List of instrument
- 1. Presented By :- Pawar Parmeshwar U. Ivth Sem. of EEGuidance By :- Mulje Mam, (Lectures of Electrical Department )
- 2. An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milli ampere or microampere range, are designated as milli ammeters or micro ammeters 1. Ammeter
- 3. A barometer is a scientific instrument used in meteorology to measure atmospheric pressure. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Numerous measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, high pressure systems and frontal boundaries. 2. Barometerair pressure
- 4. 3. Clock A clock is an instrument to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". In general usage today a "clock" refers to any device for measuring and displaying the time. Watches and other timepieces that can be carried on one's person are often distinguished from clocks
- 5. 4. Dynamometerforce, torque or power A dynamometer or "dyno" for short, is a device for measuring force, torque, or power. For example, the power produced by an engine, motor or other rotating prime mover can be calculated by simultaneously measuring torque and rotational speed (RPM).
- 6. electric charge 5. Electrometer An electrometer is an electrical instrument for measuring electric charge or electrical potential difference. There are many different types, ranging from historical handmade mechanical instruments to high-precision electronic devices.
- 7. 6. frequency counterfrequency of alternating current A frequency counter is an electronic instrument, or component of one, that is used for measuring frequency. Frequency counters usually measure the number of oscillations or pulses per second in a repetitive electronic signal. Such an instrument is sometimes referred to as a Cytometer, particularly one of Chinese manufactures
- 8. 7. Galvanometer A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection electric current through its coil in a magnetic field. electricity
- 9. 8. Hydrometer A hydrometer is an instrument that measures the specific gravity (relative density) of liquids. The ratio of the density of the liquid to the density of water. A hydrometer is usually made of glass, and consists of a cylindrical stem and a bulb weighted with mercury or lead shot to make it float upright. density of the liquid
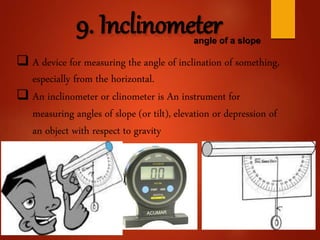
- 10. 9. Inclinometerangle of a slope A device for measuring the angle of inclination of something, especially from the horizontal. An inclinometer or clinometer is An instrument for measuring angles of slope (or tilt), elevation or depression of an object with respect to gravity
- 11. 10. katharometercomposition of gases The thermal conductivity detector (TCD), also known as a Katharometer, is a bulk property detector and a chemical specific detector commonly used in gas chromatography. This detector senses changes in the thermal conductivity of the column effluent and compares it to a reference flow of carrier gas.
- 12. 11. load cellmeasurement of force A load cell is a transducer that is used to create an electrical signal whose magnitude is directly proportional to the force being measured. The various types of load cell sinclude hydraulic load cells, pneumatic load cells and strain gauge load cells.
- 13. An instrument designed to measure electric current, voltage, and usually resistance, typically over several ranges of value. A multimeter is used to make various electrical measurements, such as AC and DC voltage, AC and DC current, and resistance. 12. Multimeter electrical potential, resistance, and current
- 14. A nephelometer is an instrument for measuring concentration of suspended particulates in a liquid or gas colloid. A nephelometer measures suspended particulates by employing a light beam (source beam) and a light detector set to one side (often 90°) of the source beam. 13. Nephelometer particle in a liquid
- 15. An ohmmeter is an electrical instrument that measures electrical resistance, the opposition to an electric current. 14. Ohmmeterelectrical resistance
- 16. A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of a surface. Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. 15. Pyrometerhigh temperature
- 17. A Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) measures a mass variation per unit area by measuring the change in frequency of a quartz crystal resonator. The resonance is disturbed by the addition or removal of a small mass due to oxide growth/decay or film deposition at the surface of the acoustic resonator. 16. Quartz Crystal Microbalance thickness of deposited thin film
- 18. A radiometer or roentgenometer is a device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of electromagnetic radiation. radiant flux of electromagnetic radiation 17. Radiometer
- 19. 18. SWR meterstanding wave ratio The SWR Meter or VSWR (voltage standing wave ratio) meter measures the standing wave ratio in a transmission line.
- 20. 19. Tachometer A tachometer (revolution-counter, tach, rev-counter, RPM gauge) is an instrument measuring the rotation speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. The device usually displays the revolutions per minute (RPM) on a calibrated analogue dial, but digital displays are increasingly common. rotation speed of a shaft
- 21. 20. UV Meter "Ultraviolet" means "beyond violet" (from Latin ultra, "beyond"), violet being the colour of the highest frequencies of visible light. Ultraviolet light has a higher frequency than violet light. ultraviolet light
- 22. 21. Voltmeterelectric potential, voltage A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to digital converter. The voltmeter in a circuit is represented by encircled 'V'.
- 23. electrical power 22. Wattmeter It is an instrument for measuring the electric power (or the supply rate of electrical energy) in watts of any given circuit. Electromagnetic wattmeter's are used for measurement of utility frequency and audio frequency power; other types are required for radio frequency measurements.
- 24. An instrument for ascertaining the degree of fermentation occasioned by the mixture of different liquids and the degree of heat which they acquire in fermentation. 23. zymometermixture of different liquids