A Quick Guide to Maintenance Function
- 2. Introduction Not quite sure if this book would be useful for you? If you belong to any of the category of people mentioned below, then this book is for you. • Manufacturing Sector expects the engineers to be Job- ready. However, the engineering curriculum does not cover some of the basics required in the manufacturing sector. This book would help in understanding the basics, so that a fresh engineer can perform his role immediately aCer joining the company. Fresh Engineers interested in joining Manufacturing Sector • This book can serve as an “InducIon Manual” for the new Supervisors and Engineers in the shop floor. Job ResponsibiliIes, Do’s and Don’ts for each role, Tools and Techniques and MIS reports are explained for each department. This would help in faster career growth. Supervisors / Engineers in the Shop floor • This book can serve as a Quick Guide to teach you and your employees, the basics of manufacturing organizaIon. This would also help you in managing your people, building the organizaIon to the next level by creaIng strong processes. Second GeneraIon Entrepreneurs
- 3. Why this book? • In India, several studies conducted on the employability skills state that only 5% to 10% of the Engineers graduating from the Institutions are Job-Ready / Employable. • Industries require workforce which are readily employable, so that they do not have to spend a lot of money and effort on providing basic skills and on- the-Job training • While large organisations have Induction training for their employees, many medium and small scale companies do not have proper structure to provide this training • Their employees work with very little awareness of the best practices of the industry, making them frustrated, fire-fighting for day-to-day activities and results in a lot of stress • This also makes the companies uncompetitive, leading to poor business performance, resulting in poor motivation of the people, and this becomes a vicious cycle • This publication is aimed at providing the fundamentals of manufacturing management which are not offered by any of our institutions/curriculum to Engineers and Diploma Holders who are joining Manufacturing Industry • This is our initiative to empower the professionals in performing more efficiently and effectively helping the organization and the nation • In addition, this gives us immense satisfaction that we are giving something back to the ecosystem we are working in and are able to challenge the traditional way of thinking and practices.
- 4. What do we cover in the book? A typical manufacturing company has Production, Production Planning, Quality, Stores, Purchase, Maintenance, Finance & Accounts, Marketing, Human Resources, Admin , Information Technology and Sales functions. However, we would cover 1. Production 2. Production Planning 3. Purchase 4. Stores 5. Quality 6. Maintenance functions in this book, since these are the major areas, an Engineer or a Diploma/Degree Holder joins after his/her degree.
- 5. Structure of the contents Each department / function is explained in the following structure: • General Introduction to the Function / Department • Organization Structure of the function • Roles and Responsibilities of the key incharges • Process Flow in the function • Tools and Techniques required in the function • Pictures and tables to demonstrate the activities (wherever applicable) • MIS Reports and the Analysis to be done • Key Result Areas (KRAs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for each function
- 7. Introduction to Manufacturing Company A manufacturing company produces goods (or materials) using tools, machines, chemical processing, biologic processing or formulation and with the use of people. Manufacturing ranges from small hand-made products (Handicrafts industry) to large / Hitech products (Aircraft / Bullet Trains). A typical manufacturing company procures many parts/raw materials from various suppliers (or Vendors), process them (discrete manufacturing or flow manufacturing) and sell to its customers. These customers may be the end users of the product or may use the products to make other products. For e.g. A glass manufacturing company procures silica and other raw materials for making glass. This can either be sold as end product to consumers (for home use) or to an Automotive factory to use these glass for cars (of course, the grades would be different). In this book, we consider a typical manufacturing company consisting of a few discrete manufacturing processes (e.g., Turning, Milling, Polishing, etc.).
- 8. There are various functions (or departments) in organisations, each focusing on a few major activities. 1. Production Function - Focuses on the manufacturing of the product 2. Purchase Function - Focuses on purchasing / buying the raw materials and consumables required for the production 3. Stores Function - Focuses on the receiving the incoming raw materials, holding them properly and issuing them to the user department when there is a need for the materials 4. Maintenance - To keep all the machines ready for production. To prevent break-downs of machines, Each function consists of a group of persons (or a single person) performing their tasks. A company is headed by the CEO / Directors / Owners depending on its structure. Various levels of managers across various functions report to the CEO / Directors. Supervisors / In-charges report to the managers and they manage the operators (shop floor employees across various levels) Pic: 1.1 - Various Levels of Employees CEO / VP / Promoter Process steps that take time, (VA) A process step that transforms or shapes a product or service, which is eventually sold to a customer. resources, or space, but do not add value to the product or service. Directors / Promoters Managers (various levels) Supervisors / Incharges (various levels) Operators / Employees (various levels) Senior Management Level Middle Management Level Junior Management Level Employee Level
- 9. Internal and External Customer External Customer: A customer who buys the product / services of a company. All the functions in an organization exist to fulfil the need of these end customers. This customer is not a part of your organization but pays your organization for the products / services. Internal Customer: A member of the organization providing goods / services for other members inside the organization. For e.g. Stores issues raw materials to production. So Production function is a customer for Stores. Inside Production function, each operation sends the product to the next operation thus becomes a supplier to the next operation. These are called Internal Customers and Internal Suppliers. Pic: 1.2 - Internal Suppliers and Customers Stores Production Internal CustomerInternal Supplier
- 10. Goals of each department Each department works with a set of goals which are aimed at satisfying / exceeding their Internal / External customer’s needs. These goals are called Key Result Areas (KRA’s) or Department Objectives / Targets. Generally there are 6 major categories of objectives / KRAs: 1. Productivity 2. Quality 3. Cost 4. Delivery 5. Safety 6. Morale These KRA’s needed to be measured through various Indicators. They are called Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). For e.g. Productivity can be measured by indicators like “output per person per day”, “Planned production vs. achieved production”, “Utilisation of the machine”, etc. Similarly, Quality can be measured by “Reduction in defectives”, “% of yield”, etc. All the departments will have KRAs and KPIs to measure their performance. Generally there would be a Monthly Review Meeting (MRM) to discuss the performance and take corrective and preventive actions.
- 12. Maintenance Function • Maintenance function ensures that all the machines and equipments related to the production and other key functions in the organization are maintained and function properly • Maintenance Function plans for the spares and consumables for the maintenance • They co-ordinate with outside agencies / other functions in case of layout change / wiring / machine movement, etc. • Maintenance should ensure that there should not be any breakdowns of any machines We have used a few pictures in this book, which were taken from public sources. These are only for educational purposes. We do not own these images. The Author and Hash Management Services LLP will not take ownership for these images and any liability arising out of these images.
- 13. Job Responsibilities of Maintenance Engineer Following are the critical job responsibilities of Maintenance Function • To bring the Machine to Basic condition • Taking Machines to Higher Levels of Performance • To Move towards Zero Failures , Zero Defects & Zero Accidents • There are 2 basic types of maintenance o Break-down Maintenance – Done after the Machine breaks down o Preventive Maintenance – before the Machine breaks down - done by the Maintenance team at regular intervals to keep the machine in working condition § Autonomous Maintenance (AM) is a part of Preventive Maintenance (PM) § AM is done by the operator themselves on a daily basis • Over a period of time, Break-downs of machines should become zero! Pic: 5.1 - Types of Maintenance
- 14. Break-Down Maintenance • Once a particular machine breaks down, the operator informs the production supervisor to raise a complaint to the Maintenance team • Maintenance team rushes to the machine and fix the issue • Most companies have a Service Level Agreement with the Maintenance team to attend the machines (e.g. maintenance team personnel should reach the machine with in 30 min) Preventive Maintenance This is a schedule based maintenance program, which would be done by the maintenance team Daily / weekly / fortnightly / monthly / quarterly plan for all machines A preventive Maintenance calendar should be created covering all major machines in the company and person responsible for the same
- 15. Autonomous Maintenance (AM) • Would be done by the operator themselves • Cleaning / Lubrication / Re-tightening / Inspection are covered under Autonomous Maintenance • Minor spare change can also be covered under AM Steps for Implementing AM • Preparation • Cleaning and Inspection • Eliminate Problem Sources and abnormalities • Cleaning, Lubrication, Re-tightening, Inspection – Checklists and Audits • Visual Management Please note that this list covers only the basics. This is not the exhaustive list of steps as prescribed by the TPM model
- 16. Step 1 - Preparation • Identify the Machine parts and the purpose /activity of the part in the machine • Know the function of the machine • Know the safety aspect of the machine • Operator Training to handle the machine Step 2 - Cleaning and Inspection • Initial Cleaning of the Machine • Identification of • Abnormality • Hard to Access area • Source of Contamination & Localization • Unsafe Conditions Knowing the machine and its parts is the Primary Step
- 17. Initial Cleaning of the Machine • Before cleaning, all WIP materials in the machine to be properly covered. • Cleaning Agent should not be used on the Machine parts where there is direct contact with the materials • Cleaning tools: o Cotton Waste o Tool Box / Trolley o Wire Brushes o Ladder , Screw Driver o Emery Sheet - Medium o Cleaning Agent – Kerosene , Soap oil Pic: 5.2 - Cleaning the Machine
- 18. Identification of Abnormality Pic: 5.3 - Abnormalities and where to find them?
- 19. Step 3 - Elimination of Abnormalities Pic: 5.4 - Types of Abnormalities Missing Nut Nut Fixed Missing Screw Screw Fixed
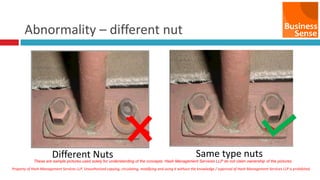
- 20. Step 3 - Elimination of Abnormalities Pic: 5.5 - Types of Abnormalities Different Nut Same type nuts No Grease Grease Filled
- 21. Step 3 - Elimination of Abnormalities Pic: 5.6 - Types of Abnormalities Oil Leak from machine Oil Leak Fixed No guard for drive Guard Fixed
- 22. Step 4 - Checklists and Audit Templates List of Abnormalities - Template Maintenance Checklists - Template Pic: 5.7 - Checklist and Audit Templates
- 23. Step 4 - Audit Plan Audit Plan - Template Pic: 5.8 - Audit Plan for Maintenance Breakdown Register - Template
- 24. Step 5 - Visual Management • Bolt Alignment – look at the markings for alignment • Markings to show the working range • Needle should always between the red marks • Look at the calibration date sticker Pic: 5.9 - Visual Management
- 25. Step 5 - Visual Management • Markings to show the level of the grease in the reservoir. • Look at the red, yellow and green levels • Visuals showing the details of Motor HP, Motor RPM, Sprocket and Chain Details • Chain rotation direction and eye symbol for inspection area Pic: 5.10 - Visual Management
- 26. Step 5 - Visual Management • Lever Open and Close markings • Pressure markings in the pipes and the direction of flow Pic: 5.11 - Visual Management
- 27. What are the KRAs and KPIs of your department? Goals / KRAs Performance Indicators / KPIs Measure Current Level Target Productivity No Breakdowns of machines in nos 3 0 Productivity No Accidents in the shop floor in nos 1 0 Productivity Autonomous Maintenance carried out in all machines in % 70% 100% Quality Time taken to fix the machines (Mean Time to Repair - MTTR) in minutes 10 5 Prepare your department’s KRA’s in case your organization does not have them.
- 28. Learning’s from the Section At the end of Maintenance Section, Are you clear on the following? • Types of Maintenance (Breakdown / Preventive / Autonomous) • Types of Abnormalities • Where to find the Abnormalities • Check lists and Audit Plans for Maintenance • Visual Management
- 29. Interested in buying the book? Please click on any of the following links to buy. View Listing Print Book India View Listing View Listing View Listing View Listing View Listing International Print Books View Listing View Listing eBooks View Listing View Listing View Listing View Listing
- 30. Meet the Author Ananth is the CEO and Founder of Hash Management Services LLP. Ananth has over 12 years of experience in the areas of Implementation of Lean Manufacturing concepts, Quality Management, and Supply Chain Management initiatives. Some of the industries he works/worked with are Textiles, Leather and Footwear, Castings and Forgings, Electronic Equipment, Pump Manufacturing, Fabrication, White goods, Heavy Engineering and Light Engineering sectors. He works with Industry bodies like CII, FICCI and currently working with International Labour Organization (ILO) for implementing their SCORE Program in a few auto ancillaries in Chennai. He is also an empaneled Lean Manufacturing Consultant (LMC) with National Productivity Council (NPC) and working on Implementing Lean Manufacturing principles for Small and Medium Enterprises. Prior to Hash Management Services LLP, he was a consultant with Deloitte`s consulting practice in India. Earlier, Ananth worked with Titan Industries Ltd, as a Senior Engineer responsible for productivity improvements and various quality initiatives. He holds PGDM from the IFMR, Chennai and a Bachelors degree in Mechanical Engineering from the Government College of Engineering, Tirunelveli. Please visit www.hashllp.com to know more about the ways we help manufacturing companies improve their operations and profitability.
- 31. Disclaimer The advice contained in this material is for a specific audience and not for general public. The author designed the information to present his opinion about the subject matter. The reader must carefully investigate all aspects of any business decision before committing him or herself. The author obtained the information contained herein from sources he believes to be reliable and from his own personal experience, but he neither implies nor intends any guarantee of accuracy. The author particularly disclaims any liability, loss or risk taken by individuals who directly or indirectly act on the information herein. The author believes the advice presented here is sound, but the readers cannot hold him responsible for either the take or the result of those actions.
- 32. Acknowledgements This book would not have been a reality without the contribution from V N Shiju who worked with me on creating the contents, L S Kannan contributed Quality section, Veerabaghu, my mentor and guide, my wife Jeyalakshmi who helped me in documentation, A S Senthil Kumar, my first boss who helped me understand the basics of manufacturing industry, my colleagues at Deloitte and all my friends who stood by me during some of the toughest times in my life.