Preeclampsia
- 1. PREECLAMPSIA DRA. MERLY MUÑOZ ESPINOSA GINECO – OBSTETRICIA USCO 2008
- 2. PREECLAMPSIA Hipertensión y proteinuria posterior a las 20 semanas de gestación Criterio diagnostico para preeclampsia Proteinuria de ≥0.3 gramos (300mg/dl) en 24 horas - En orina Y Presión arterial Diastólica ≥ 90 mmHg Ó Presión arterial Sistólica ≥ 140 mmHg
- 3. PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA PREECLAMPSIA New onset proteinuric hypertension and at least one of the following: Blurred vision, scotomata, altered mental status, severe headache Symptoms of central nervous system dysfunction Right upper quadrant or epigastric pain Nausea, vomiting Symptoms of liver capsule distention Serum transaminase concentration at least twice normal Hepatocellular injury Systolic blood pressure ≥ 160 mm Hg or diastolic ≥ 110 mm Hg (two at least six hours) Severe blood pressure elevation Less than 100,000 platelets per cubic millimeter Thrombocytopenia 5 or more grams in 24 hours Proteinuria <500 mL in 24 hours Oliguria Severe fetal growth restriction Pulmonary edema or cyanosis Cerebrovascular accident
- 4. DIAGNOSTICO METAS Diagnostico soportado Excluyendo otros desordenes Valoración de severidad Leve – Severa PREECLAMPSIA
- 5. INCIDENCIA Desordenes hipertensivos complican 10-20% de embarazos Preeclampsia ocurre en 3-14% de todos los embarazos del mundo 5-8% en usa Preeclampsia leve 75% - usa Preeclampsia severa 25% - usa 10% ocurren en <34 semanas Sobre agregada 3% PREECLAMPSIA Hall, DR, Odendaal, HJ, Steyn, DW, Grive, D. Urinary protein excretion and expectant management of early onset, severe preeclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002; 77:1. Working group report on high blood pressure in pregnancy. National Institutes of Health, Washington, DC 2006
- 6. FACTORES DE RIESGO PREECLAMPSIA Unexplained fetal growth restriction Hydrops fetalis Male partner whose previous partner had preeclampsia High body mass index 2.93 Multifetal gestation 3.56 Diabetes mellitus (pregestational and gestational) Vascular or connective tissue disease Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome or inherited thrombophilia Chronic renal disease Chronic hypertension 2.90 Family history of pregnancy-induced hypertension 1.96 Age >40 years or <18 years 7.19 Preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy 25-75% Nulliparity RELATIVE RISK FACTOR
- 7. PATOGENESIS PREECLAMPSIA SYSTEMIC ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION Fms–like tyrosine kinase-1 Vascular endothelial growth factor Antagonizes placental growth factor Hypothesis for the role of sFlt1 in preeclampsia
- 8. PATOGENESIS PREECLAMPSIA Stereographic representation of myometrial and endometrial arteries in the macaque
- 9. PATOGENESIS PREECLAMPSIA Exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the fetus and the mother depends on adequate placental perfusion by maternal vessels. Abnormal placentation in preeclampsia Hypoperfusion
- 11. LABORATORIOS Hematocrito Hemoconcentración Plaquetas Trombocitopenia Cuantificación de excreción de proteína ≥ 300mg en 24 horas 1+ en 2 muestras de orina (4 horas) 3+ ó ≥5gr por día (Severidad) PREECLAMPSIA
- 12. LABORATORIOS Depuración de creatinina Concentración de creatinina sérica ALT – AST Elevadas LDH – Elevada Hemólisis microangiopatica Evaluación Bienestar fetal PBF – Ecografía PREECLAMPSIA
- 13. MANEJO Parto Edad gestacional Severidad de preeclampsia Condiciones maternas y fetales PREECLAMPSIA Disfunción Órganos maternos Monitoreo no reactivo PARTO Cualquier edad gestacional
- 14. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA LEVE Embarazo a termino Inducir (Bishop ≥6) Maduración cervical (Cervix desfavorable) PREECLAMPSIA Anterior Midposition Posterior Position of the cervix Soft Medium Firm Cervical consistency +1, +2 -1, 0 -2 -3 Station* 80 60-70 40-50 0-30 Effacement, percent 5-6 3-4 1-2 Closed Dilation, cm 3 2 1 0
- 15. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA LEVE Embarazo pretermino Manejo expectante Crecimiento y maduración fetal PREECLAMPSIA HOSPITALIZACIÓN VS AMBULATORIO ? Nicholson, JM. The impact of the interaction between increasing gestational age and obstetrical risk on birth outcomes evidence of a varying optimal time of delivery. J Perinatol 2006; 26:392 Sibai, BM. Diagnosis and management of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 2003; 102:181
- 16. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA LEVE AMBULATORIO Monitorización c/ 3 día (Materno-fetal) Consultar inmediatamente por síntomas Cefalea severa ó persistente, cambios visuales Dolor en HCD ó epigastralgia, nauseas, vomito Disnea ó disminución de orina Signos de alarma PREECLAMPSIA Barton, JR, Istwan, NB, Rhea, D, et al. Cost-savings analysis of an outpatient management program for women with pregnancy-related hypertensive conditions. Dis Manag 2006; 9:236.
- 17. LABORATORIOS – SEGUIMIENTO Laboratorios mínimos Plaquetas, creatinina y ALT-AST 2 veces por semana Signos y síntomas de progresión de enf. Otros laboratorios Hematocrito Hemoconcentración – Hemólisis LDH Proteinuria en 24 horas (5gr/24hrs) PREECLAMPSIA Working group report on high blood pressure in pregnancy. National Institutes of Health, Washington, DC 2006
- 18. TRATAMIENTO HTA Antihipertensivos en HT leve No disminuye morbi-mortalidad No es terapia de rutina Restricción de sodio y diuréticos Actividad física restringida Disminuye TA Eficacia en resultado perinatal PREECLAMPSIA ? ? Ganzevoort, W, Rep, A, Bonsel, GJ, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing two temporising management strategies one with and one without plasma volume expansion, for severe and early onset pre-eclampsia. BJOG 2005; 112:1358
- 19. MANEJO Nuevas terapias – Investigación L-arginina Precursor fisiológico para óxido nítrico No mejoro resultado materno-fetal Valoración de bienestar fetal Mejor método para monitorización ? Movimientos fetales – Monitoreo NST – PBF PREECLAMPSIA Ganzevoort, W, Rep, A, Bonsel, GJ, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing two temporising management strategies one with and one without plasma volume expansion, for severe and early onset pre-eclampsia. BJOG 2005; 112:1358
- 20. MANEJO Valoración de crecimiento fetal Restricción de crecimiento Estimación por ecografía RCIU – Oligoamnios PREECLAMPSIA PRIMERA MANIFESTACIÓN PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA DOPPLER FETAL
- 21. MANEJO DOPPLER PREECLAMPSIA
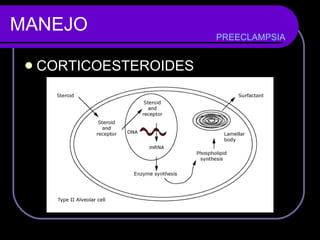
- 22. MANEJO CORTICOESTEROIDES Preeclampsia acelera la maduración fetal Común Enf Membrana hialina Corticoesteroides antenatales ≤ 34 semanas Dosificación Betametasona 12mg IM cada 24 horas 2 dosis PREECLAMPSIA ? The association between hyaline membrane disease and preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007; 191:1414.
- 24. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA Parto Especialista en medicina materno fetal Preeclampsia en 32 – 34 semanas No hay indicación de cesárea inmediata Inducción ó maduración cervical PREECLAMPSIA Alexander, JM, Bloom, SL, McIntire, DD, Leveno, KJ. Severe preeclampsia and the very low birth weight infant: is induction of labor harmful?. Obstet Gynecol 1999; 93:485 ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia Number 33, January 2002. Obstet Gynecol 2002; 99:159
- 25. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA Embarazo a termino - pretermino Inducir (Bishop ≥6) Maduración cervical (Cervix desfavorable) PREECLAMPSIA Coppage, KH, Polzin. Severe preeclampsia and delivery outcomes: Is immediate cesarean delivery beneficial? Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006; 186:921 Anterior Midposition Posterior Position of the cervix Soft Medium Firm Cervical consistency +1, +2 -1, 0 -2 -3 Station* 80 60-70 40-50 0-30 Effacement, percent 5-6 3-4 1-2 Closed Dilation, cm 3 2 1 0
- 26. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA Monitoreo intraparto Empeoramiento de hipertensión Deterioro materno de la función hepática, renal, cardiopulmonar ó hematológica. Insuficiencia placentaria Abruptio placentae PREECLAMPSIA Coppage, KH, Polzin. Severe preeclampsia and delivery outcomes: Is immediate cesarean delivery beneficial? Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006; 186:921
- 27. MANEJO PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA Monitoreo hemodinámica invasivo Puede ser usado en pacientes complicadas Enfermedades cardiacas severas Enf renales severas Oliguria Hipertensión refractaria Edema pulmonar PREECLAMPSIA No ser expuestas a los riesgos asociados con cateterización arterial y venosa ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33, January 2002. Obstet Gynecol 2002; 99:159.
- 28. COMPLICACIONES CVC PREECLAMPSIA Nerve injury Myocardial perforation Catheter embolization Catheter migration Venous thrombosis, pulmonary emboli Infection DELAYED Pneumothorax or hemothorax Catheter malposition Thoracic duct injury (with left SC or left IJ approach) Air embolism Arrhythmia Arterial puncture Bleeding IMMEDIATE
- 29. TERAPIA ANTICONVULSIVANTE Anteparto ó en trabajo de parto Terapia continuada por 24 horas postparto (Rango de 12 a 48 horas) SULFATO DE MAGNESIO Droga de elección para prevenir la eclampsia. Mas efectiva que la fenitoina ó drogas antihipertensivas como nimodipino PREECLAMPSIA A comparison of magnesium sulfate with phenytoin for the prevention of eclamspia N Engl J Med 1995; 333:201 A comparison of magnesium sulfate and nimodipine for the prevention of eclampsia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348:304
- 30. SULFATO MAGNESIO Mecanismo de acción como anticonvulsivante Vasodilatación de la vasculatura cerebral Inhibición de la agregación plaquetaria Protección de las células endoteliales desde el daño de los radicales libres Prevención de la entrada del Ion calcio dentro de las células isquemicas Disminución relación acetilcolina Antagonista competitivo del receptor PREECLAMPSIA Duley, L, Henderson-Smart, D. Magnesium sulphate versus phenytoin for eclampsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; :CD000128. ?
- 31. SULFATO MAGNESIO PREECLAMPSIA SEVERA Terapia anticonvulsivante Estudio Magpie > 10.000 mujeres Sulfato de magnesio a dosis Carga 4g EV – Mantenimiento 1g/hora Carga 5g IM – Seguido 5gr cada 4 horas IM PREECLAMPSIA PREECLAMPSIA LEVE – CONTROVERSIAL Do women with pre-eclampsia, and their babies, benefit from magnesium sulphate? The Magpie Trial: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2002; 359:1877 LEVE – 75% SEVERA – 25% NNT SEVERA – 63 LEVE – 109
- 32. MANEJO WHO – FIGO – ISSHP Terapia de sulfato de magnesio es recomendada para prevención de eclampsia en mujeres con preeclampsia. (No distingue entre leve o severa) ACOG Sulfato de magnesio en preeclampsia severa Falta consenso en preeclampsia leve PREECLAMPSIA
- 33. DISCUSIÓN No tratamiento fue asociado Reducción de mortalidad neonatal y efectos adversos maternos Incremento en el riesgo de muerte materna y compromiso neurológico en el infante PREECLAMPSIA ADMINISTRACIÓN INTRAPARTO DE SULFATO DE MAGNESIO COMO PROFILAXIS EN PREECLAMPSIA LEVE NO ADMON EN HIPERTENSIÓN GESTACIONAL NO PROTEINURICA NO PREVIENE PROGRESIÓN DE ENFERMEDAD 10-15% P. LEVE PROGRESAN A P. SEVERA
- 34. SULFATO DE MAGNESIO Iniciado al tiempo al inicio del trabajo de parto ó la inducción, ó previo a cesárea Dosis de carga es de 4 – 6 gramos EV Dosis de mantenimiento 1-3gr por hora PREECLAMPSIA RECOMENDADO: DOSIS DE CARGA 6 GRS EV EN 15-20 MINUTOS DOSIS MANTENIMIENTO 2 GRS/HR EN INFUSIÓN CONTINUA Sibai, BM. Magnesium sulfate prophylaxis in preeclampsia: Lessons learned from recent trials. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004 ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33, Obstet Gynecol 2002 Alexander, JM, McIntire, DD, Leveno, KJ, Cunningham, FG. Selective magnesium sulfate prophylaxis for the prevention of eclampsia in women with gestational hypertension. Obstet Gynecol 2006
- 35. SULFATO DE MAGNESIO Excretado por los riñones Insuficiencia renal (Creatinina >1.0mg/dL) Dosis de carga estándar Reducir dosis de mantenimiento 1g por hora Si creatinina >2.5mg/dL Dosis de carga sin dosis de mantenimiento Monitoreo de niveles de magnesio serico cada 6 horas PREECLAMPSIA
- 36. SULFATO MAGNESIO Contraindicado Miastenia gravis Puede precipitar a crisis miastenica severa Uso concomitante de sulfato con bloqueadores de canales de calcio puede resultar en hipotensión PREECLAMPSIA
- 37. SULFATO DE MAGNESIO MONITORIZACION Fase de mantenimiento Reflejo patelar presente PREECLAMPSIA HIPERMAGNESEMIA RESPIRACIÓN > 12 X MIN GASTO URINARIO >100ML/ 4HR RANGO TERAPEUTICO 4.8 – 8.4 MG/DL (2.0 A 3.5 mmol/L)
- 38. SULFATO MAGNESIO Continuado por 24 horas postparto Preeclampsia leve 12 horas Preeclampsia severa ó eclampsia 24 – 48 horas PREECLAMPSIA
- 39. SULFATO MAGNESIO COMPLICACIONES – EFECTOS Infusión rápida Diaforesis, sensación de calor, flushing Vasodilatación periférica, ↓ en TA Nauseas, vomito, visión borrosa y palpitaciones Efecto tocolítico Atonia uterina – Hemorragia postparto PREECLAMPSIA
- 40. SULFATO MAGNESIO TOXICIDAD Relacionada con niveles sericos Pérdida de reflejos tendinosos 9-12mg/dL (4-5) Parálisis respiratoria 12-18mg/dL (5-7.5mmol/L) Compromiso cardiaco 24-30mg/dL (10-12.5m/L) Gluconato de calcio 1 gramo endovenoso en 5-10 min PREECLAMPSIA
- 41. ANESTESIA Técnica neuroaxial Epidural ó espinal En ausencia de trombocitopenia Problemas Edema de la vía aérea Exacerbación de la hipertensión Observación por fibra óptica TraqueoStomía PREECLAMPSIA Working group report on high blood pressure in pregnancy. National Institutes of Health, Washington, DC 2000 Randomized comparison of general and regional anesthesia for cesarean delivery in pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 1995; 86:193 INTUBACION
- 42. MANEJO Labetalol Hipertensión exacerbada durante la inducción y/ó intubación PREECLAMPSIA Injection, solution: 5 mg/mL (4 mL, 20 mL, 40 mL) Trandate®: 5 mg/mL (20 mL, 40 mL) Tablet: 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg Trandate®: 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg DOSAGE FORMS I.V. bolus: 20 mg IVP over 2 minutes, may give 40-80 mg at 10-minute intervals, up to 300 mg total dose. I.V. infusion (acute loading): Initial: 2 mg/minute; titrate to response up to 300 mg total dose. Administration requires the use of an infusion pump. DOSING Crosses the placenta. Persistent bradycardia, hypotension Safe during pregnancy Cases of neonatal hypoglycemia during breast-feeding. PREGNANCY IMPLICATIONS Beta Blocker With Alpha-Blocking Activity PHARMACOLOGIC CATEGORY
- 43. RESULTADOS ADVERSOS MATERNOS Disfunción en SNC, hepático y renal Hemorragia cerebral, ruptura hepática, falla renal Sangrado relacionado a trombocitopenia Parto pretermino RCIU Abruptio placentae Muerte perinatal Factores que influyen Edad gestacional Severidad de enf Condiciones medicas coexistentes Gestación múltiple Diabetes mellitus Enfermedad renal Trombofilia Hipertensión preexistente PREECLAMPSIA
- 44. RESULTADOS PREECLAMPSIA Adapted from data in Hauth, JC, Ewell, MG, Levine, RJ, et al. Obstet Gynecol 2000; 95:24 0.9 0.5 0.5 Neonatal death 0.9 0.5 0.9 Fetal death 0 0.5 0.2 Brain hemorrhage 15.7 3.2 3.8 Respiratory difficulty 42.6 27.3 12.9 Admission to NICU 18.5 10.2 4.2 Growth restriction Fetal or neonatal 18.5 1.9 3.2 Delivery <34 weeks 34.9 30.9 13.3 Cesarean delivery 58.7 41.5 12.1 Induced labor 3.7 0.5 0.7 Placental abruption 12.8 5.1 0.3 Kidney dysfunction 20.2 3.2 0.2 Liver dysfunction Maternal Severe preeclampsia (percent) Mild preeclampsia (percent) Normal blood pressure, (percent) Outcome measure
- 45. RESULTADOS 1 Muerte materna por cada 100.000 NV Tasa de caso-fatalidad 6.4 muerte/10000c PREECLAMPSIA MORTALIDAD PREECLAMPSIA- ECLAMPSIA HEMORRAGIA ENFERMEDAD TROMBOEMBOLICA
- 46. POST-PARTO Resuelve hipertensión y proteinuria Medicamentos antihipertensivos Suspender al retorno de niveles normales PREECLAMPSIA
- 47. CLASIFICACION Investigadores de Mississippi SINDROME HELLP Martin, JN Jr, Rose, CH, Briery, CM. Understanding and managing HELLP syndrome: the integral role of aggressive glucocorticoids for mother and child. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006; 195:914 Plaquetas – 100000-150000c/mL AST ó ALT ≥40 Iu/L, LDH ≥ 600IU/L CLASE 3 Plaquetas – 50.000 y 100000c/mL, AST ó ALT ≥70 Iu/L, LDH ≥ 600IU/L CLASE 2 Plaquetas ≤50.000cel/mL, AST ó ALT ≥70 Iu/L, LDH ≥ 600IU/L CLASE 1