09 review
- 1. 1 CHAPTER 9: Moments of Inertia ! Moment of Inertia of Areas ! Second Moment, or Moment of Inertia, of an Area ! Parallel-Axis Theorem ! Radius of Gyration of an Area ! Determination of the Moment of Inertia of an Area by Integration ! Moments of Inertia of Composite Areas ! Polar Moment of Inertia
- 2. 2 9.1 Moment of Inertia: Definition x y y x dA=(dx)(dy) ∫= A x dAyI 2 )( O ∫= A y dAxI 2 )(
- 3. 3 x y x´= Centroidal axis y´ = Centroidal axis CG dy y´ dx x´ dA ∫ += A yx dAdyI 2 )'( ∫ ++= A yy dAddyy ])())('(2)'[( 22 ∫∫∫ ++= A y A y A dAddAdydAy 22 )())('(2)'( ∫∫ ++= A y A yx dAddAydI 2 '2 0, y´ = 0 AdII yxx 2 0 ++= AdII xyy 2 0 ++= 9.2 Parallel-Axis Theorem of an Area 2 AdJJ CO += O
- 4. 4 y x kx O A A J k A I k A I k O O y y x x === 9.3 Radius of Gyration of an Area 2 The radius of gyration of an area A with respect to the x axis is defined as the distance kx, where Ix = kx A. With similar definitions for the radii of gyration of A with respect to the y axis and with respect to O, we have
- 5. 5 The rectangular moments of inertia Ix and Iy of an area are defined as These computations are reduced to single integrations by choosing dA to be a thin strip parallel to one of the coordinate axes. The result is x y y dx x ∫∫ == dAxIdAyI yx 22 dxyxdIdxydI yx 23 3 1 == 9.4 Determination of the Moment of Inertia of an Area by Integration
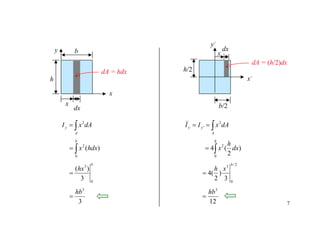
- 6. 6 x´ y´ b/2 h/2 • Moment of Inertia of a Rectangular Area. x y b h y dy ∫= A x dAyI 2 ∫= h bdyy 0 2 )( h by 0 3 3 )( = y dy ∫== A xx dAyII 2 ' ∫= h dy b y 0 2 ) 2 (4 2/ 0 3 3 ) 2 (4 h yb = 3 3 bh = 12 3 bh = dA = bdy dA = (b/2)dy
- 7. 7 x´ y´ b/2 h/2 x y b h ∫= A y dAxI 2 ∫= b hdxx 0 2 )( b hx 0 3 3 )( = ∫== A yy dAxII 2 ' ∫= h dx h x 0 2 ) 2 (4 2/ 0 3 3 ) 2 (4 b xh = 3 3 hb = 12 3 hb = x dx x dx dA = hdx dA = (h/2)dx
- 8. 8 x y b h/2 h/2 12 3 bh Ix = 3 3 bh Ix = 2 AdII xx += 2 3 ) 2 )(( 12 h bh bh += 412 33 bhbh += 3 3 bh Ix =
- 9. 9 dIx = y2 dA dA = l dy Using similar triangles, we have dy h yh bdA h yh bl h yh b l − = − = − = Integrating dIx from y = 0 to y = h, we obtain ∫∫ ∫ −= − = = hh x dyyhy h b dy h yh by dAyI 0 32 0 2 2 )( 12 ] 43 [ 3 0 43 bhyy h h b h =−= • Moment of Inertia of a Triangular Area. 2 AdII xx += 36 ) 3 )( 2 ( 12 3 2 3 2 bhhbhbh AdII xx =−= −= y x h b/2 h-y b/2 dy yl
- 10. 10 Example 9.1 Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area shown with respect to each of the coordinate axes. x y a y = kx2 b
- 11. 11 x y a y = kx2 b • Moment of Inertia Ix. dy dA = (a-x)dy 2 kxy = 2 kab = 2 a b k = 2/1 2/1 2 2 y b a xorx a b y == Substituting x = a and y=b ∫= A x dAyI 2 ∫ −= b dyxay 0 2 )( ∫ −= b dyy b a ay 0 2/1 2/1 2 )( dyy b a dyya bb ∫∫ −= 0 2/5 2/1 0 2 bb y b aay 0 2/7 2/1 0 3 ) 7 2 ( 3 −= ) 7 2 ( 3 2/7 2/1 3 b b aab −= 7 2 3 33 abab −= 21 3 ab =
- 12. 12 x y a y = kx2 b • Moment of Inertia Iy. 2 2 x a b y = ∫= A y dAxI 2 ∫= a ydxx 0 2 dx dA = ydx ∫= a dxx a b x 0 2 2 2 )( ∫= a dxx a b 0 4 2 a x a b 0 5 2 ) 5 )((= ) 5 )(( 5 2 a a b = 5 3 ba =
- 13. 13 Example 9.2 Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area shown with respect to each of the coordinate axes. x y y2 = x2 y1 = x (a,b)
- 14. 14 x y y2 = x2 y1 = x (a,b) dy dA = (x2 - x1)dy ∫= A x dAyI 2 ∫ −= b dyxxy 0 2 )( 12 ∫ −= b dyyyy 0 2/12 )( ∫∫ −= bb dyydyy 0 3 0 2/5 )()( bb y y 0 4 0 2/7 47 2 −= • Moment of Inertia Ix. 47 2 4 2/7 b b −=
- 15. 15 x y y2 = x2 y1 = x (a,b) • Moment of Inertia Iy. ∫= A y dAxI 2 ∫ −= a dxyyx 0 1 2 )( 2 dx dA = (y1 - y2)dx ∫ −= a dxxxx 0 22 )( ∫∫ −= aa dxxdxx 0 4 0 3 )()( aa xx 0 5 0 4 54 −= 54 54 aa −=
- 16. 16 The parallel-axis theorem is used very effectively to compute the moment of inertia of a composite area with respect to a given axis. d c o centroid are related to the distance d between points C and O by the relationship 2 AdJJ CO += 9.5 Moment of Inertia of Composite Areas A similar theorem can be used with the polar moment of inertia. The polar moment of inertia JO of an area about O and the polar moment of inertia JC of the area about its
- 17. 17 Example 9.3 Compute the moment of inertia of the composite area shown. 75 mm 75 mm 100 mm 25 mm x
- 18. 18 SOLUTION 75 mm 75 mm 100 mm x 25 mm = (dy)Cir Ciryxctx AdI bh I )() 3 ( 2 Re 3 +−= Circt ])75)(25()25( 4 1 [])150)(100( 3 1 [ 224 Re 3 ×+−= ππ = 101x106 mm4
- 19. 19 Example 9.4 Determine the moments of inertia of the beam’s cross-sectional area shown about the x and y centroidal axes. 400 Dimension in mm 100 400 100 600 100 x y C
- 20. 20 400 Dimension in mm 100 400 100 600 100 x y C SOLUTION A dyA B dyD D CyxByxAyxx AdIAdIAdII )()()( 222 +++++= ])200)(300100()300)(100( 12 1 [ ]0)100)(600( 12 1 [])200)(300100()300)(100( 12 1 [ 23 323 ×++ ++×+= = 2.9x109 mm4 0
- 21. 21 400 Dimension in mm 100 400 100 600 100 x y C CxyBxyAxyy AdIAdIAdII )()()( 222 +++++= C BA ])250)(300100()100)(300( 12 1 [ ]0)600)(100( 12 1 [])250)(300100()100)(300( 12 1 [ 23 323 ×++ ++×+= = 5.6x109 mm4 A dxA dxD D 0
- 22. 22 Example 9.5 (Problem 9.31,33) Determine the moments of inertia and the radius of gyration of the shaded area with respect to the x and y axes. 6 mm O x y 24 mm 24 mm 6 mm 12 mm12 mm 24 mm 24 mm 8 mm
- 23. 23 6 mm O x y 24 mm 24 mm 6 mm 12 mm12 mm 24 mm 24 mm 8 mm SOLUTION A dyA B Ix = 390x103 mm4 mm A I k x x 9.21 )]648()488()624[( 10390 3 = ×+×+× × == CyxByxAyxx AdIAdIAdII )()()( 222 +++++= Iy = 64.3x103 mm4 CBA ])48)(6( 12 1 [])8)(48( 12 1 [])24)(6( 12 1 [ 333 ++= 0 00 CxyBxyAxyy AdIAdIAdII )()()( 222 +++++= mm A I k y y 87.8 )]648()488()624[( 103.64 3 = ×+×+× × == 0 C B A ])27)(648()6)(48( 12 1 [ ]0)48)(8( 12 1 [ ])27)(624()6)(24( 12 1 [ 23 3 23 ×++ ++ ×+= C dyC
- 24. 24 Example 9.6 (Problem 9.32,34) Determine the moments of inertia and the radius of gyration of the shaded area with respect to the x and y axes. 2 m O 1 m 1 m 1 m 1 m 0.5 m0.5 m 2 m 2 m 0.5 m0.5 m x y
- 25. 25 2 m O 1 m 1 m 1 m 1 m 0.5 m0.5 m 2 m 2 m 0.5 m0.5 m x y A B dyB C dyC Ix = 46 m4 m A I k x x 599.1 )]14()24()65[( 46 = ×−×−× == 14 2 24 2 65 2 )()()( ××× +−+−+= CyxByxAyxx AdIAdIAdII 0 C BA ])5.1)(14()1)(4( 12 1 [ ])2)(42()2)(4( 12 1 []0)6)(5( 12 1 [ 23 233 ×+− ×+−+= Iy = 46.5 m4 CBA ])4)(1( 12 1 [])4)(2( 12 1 [])5)(6( 12 1 [ 333 −−= 0 00 CxyBxyAxyy AdIAdIAdII )()()( 222 +−+−+= m A I k y y 607.1 )]14()24()65[( 5.46 = ×−×−× ==
- 26. 26 Example 9.7 Determine the moments of inertia and the radius of gyration of the shaded area with respect to the x and y axes and at the centroidal axes. 1 cm 1 cm 5 cm 1 cm 5 cm x y
- 27. 27 1 cm 1 cm 5 cm 1 cm 5 cm x y CG Y ∑∑ = AyAY cm Y 5.2 )15(3 )51)(5.0()]15)(5.3[(2 = × ×+× = 4 2 2 25.51 )5.2)(15(145 cm AdII yxx = −= −= • Moments of inertia about centroid 4 23 23 25.51 ])2)(15()1)(5( 12 1 [( ])1)(15()5)(1( 12 1 [(2 cm I OR x = ×++ ×+= cm A I kk x yx 848.1 15 25.51 ==== 4 323 145 )1)(5( 3 1 ])5.3)(15()5)(1( 12 1 [(2 cm Ix = +×+= • Moments of inertia about x axis 4 323 25.51 )5)(1( 12 1 ])2)(15()1)(5( 12 1 [(2 cm II yy = +×+== 0.5 3.5 2
- 28. 28 Example 9.8 The strength of a W360 x 57 rolled-steel beam is increased by attaching a 229 mm x 19 mm plate to its upper flange as shown. Determine the moment of inertia and the radius of gyration of the composite section with respect to an axis which is parallel to the plate and passes through the centroid C of the section. C 229 mm 19 mm 358 mm 172 mm
- 29. 29 229 mm 172 mm SOLUTION 19 mm 358 mm x O C x´ Y 188.5 mm The wide-flange shape of W360 x 57 found by referring to Fig. 9.13 A = 7230 mm2 4 2.160 mmIx = AyAY Σ=Σ Aplate = (229)(19) = 4351 mm2 )7230)(0()4351)(5.188()72304351( +=+Y mmY 8.70= • Centroid • Moment of Inertia flangewidexplatexx III −+= )()( ''' flangewidexplatex YAIAdI −+++= )()( 2 ' 2 ' [ ] 46 26 23 108.256 )8.70)(7230(102.160 )8.705.188)(4351()19)(229( 12 1 mm×= +×+ −+= • Radius of Gyration )72304351( 108.256 6 '2 ' + × == A I k x x mmkx 149' = 46 ' 10257 mmIx ×= d
- 30. 30 The polar moment of inertia of an area A with respect to the pole O is defined as The distance from O to the element of area dA is r. Observing that r 2 =x 2 + y 2 , we established the relation y xx y r A dA O ∫= dArJO 2 yxO IIJ += 9.6 Polar Moment of Inertia
- 31. 31 Example 9.9 (a) Determine the centroidal polar moment of inertia of a circular area by direct integration. (b) Using the result of part a, determine the moment of inertia of a circular area with respect to a diameter. y x r O
- 32. 32 u du O y x r SOLUTION a. Polar Moment of Inertia. duudAdAudJO π22 == ∫∫ ∫ === rr OO duuduuudJJ 0 3 0 2 2)2( ππ 4 2 rJO π = b. Moment of Inertia with Respect to a Diameter. xyxO IIIJ 2=+= xIr 2 2 4 = π 4 4 rII xdiameter π ==


![3
x
y
x´= Centroidal axis
y´ = Centroidal axis
CG
dy
y´
dx x´
dA
∫ +=
A
yx dAdyI 2
)'(
∫ ++=
A
yy dAddyy ])())('(2)'[( 22
∫∫∫ ++=
A
y
A
y
A
dAddAdydAy 22
)())('(2)'(
∫∫ ++=
A
y
A
yx dAddAydI
2
'2
0, y´ = 0
AdII yxx
2
0 ++=
AdII xyy
2
0 ++=
9.2 Parallel-Axis Theorem of an Area
2
AdJJ CO +=
O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-3-320.jpg)




![9
dIx = y2 dA dA = l dy
Using similar triangles, we have
dy
h
yh
bdA
h
yh
bl
h
yh
b
l −
=
−
=
−
=
Integrating dIx from y = 0 to y = h, we obtain
∫∫
∫
−=
−
=
=
hh
x
dyyhy
h
b
dy
h
yh
by
dAyI
0
32
0
2
2
)(
12
]
43
[
3
0
43
bhyy
h
h
b h
=−=
• Moment of Inertia of a Triangular Area.
2
AdII xx +=
36
)
3
)(
2
(
12
3
2
3
2
bhhbhbh
AdII xx
=−=
−=
y
x
h
b/2
h-y
b/2
dy
yl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-9-320.jpg)








![18
SOLUTION
75 mm
75 mm
100 mm
x
25 mm
= (dy)Cir
Ciryxctx AdI
bh
I )()
3
(
2
Re
3
+−=
Circt ])75)(25()25(
4
1
[])150)(100(
3
1
[ 224
Re
3
×+−= ππ
= 101x106 mm4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-18-320.jpg)

![20
400
Dimension in mm
100
400
100
600
100
x
y
C
SOLUTION
A
dyA
B
dyD
D
CyxByxAyxx AdIAdIAdII )()()(
222
+++++=
])200)(300100()300)(100(
12
1
[
]0)100)(600(
12
1
[])200)(300100()300)(100(
12
1
[
23
323
×++
++×+=
= 2.9x109 mm4
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-20-320.jpg)
![21
400
Dimension in mm
100
400
100
600
100
x
y
C
CxyBxyAxyy AdIAdIAdII )()()(
222
+++++=
C
BA
])250)(300100()100)(300(
12
1
[
]0)600)(100(
12
1
[])250)(300100()100)(300(
12
1
[
23
323
×++
++×+=
= 5.6x109 mm4
A
dxA
dxD
D
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-21-320.jpg)

![23
6 mm
O
x
y
24 mm
24 mm
6 mm
12 mm12 mm
24 mm 24 mm
8 mm
SOLUTION
A
dyA
B
Ix = 390x103 mm4
mm
A
I
k x
x 9.21
)]648()488()624[(
10390 3
=
×+×+×
×
==
CyxByxAyxx AdIAdIAdII )()()(
222
+++++=
Iy = 64.3x103 mm4
CBA ])48)(6(
12
1
[])8)(48(
12
1
[])24)(6(
12
1
[ 333
++=
0 00
CxyBxyAxyy AdIAdIAdII )()()(
222
+++++=
mm
A
I
k
y
y 87.8
)]648()488()624[(
103.64 3
=
×+×+×
×
==
0
C
B
A
])27)(648()6)(48(
12
1
[
]0)48)(8(
12
1
[
])27)(624()6)(24(
12
1
[
23
3
23
×++
++
×+=
C
dyC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-23-320.jpg)

![25
2 m
O
1 m
1 m
1 m
1 m
0.5 m0.5 m 2 m 2 m
0.5 m0.5 m
x
y
A
B
dyB
C
dyC
Ix = 46 m4
m
A
I
k x
x 599.1
)]14()24()65[(
46
=
×−×−×
==
14
2
24
2
65
2
)()()( ××× +−+−+= CyxByxAyxx AdIAdIAdII
0
C
BA
])5.1)(14()1)(4(
12
1
[
])2)(42()2)(4(
12
1
[]0)6)(5(
12
1
[
23
233
×+−
×+−+=
Iy = 46.5 m4
CBA ])4)(1(
12
1
[])4)(2(
12
1
[])5)(6(
12
1
[ 333
−−=
0 00
CxyBxyAxyy AdIAdIAdII )()()(
222
+−+−+=
m
A
I
k
y
y 607.1
)]14()24()65[(
5.46
=
×−×−×
==](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-25-320.jpg)

![27
1 cm 1 cm
5 cm
1 cm
5 cm
x
y
CG
Y
∑∑ = AyAY
cm
Y
5.2
)15(3
)51)(5.0()]15)(5.3[(2
=
×
×+×
=
4
2
2
25.51
)5.2)(15(145
cm
AdII yxx
=
−=
−=
• Moments of inertia about centroid
4
23
23
25.51
])2)(15()1)(5(
12
1
[(
])1)(15()5)(1(
12
1
[(2
cm
I
OR
x
=
×++
×+=
cm
A
I
kk x
yx 848.1
15
25.51
====
4
323
145
)1)(5(
3
1
])5.3)(15()5)(1(
12
1
[(2
cm
Ix
=
+×+=
• Moments of inertia about x axis
4
323
25.51
)5)(1(
12
1
])2)(15()1)(5(
12
1
[(2
cm
II yy
=
+×+==
0.5
3.5
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-27-320.jpg)

![29
229 mm
172 mm
SOLUTION
19 mm
358 mm x
O
C x´
Y
188.5 mm
The wide-flange shape of W360 x 57
found by referring to Fig. 9.13
A = 7230 mm2 4
2.160 mmIx =
AyAY Σ=Σ
Aplate = (229)(19) = 4351 mm2
)7230)(0()4351)(5.188()72304351( +=+Y
mmY 8.70=
• Centroid
• Moment of Inertia
flangewidexplatexx III −+= )()( '''
flangewidexplatex YAIAdI −+++= )()( 2
'
2
'
[ ]
46
26
23
108.256
)8.70)(7230(102.160
)8.705.188)(4351()19)(229(
12
1
mm×=
+×+
−+=
• Radius of Gyration
)72304351(
108.256 6
'2
'
+
×
==
A
I
k x
x
mmkx 149' =
46
' 10257 mmIx ×=
d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09review-151108003803-lva1-app6892/85/09-review-29-320.jpg)


