Python SQite3 database Tutorial | SQlite Database
- 1. Python Database - CRUD 1. CREATE,INSERT 2. READ 3. UPDATE 4. DELETE Elangovan Tech Notes 1
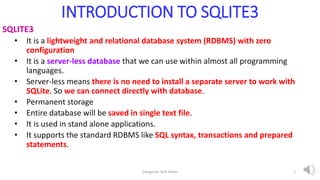
- 2. INTRODUCTION TO SQLITE3 SQLITE3 • It is a lightweight and relational database system (RDBMS) with zero configuration • It is a server-less database that we can use within almost all programming languages. • Server-less means there is no need to install a separate server to work with SQLite. So we can connect directly with database. • Permanent storage • Entire database will be saved in single text file. • It is used in stand alone applications. • It supports the standard RDBMS like SQL syntax, transactions and prepared statements. Elangovan Tech Notes 2
- 3. SQLITE3-DB Browser SQLITE3-DB Browser • Download the DB Browser software “DB.Browser.for.SQLite-3.11.0-beta3-win64” for visual • This is optional one. It is a high quality, visual and open source tool used for creating, designing and editing the database files which are compatible with SQLite database. Home page of SQLite DB Browser Elangovan Tech Notes 3
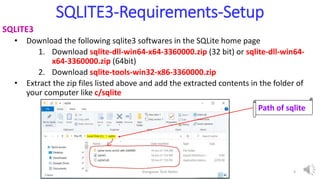
- 4. SQLITE3-Requirements-Setup SQLITE3 • Download the following sqlite3 softwares in the SQLite home page 1. Download sqlite-dll-win64-x64-3360000.zip (32 bit) or sqlite-dll-win64- x64-3360000.zip (64bit) 2. Download sqlite-tools-win32-x86-3360000.zip • Extract the zip files listed above and add the extracted contents in the folder of your computer like c/sqlite Path of sqlite Elangovan Tech Notes 4
- 5. Popular Usages of SQLite SQLITE3 • This database can be used for the following areas 1. Database for Gadgets • Mobiles, PDAs, MP3 Players, etc,… 2. Website Database 3. Internal Database (Temporary Database) Elangovan Tech Notes 5
- 6. SQLITE3-DB-OPERATIONS SQLITE3 • Python supports the following operations mentioned below with help of sqlite3 lightweight database. They are 1. Database Creation 2. Table Creation 3. Record Insertion 4. Record Deletion 5. Record Updation 6. Table Retrieval (Retrieval via cursor object) Elangovan Tech Notes 6
- 7. Cursor Importance of Cursor • To retrieve the SQLite statements in python code, we need a cursor object. We can create it by using the built-in instance method like cursor() of connection object • To execute the sql query, first we should establish the database connection and then create an object of the cursor using the connection object as shown in below Cursor Object Creation • We can execute any sql query using the execute() method of cursor object. // connect and create the database using connect() method con=sqlite3.connect(‘ganesh.db’) // create the cursor object using cursor() method of connection object cc=con.cursor() Elangovan Tech Notes 7
- 8. Important Methods-SQLite BUILT-IN METHODS • SQLite provides several methods for CRUD. They are 1. connect() connecting DB 2. execute() executing SQL queries like insert, delete, select,… 3. cursor() needed for data retrieval (use of select query) 4. fetchall() read all the records from table 5. commit() saves the current transactions 6. close() close the DB connection 1. connect(database-name) • It is used to connect the database with specified path • It takes one plus arguments where first argument is the name of the database • Return type : Connection Elangovan Tech Notes 8
- 9. Important Methods-SQLite- (Con) BUILT-IN METHODS 2. execute(query, optional parameters) • It is an instance method of connection object • It is used to execute sql queries such as select, insert, delete, update queries • It will execute only one sql query at a time • It takes one plus arguments. Where first argument is the sql query and second argument can be optional parameters • Return type : Cursor 3. cursor() • It is an instance method of connection object • It is used to create a cursor object which will be used throughout of your database with python • It takes one optional argument called Cursor class • Return type : Cursor Elangovan Tech Notes 9
- 10. Important Methods-SQLite- (Con) BUILT-IN METHODS 4. fetchall() • It is an instance method of cursor object • It is used to read all the rows of a table (records) returning a list type. An empty list will be returned, if no rows are available • Return type : list 5. commit() • It is an instance method of connection object • This method is used to save the current transaction. If you don’t call this method for DML queries like insert, delete, update,etc, then these changes will not be reflected in the database connection. • Return type : NoneType Elangovan Tech Notes 10
- 11. Important Methods-SQLite- (Con) BUILT-IN METHODS 6. close() • It is an instance method of connection object • It is used to close the database connection and returns nothing • It is a note that, if you close the database connection without calling commit() method, then the changes will not be saved (changes will be lost) • Return type : NoneType 5. total_changes • It is an instance proprty of connection object • This property just returns the total number of table rows that have been inserted, deleted and modified • Return type : int Elangovan Tech Notes 11
- 12. Database Creation Creating database using Sqlite3 • To create a database, just call connect() method SQLite3 module, then the database will be automatically created based on the specified path in your machine. • This database is created and saved on disk. Elangovan Tech Notes 12
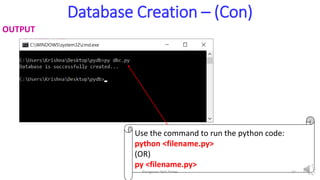
- 13. Database Creation – (Con) SOURCE CODE import sqlite3 # create the database by starting the connection with sqlite try: con=sqlite3.connect("ganesh.db") print("Database is successfully created...") except Error: print("Error in creating the database") finally: con.close() Close the database using close() method Connect and create the new database like ganesh.db in the current folder This is the name of the database Elangovan Tech Notes 13
- 14. Database Creation – (Con) OUTPUT Use the command to run the python code: python <filename.py> (OR) py <filename.py> Elangovan Tech Notes 14
- 15. Database Creation – (Con) VERIFICATION FOR NEWLY CREATED DATABASE Elangovan Tech Notes 15
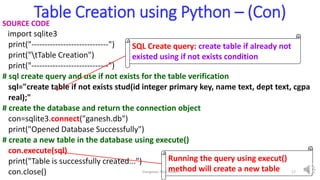
- 16. 1. Table Creation using Python CREATING A TABLE • To create a table in sqlite3 via python, use the following below 1. Create a connection object using connect() method of sqlite3 2. Define the create query for new table and store it in variable 3. Call this query using execute() method of connection object and then the new table will be created in the input database used Elangovan Tech Notes 16
- 17. Table Creation using Python – (Con) SOURCE CODE import sqlite3 print("-----------------------------") print("tTable Creation") print("-----------------------------") # sql create query and use if not exists for the table verification sql="create table if not exists stud(id integer primary key, name text, dept text, cgpa real);" # create the database and return the connection object con=sqlite3.connect("ganesh.db") print("Opened Database Successfully") # create a new table in the database using execute() con.execute(sql) print("Table is successfully created...") con.close() SQL Create query: create table if already not existed using if not exists condition Running the query using execut() method will create a new table Elangovan Tech Notes 17
- 18. Table Creation using Python – (Con) OUTPUT Elangovan Tech Notes 18
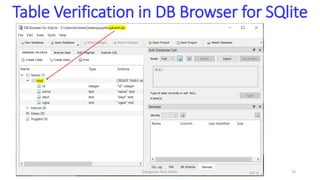
- 19. Table Verification in DB Browser for SQlite Elangovan Tech Notes 19
- 20. 1.1 Data Insertion Data Insertion • To insert the data into a table in sqlite3 via python, use the following below 1. Create a connection object 2. Define the insert query based on your requirement and call this query using execute() method of connection object and then record will be inserted 3. Commit the changes using commit() method of connection object 4. Close the database using close() method Elangovan Tech Notes 20
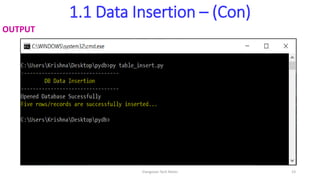
- 21. 1.1 Data Insertion – (Con) SOURCE CODE print("---------------------------------") print("tDB Data Insertion") print("---------------------------------") # connect & open existing DB con=sqlite3.connect("ganesh.db") print("Opened Database Sucessfully") # add the insert queries as you want in the execute() method of connection object con.execute("insert into stud values(1,'Sachin','IT',9.55)") con.execute("insert into stud values(5,'John','CS',7.55)") con.execute("insert into stud values(7,'Rohit','IT',9.90)") con.execute("insert into stud values(12,'Venkat','CS',9.95)") con.execute("insert into stud values(14,'Dravid','IT',8.70)") Execution of Insert queries using execute() method of connection object Open the existing Database Elangovan Tech Notes 21
- 22. 1.1 Data Insertion – (Con) SOURCE CODE # commit the changes con.commit() print("Five rows/records are successfully inserted...") # close the DB con.close() Close the database using close() method Saves the DB changes Elangovan Tech Notes 22
- 23. 1.1 Data Insertion – (Con) OUTPUT Elangovan Tech Notes 23
- 24. 1.1 Data Insertion – (Con) PROOF FOR DATA INSERTION OPERATION [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool] Elangovan Tech Notes 24
- 25. 2. Data Retrieval (Read) DATA RETRIEVAL • To display the data from database table, do the following things mentioned below 1. Connect and open the existing database using connect() method 2. Create cursor object for data retrieval using connection object 3. Execute the select query using cursor object with execute() method 4. Read all data from table using cursor and store them to list based result set 5. Iterate the result set via looping (for or while loop) 6. Display the records (via rows or columns) Elangovan Tech Notes 25
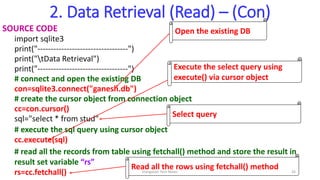
- 26. 2. Data Retrieval (Read) – (Con) SOURCE CODE import sqlite3 print("----------------------------------") print("tData Retrieval") print("----------------------------------") # connect and open the existing DB con=sqlite3.connect("ganesh.db") # create the cursor object from connection object cc=con.cursor() sql="select * from stud" # execute the sql query using cursor object cc.execute(sql) # read all the records from table using fetchall() method and store the result in result set variable “rs” rs=cc.fetchall() Open the existing DB Execute the select query using execute() via cursor object Select query Read all the rows using fetchall() method Elangovan Tech Notes 26
- 27. 2. Data Retrieval (Read) – (Con) SOURCE CODE print("ID Name Dep CGPA") for row in rs: print(row[0],row[1],row[2],row[3]) # close the DB con.close() Iterate the records ONE BY ONE from result set (rs) using for loop The cursor initially points to 0th row before loop. In the loop, it starts from 1st row and ends at last row if next row is unavailable. Here column names are labeled with index numbers 0 to n-1 Where row[0] -> First Column, row[1] -> Second Column row[2] -> Third Column, row[3] -> Fourth Column Close the DB Elangovan Tech Notes 27
- 28. 2. Data Retrieval (Read) – (Con) OUTPUT Elangovan Tech Notes 28
- 29. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) DATA UPDATE • To update the record from database table, do the following things mentioned below 1. Connect and open the existing database using connect() method 2. Define the update query and substitute it in the execute() method of connection object 3. Execute the query using execute() method of connection object 4. Commit the changes using commit() method of connection object 5. Close the DB. Elangovan Tech Notes 29
- 30. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) SOURCE CODE import sqlite3 print("---------------------------------") print("tData Updation") print("---------------------------------") # connect and open the existing DB con=sqlite3.connect("ganesh.db") # define the update query usql="update stud set name='Velan', dept='SE' where id=5" # execute the update query using execute() method of connection object con.execute(usql) con.commit() Update the record number 5 Elangovan Tech Notes 30
- 31. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) SOURCE CODE print("One Record is successfully updated...") print("Total Rows are affected...",con.total_changes) # close the DB con.close() Elangovan Tech Notes 31
- 32. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) OUTPUT Elangovan Tech Notes 32
- 33. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) Before Update (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool] Elangovan Tech Notes 33
- 34. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) After Update (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool] Elangovan Tech Notes 34
- 35. 4. Data Deletion (CRUD) DATA DELETION • To delete the record from database table, do the following things mentioned below 1. Connect and open the existing database using connect() method 2. Define the update query and substitute it in the execute() method of connection object 3. Execute the query using execute() method of connection object 4. Commit the changes using commit() method of connection object 5. Close the DB. Elangovan Tech Notes 35
- 36. 4. Data Deletion (CRUD) – (Con) SOURCE CODE import sqlite3 print("-------------------------------") print("tData Deletion") print("-------------------------------") # connect and open the DB con=sqlite3.connect("ganesh.db") # delete query dsql="delete from stud where id=7" # execute the delete query using execute() method of connection object con.execute(dsql) con.commit() Delete the 7th record Save this transaction in DB using commit() method Elangovan Tech Notes 36
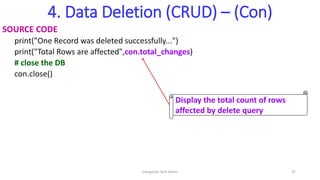
- 37. 4. Data Deletion (CRUD) – (Con) SOURCE CODE print("One Record was deleted successfully...") print("Total Rows are affected",con.total_changes) # close the DB con.close() Display the total count of rows affected by delete query Elangovan Tech Notes 37
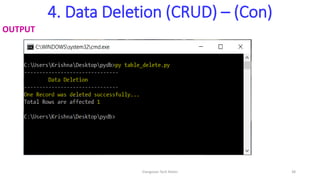
- 38. 4. Data Deletion (CRUD) – (Con) OUTPUT Elangovan Tech Notes 38
- 39. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) Before Delete (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool] Elangovan Tech Notes 39
- 40. 3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con) After Delete (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool] Before deletion, total records were 5. After the deletion of one record, the total count of records are 4. Elangovan Tech Notes 40
- 41. Thank You Elangovan Tech Notes 41
- 42. Live Demo Click the link below to watch the demo step by step https://youtu.be/0yxhJ8amoi8 Elangovan Tech Notes 42
- 43. ETS Tutorial - YouTube Channel Visit our YouTube Channel Elangovan Tech Notes (ETS) • Python Tutorial • C# Tutorial • Java Tutorial • Shell Scripting • PHP Tutorial https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC-yI6rR_EGSY8cVs4qHo0BQ Elangovan Tech Notes 43

















![1.1 Data Insertion – (Con)
PROOF FOR DATA INSERTION OPERATION [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool]
Elangovan Tech Notes 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonsqlite3database-210911074227/85/Python-SQite3-database-Tutorial-SQlite-Database-24-320.jpg)

![2. Data Retrieval (Read) – (Con)
SOURCE CODE
print("ID Name Dep CGPA")
for row in rs:
print(row[0],row[1],row[2],row[3])
# close the DB
con.close()
Iterate the records ONE BY ONE
from result set (rs) using for loop
The cursor initially points to 0th row before
loop. In the loop, it starts from 1st row and
ends at last row if next row is unavailable.
Here column names are labeled with index numbers 0 to n-1
Where
row[0] -> First Column, row[1] -> Second Column
row[2] -> Third Column, row[3] -> Fourth Column
Close
the DB
Elangovan Tech Notes 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonsqlite3database-210911074227/85/Python-SQite3-database-Tutorial-SQlite-Database-27-320.jpg)





![3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con)
Before Update (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool]
Elangovan Tech Notes 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonsqlite3database-210911074227/85/Python-SQite3-database-Tutorial-SQlite-Database-33-320.jpg)
![3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con)
After Update (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool]
Elangovan Tech Notes 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonsqlite3database-210911074227/85/Python-SQite3-database-Tutorial-SQlite-Database-34-320.jpg)


![3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con)
Before Delete (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool]
Elangovan Tech Notes 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonsqlite3database-210911074227/85/Python-SQite3-database-Tutorial-SQlite-Database-39-320.jpg)
![3. Data Updation (CRUD) – (Con)
After Delete (Table Data) [DB Browser for SQLite – Tool]
Before deletion, total records were 5.
After the deletion of one record, the
total count of records are 4.
Elangovan Tech Notes 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonsqlite3database-210911074227/85/Python-SQite3-database-Tutorial-SQlite-Database-40-320.jpg)


