variable
- 37. Defining Variable with DATA Statement * Syntax DATA var[( length )] [Type type ] [Decimals number ]. DATA var LIKE Table-Field [VALUE initial value ].
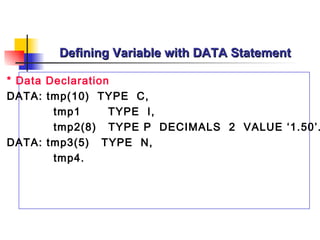
- 38. Defining Variable with DATA Statement * Data Declaration DATA: tmp(10) TYPE C, tmp1 TYPE I, tmp2(8) TYPE P DECIMALS 2 VALUE ‘1.50’. DATA: tmp3(5) TYPE N, tmp4.
- 39. Defining Variable with DATA Statement * Data Declaration DATA customerno LIKE customers-id. DATA matnr LIKE mara-matnr . DATA customerno TYPE customers-id. DATA matnr TYPE mara-matnr.
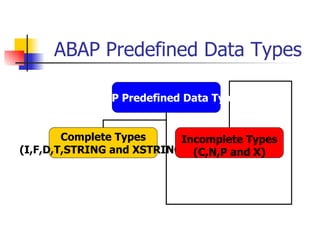
- 40. ABAP Predefined Data Types ABAP Predefined Data Types Complete Types (I,F,D,T,STRING and XSTRING) Incomplete Types (C,N,P and X)
- 41. Variable Data Type C , N and X length between 1 – 65535 (Default 1) Data Type P length between 1 – 16 (Default 8) and decimals length between 0 – 31 Data Type I value between – 2 31 to 2 31 – 1 or –2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 DATA tmp(10) TYPE C. DATA tmp(5) TYPE P DECIMALS 2. DATA tmp TYPE I. tmp = 1000000.
- 42. Data type N data tmp(5) type N. tmp = ‘Xca9yy23K6’.
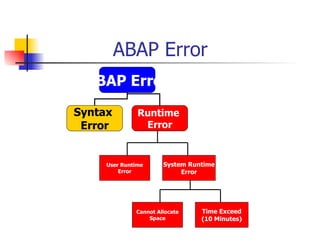
- 43. ABAP Error System Runtime Error User Runtime Error Time Exceed (10 Minutes) Cannot Allocate Space ABAP Error Syntax Error Runtime Error
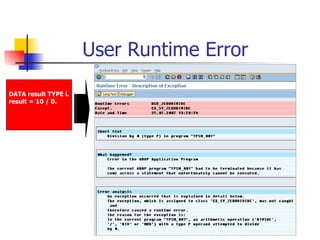
- 44. User Runtime Error DATA result TYPE i. result = 10 / 0.
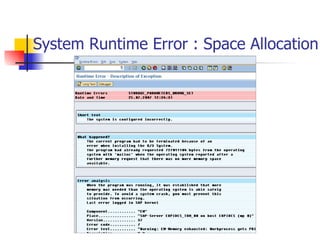
- 45. System Runtime Error : Space Allocation
- 46. System Runtime Error : Time Exceed
- 47. Non-elementary Type * Data Declaration TYPES tname(30) TYPE c. DATA: customer_name TYPE tname, firstname TYPE tname.
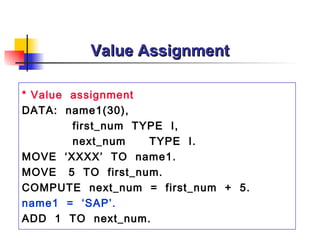
- 48. Value Assignment * Value assignment DATA: name1(30), first_num TYPE I , next_num TYPE I. MOVE ‘XXXX’ TO name1. MOVE 5 TO first_num. COMPUTE next_num = first_num + 5. name1 = ‘SAP’. ADD 1 TO next_num.
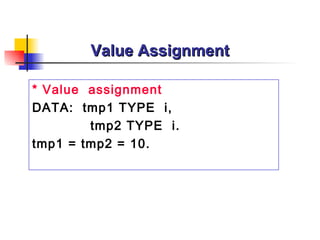
- 49. Value Assignment * Value assignment DATA: tmp1 TYPE i , tmp2 TYPE i . tmp1 = tmp2 = 10.
- 50. ABAP Practice ต้องการให้สร้างตัวแปรชื่อ firstname และ lastname โดยให้ค่าชื่อของคุณกับ ตัวแปร firstname และนามสกุลของคุณให้กับตัวแปร lastname พร้อมทั้งแสดง ค่าข้อมูล firstname กับ lastname ออกมาที่หน้าจอ
- 51. Structure
- 52. Structure * Syntax DATA BEGIN OF < structure name >. DATA field1. DATA field2. … … DATA END OF < structure name >.
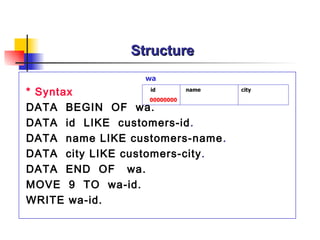
- 53. Structure * Syntax DATA BEGIN OF wa. DATA id LIKE customers-id . DATA name LIKE customers-name . DATA city LIKE customers-city . DATA END OF wa. MOVE 9 TO wa-id. WRITE wa-id. id city wa 00000000 name
- 54. Defining Structure (Include Structure) * Include Structure DATA BEGIN OF wa. INCLUDE STRUCTURE customers. DATA tel(7). DATA END OF wa.
- 55. Defining Structure * LIKE option DATA wa LIKE customers. wa-id = 1. wa-name = ‘John’. WRITE: wa-id, wa-name.
- 56. ABAP Practice ต้องการให้สร้าง Structure ชื่อ myname โดยมีฟิลด์ firstname และ lastname โดยให้ค่าชื่อของคุณกับฟิลด์ firstname และนามสกุลของคุณให้กับฟิลด์ lastname พร้อมทั้งแสดงค่าข้อมูลของ Structure ที่ชื่อ myname ทั้งฟิลด์ firstname และ lastname ออกมาที่หน้าจอ
- 57. Constants
- 58. Constants * Constant variable CONSTANTS max_no TYPE I VALUE 999. DATA counter TYPE I VALUE max_no. WRITE: max_no, counter.
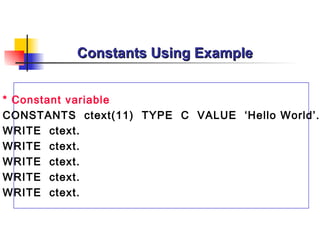
- 59. Constants Using Example * Constant variable CONSTANTS ctext(11) TYPE C VALUE ‘Hello World’. WRITE ctext. WRITE ctext. WRITE ctext. WRITE ctext. WRITE ctext.
- 60. System Fields The system fields (structure syst) are filled by the runtime environment. You can use them to query the system status in an ABAP program You should access them only for reading sy-datum = Current date of application server sy-uzeit = Current time of application server sy-datlo = Current date of SAP GUI sy-timlo = Current time of SAP GUI sy-mandt = Current client logon sy-subrc = Return value of ABAP statement syst-datum
- 61. ABAP System Fields : Structure SYST (SE11)
- 62. DATE * Fixed Length 8 * Include Representation ‘ YYYYMMDD ’ DATA today TYPE D. today = sy-datum. WRITE today. today = ‘19991231’. WRITE today.
- 63. TIME * Fixed Length 6 * Format ‘HHMMSS’ DATA times TYPE T. times = sy-uzeit. WRITE times. HHMMSS
- 64. MOVE Statement DATA wa LIKE customers . DATA vender LIKE customers. wa -id = ‘1234’. wa -name = ‘Test#1’. MOVE wa TO vender. WRITE: wa -id, vender-name. “ vender = wa.
- 65. MOVE-CORRESPONDING Statement DATA: begin of wa1, f1,f2,f4, end of wa1 . DATA: begin of wa2, f2,f1,f3, end of wa2 . … MOVE -CORRESPONDING wa1 TO wa2 . WRITE: wa1-f1 , wa2-f1 .
- 66. Field-symbols
- 67. Field-symbols Data: name (4) Value ‘Test’, num Type I Value 10, today Type D Value ‘19980429’. Field-symbols <temp>. Assign name To <temp>. Write <temp>. Assign num To <temp>. Write <temp>. Assign today To <temp>. Write <temp>.
- 68. Field-symbols : UNASSIGN d ata: name (4) Value ‘Test’, f ield-symbols <temp>. a ssign name To <temp>. w rite <temp>. una ssign <temp>.
- 69. CLEAR Statement Example: DATA tmp type i value 9. tmp = 10. CLEAR tmp. “ Clear statement sets a field to an initial value appropriate for its type” CLEAR < data object >.
- 70. CLEAR Structure DATA wa like customers. … CLEAR wa.
- 71. ABAP Report : Program Structure Report ztest. *Data objects declaration data ... data begin of ... *Program Logic(Data objects processing) … write ….
- 72. ABAP Practice

































![Defining Variable with DATA Statement * Syntax DATA var[( length )] [Type type ] [Decimals number ]. DATA var LIKE Table-Field [VALUE initial value ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abapprogrammingoverview-090715081305-phpapp02-110306232448-phpapp01/85/Abapprogrammingoverview-090715081305-phpapp02-37-320.jpg)