2 potentiometry
- 1. 2.Potentiometry Sushil D.Patil Bhujbal Knowledge City MET Institute of Pharmacy,Nashik
- 2. Objectives • understand the basic principles of potentiometry • understand the measurement of electrode potential and pH, pH meter& its calibration, potentiometric titrations and applications Syllabus: • Introduction, theory & principle of potentiometry, types of electrodes, Reference electrode(Normal hydrogen electrode, calomel electrode, quinhydrone electrode, silver- silver chloride electrode), indicator electrode (Glass, ion sensitive – solid, liquid and gas membrane), measurement of electrode potential and pH, pH meter& its calibration, potentiometric titrations and applications
- 3. Principles Potentiometric measurements are based upon the determination of the voltage difference, at zero current, i.e. under equilibrium conditions, between two electrodes which are plunged into a sample solution .Each of these electrodes constitutes a half-cell. The following concerning these two electrodes should be noted: • The external reference electrode (ERE), is the electrochemical reference half-cell for which the potential is constant with respect to that of the sample solution. • The Indicator electrode (IE), also known as the working electrode.
- 4. • Electrode of interest is named working electrode or the indicator electrode; the second electrode is know as reference electrode or auxiliary electrode(counter electrode). In practice the potential of the working electrode (WE)is measured with respect to the reference electrode (RE).
- 5. Electrode potentials The potential difference developed by the cell ΔE as the difference between the potential of the working electrode Ework and the reference electrode Eref The cell potential is measured as Ecell=Eind +Eref+Ej
- 6. • Reference Electrode 1.Primary Standard-Standard ( Normal) Hydrogen Electrode 2.Secondary Standard- i) Calomel Electrode ii) Silver- silver chloride Electrode • Indicator Electrode a. Metallic Indicator Electrode- i) First Kind,ii) Second Kind,iii) Third Kind & iv) Metallic redox indicator electrode b. Membrane Electrodes-i) Ion selective Electrode/membrane Electrode ,ii)Ion selective field effect transistors,iii) Molecular selective electrode system: Gas sensing probes,iv) Quinhydrine Electrode c. Biosensors
- 7. 1.Primary Standard-Standard ( Normal) Hydrogen Electrode
- 8. • The standard hydrogen electrode, or SHE, is composed of an inert solid like platinum on which hydrogen gas is adsorbed, immersed in a solution containing hydrogen ions at unit activity. The half-cell reaction for the SHE is given by • 2H+ (aq) + 2 e- H2 (g) • and the half-cell potential arbitrarily assigned a value of zero (E0 = 0.000 V). • Pt(s), H2 (g,f H2 =1.00) | H+(aq,aH =1.00) ||
- 9. • Advantages: 1.Entire pH range 2.Free from salt error 3.Fundamental electrode ( all pH measurements) • Disadvantages: 1.Difficult to get pure H2 2. Difficult maintain pressure 1 atm. 3.Not useful in presence of oxygen
- 10. 1. Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) The SCE is a half cell composed of mercurous chloride (Hg2Cl2, calomel) in contact with a mercury pool. These components are either layered under a saturated solution of potassium chloride (KCl) or within a compartment surrounded by the saturated KCl solution (called a double-junction arrangement). A platinum wire is generally used to allow contact to the external circuit. The half reaction is described by Hg2Cl2 (s) + 2 e- 2 Hg (l ) + 2 Cl- (sat’d) with an E0 value of +0.244 V. A common arrangement for the SCE is shown below, left side. In this arrangement, a paste is prepared of the calomel and solution that is saturated with KCl.
- 14. What is the difference between Voltage and EMF? • 1. EMF is the voltage generated by a source like battery or generator. • 2. We can measure voltage between any two points, but EMF exists only between the two ends of a source. • 3. Voltages in a circuit called ‘voltage drops’ are in the opposite direction of EMF and their sum is equal to EMF according to Kirchhoff’s second law.
- 15. Hg| Hg2Cl2 | (sat’d) ,KCl(x M)||. Bell Jar Type: • Mercury placed at the bottom wide mouth bottle/jar • Above this layer saturated KCl. • Platinum wire introduced through cork Side Arm Test Type: • Side arm bearing stop cork • Mercury placed at the bottom • Above this layer calomel paste saturated KCl.
- 16. Deep in test tube Type: • Two test tubes, outer tube is 15 cm long & 2 cm diameter • With opening for filling KCl & porous fiber plug • Inner tube is filled with mercury mercurous chloride & having metal wire connected through mercury.
- 17. • Advantages: 1.Entire pH range 2.Mercury ion reacts with fewer samples as compared to silver- silver electrode. 3.Sturdy electrode • Disadvantages: 1.Temperature coefficient is large 2. Take longer time to established 3.Chloride ion solution show incompatibility.
- 18. 2. Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) • The silver/silver chloride reference electrode is composed of a silver wire, sometimes coated with a layer of solid silver chloride, immersed in a solution that is saturated with potassium chloride and silver chloride. The pertinent half reaction is • AgCl (s) + e - Ag (s) + Cl- (sat’d)
- 19. • Ag| AgCl , (sat’d) ,KCl(x M)||. • Advantages: 1.Easy to manufacture 2.Showes potential rapidly & it attains equilibrium between -300C & 1350 C & is reproducible. 3.Stable & accurate even wide temperature fluctuation • Disadvantages: 1. It react with samples
- 20. Indicator Electrode • Metallic Indicator Electrode.- • i) Electrode of First Kind: An indicator electrode of first kind is pure metal electrode that is in direct equilibrium with its cation in the solution. Eg. Some metals such as silver, mercury,copper,cadmium,Zinc & lead act as indicator electrodes with respect to their own ions. A single electrode potential for silver wire dipping in to a solution of silver salts varies with the activity of silver ions according Nernst equation. Ag ++ e - Ag Ecell=E0−(0.05916/n)log(1/aAg +)
- 21. • ii) Electrode of Second Kind: • It as indicator electrode also respond activites of anion that form sparingly soluble precipates or soluble stable complexes with such cations. • Eg.Silver-silver chloride • Half cell reaction- • AgCl + e - Ag(s) + Cl- • Ecell=E0Agcl/Ag−(0.0592/n)logaCl -
- 22. • ii) Electrode of Third Kind: • These are metal electrode which are used to measure activites of ions for which no electrode of the first kind exist. • Eg.mercury serves as an indicator electrode of second kind for EDTA anion Y 4- • When a small amount of Hg Y 2- mercury chelate is added to solution containing Y 4- the half reaction at a mercury electrode is • Hg Y 2- +2 e - Hg(l) + Y 4-
- 23. • Inert or Redox Electrodes:- • These electrodes such as gold,platinum,or carbon, immersed in a solution containing both the oxidized & reduced states of homogenous & reversible • Eg.pt electrodes in the solution of iron(III) & iron(ii) ions. • Half cell reaction- • Fe+3+ e - Fe+2 • Ecell=E0 Fe+3 / Fe+2 −(0.0592/n)log[Fe+2 /Fe+3 ]
- 24. Ion selective Electrode:- • Ion selective electrode have several advantages over conventional methods of determining ionic concentration:- • They do not affect the solution being analyzed. • They are portable, not too expensive. • They are suitable for direct determination of ion activites & can be used as sensor in titrations.
- 25. Ion Exchange Process In the following ion exchange process, a lithium cation displaces a potassium cation from the organic anion, R-: KR + Li+ ⇋ LiR + K+ We can imbed the lipophilic R- in a membrane, as shown in Figure, and place it in a solution of Li+ KR(mem) + Li+(aq) ⇋ LiR(mem) + K+(aq)
- 26. Ion Selective Electrode are:- • Glass Membrane Electrode • Solid-State Electrode • Precipitate Electrode • Liquid-liquid Electrode
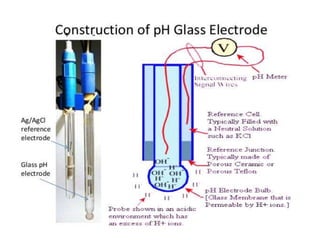
- 27. Glass Electrode(pH electrode) • This electrode most widely used for determination of hydrogen. Also H+, Na+, Ag+&Li • Three sub type of glass electrode- 1.pH type. 2.Cation Sensitive type 3.Sodium sensitive type
- 28. • Glass Membrane Structure:SiO4- framework with charge balancing cations- SiO2-72 %, Na2O- 22 %, CaO-6 %
- 31. The pH Electrode • Alkaline error – sensitive to alkali metal ions at pH greater than 12. • Acid error – at pH less than 0.5, values obtained with the pH electrode are high. • Dehydration – must keep membrane moist. • Errors in low ionic strength – varying junction potentials. • Errors in pH of standard buffer solutions
- 32. 1.Thick walled glass tubing, providing very high electrical resistance, is attached at its bottom to glass bulb. 2.A glass bulb, used to respond to changes in H+ ion concentration. It is made up of a thin wall or a membrane from oxide of sodium,calcium&silicon. The glass bulb is filled with 0.1M HCl. 3.Asilver wire, coated with silver chloride, is dipped in 0.1M HCl inside the bulb so as to make an electrical contact. It also act as a reference electrode. The potential of this reference electrode is not affected by changes in the pH of a solution.
- 33. Applications • Glass electrode is commonly used to find the pH of solutions. • It is also used as an indicator electrode for titrations involving neutralization.
- 34. Advantages:- • Response slight change in the pH of the test solution is very fast. • It is unaffected by oxidizable & reducible substances also colored liquids, gases or the presence of moderate salt except sodium salts • Lithium & silica glass membrane can be used wider range of pH. • A combination of glass electrode & ref.electrode in one single unit has increased the ease of handling the system.
- 35. Disadvantages • Glass electrode is fragile & hence, needs careful handling. • Scratches on the glass bulb alter the response from the glass electrode. • It is not used for dehydrating agents & colloidal substances. • Glass electrode provides a very high internal resistance & hence, is not useful in simple potentiometers
- 37. • The cation-exchanger is an aliphatic diester of phosphoric acid, (RO)2PO2-, where each R group is an aliphatic hydrocarbon chain containing between 8 and 16 carbons. The phosphate group can be protonated, but has a strong affinity for Ca2+. The cation exchanger is dissolved in an organic solvent and held in a porous compartment between the analyte solution and internal reference calcium chloride solution. The ion- exchanger uptakes Ca2+ into the membrane by the following mechanism, forming a complex with the structure shown in Figure Liquid Membrane Electrodes
- 38. Liquid Membrane Electrodes Ca2+ (aqueous) + 2(RO)2PO2- (organic) ⇋ [(RO)2PO2]2Ca (organic) used for calcium determination
- 39. Gas-sensing electrodes • Combined electrodes have been developed to measure dissolved gases such as • carbon dioxide CO2, ammonia NH3 and sulfur dioxide SO2. These chemical • sensors contain an internal solution that is isolated from the sample solution • by an hydrophobic membrane which is permeable to dissolved gas molecules
- 40. • For the three gases given above, the selective electrodes include • a glass electrode in contact with a bicarbonate solution of low concentration(0.01 M). • The bicarbonate solution is separated from the sample solution by a polymer membrane that allows diffusion of the gas analyte towards the inner electrode compartment.
- 41. • This diffusion in the bicarbonate brings about a change in pH in the proximity of the membrane. For other gases, such as hydrogen cyanide (HCN), fluorhydric • acid (HF) or hydrogen sulfide H2S, the signal is generated by the modification • of the concentration of anions close to the internal wall of the membrane.
- 45. Calibrating the pH electrode: Obtain two buffer solutions, one each of buffer pH 4 and buffer pH 7. Place the pH probe into the pH 4 buffer solution. Go to the menu and under the Experiment open Calibrate. Click Calibrate now. The electrode will be reading a voltage– when this value has stabilized, type in the pH of your buffer (4.0) into the “Enter Value” box under Reading 1 and then click Keep.
- 46. Rinse your electrode and place it into the pH 7 buffer solution. When the voltage has stabilized again, enter that pH value (7.0) in the box under Reading 2 and click keep. Click done to return to the graph and data table screen. Rinse the electrode and place the probe back into the pH 4 buffer to make sure it is stable. If the electrode is properly calibrated, the pH of the solution should read “4.00” ± 0.05 units.
- 47. • Submerse the electrode into the pH 7 buffer Press the calibrate button.
- 48. Wait until the pH icon stops flashing and press the calibrate button again.
- 49. • Quininydrone Electrode:- • This electrode was introduced by E.Billman in 1921. • By this electrode a rapid & easy determination of pH is possible • Quinhydrone is a 1:1 molar compound of quinone & hydroquinone & in solution it provides equimolecular quantities of these two substances. • C6H4O2.C6H4(OH)2 C6H4O2 +C6H4(OH)2 Quinhydrone quinone hydroquinone
- 50. • C6H4O2+ 2H++ 2e- C6H4(OH)2 • Quinone(Q) hydroquinone(QH2) • E =E0-2.303RT log[QH2] (:.n=2) 2F [Q] [H+] 2 =E0-2.303RT log[QH2]+ E0- 2.303RT log[H+] 2 2F [Q] 2F [QH2]=[Q] in aqueous solution of quinhydrone log[QH2] [Q] =log1=0 = E0-2.303RT x log[H+] 2F =0.591pH at 250 C
- 51. • Advantages- • It has a low resistance • Equilibrium reached quickly • Its use is not affected by dissolved oxygen • It can be used for micro-determinations • Disadvantages- • It can be used for determining pH values less than 8 only • The solution to be tested gets contaminated • Salt error defect • Can not be used in presence of oxidising &reducing agents
- 52. Potentiometric measurements • In Potentiometric methods two methods of measurements exists. • A) Measurement of electrode potential from which the concentration of an active ion may be found. • B) Measurement of changes in E.M.F.(electro motive force) brought about by the addition of the titrant could be made. • Thus the E.M.F. of the cell can be calculated as follows. • E cell = E reference + E indicator + E function
- 53. • In Potentiometric titrations, the change in the electrode potential upon the addition of the titrant are noted against the volume of the titrant & added. • At the end point the rate of the change of the potential would be the maximum. • The end point is found by plotting a curve of potential versus the volume of the titrant.
- 54. Types of Potentiometric titrations • Acid base titrations, • Redox titrations and • Precipitation titrations. • Acid base titrations:- • Neutralization of acids & bases is accompanied by the changes in the concentration of H+ & OH- ions. • The electrodes used are hydrogen electrode & N- calomel electrode (Reference electrode). • The glass electrode is usually used in conjunction with a calomel electrode that makes contact with the test solution through a salt bridge.
- 55. • A known volume of the acid to be titrated is kept in a beaker fitted with a stirrer and a standard hydrogen electrode. • It is connected to normal calomel electrode through a salt bridge. • Both the electrodes are connected to a potentiometer which records the E.M.F. of the solution. • After each addition of base from the burette, the E.M.F is measured & a graph is plotted (fig.)
- 56. • The potential of any hydrogen electrode is given by E = E0 + 0.0591 pH. • It is clear that the change in electrode potential or E.M.F. of the cell is proportional to the change in pH during titration. • The point where the E.M.F. increases rapidly gives the end point. • A more satisfactory method to find the end point is to plot ÄE/ÄV against V. • The maximum value gives the end point of the titration (fig.)
- 57. • Redox Titrations • Redox reactions can be followed by an inert indicator electrode. The electrode • assumes a potential proportional to the concentration of the reactant or the titrant. • They involve the transfer of electron from the substances being oxidized to the substance being reduced. • Ce+4+ Fe+2 Ce+3+ Fe+3 • Such titrations may be used for monitoring of cyanide wastes from metal plating industries, in water pollution, sewage treatment, agricultural and in biochemical studies.
- 58. • Precipitation titrations • Any such titration that involves insoluble salts of metals such as mercury, silver lead and copper may be followed potentiometrically. The indicator electrode may be made of the metal involved in the reaction. • The magnitude of potential change at the end point depends on the solubility of the substance being precipitated. The titration of Cl- ions with a stand and solution of AgNo3 using a silver metal indicator electrode is an example of a precipitation titration.
- 59. Advantages of Potentiometric titrations 1. The method is suitable for the analysis of dilute solutions too. 2. It could be applied for colored solutions also. 3. The interpretation of titration curves is easier. 4. The apparatus used is inexpensive, reliable and readily available. 5. Different components of different characteristic colour could be titrated at a same time.
- 60. Applications of Potentiometric titrations:- • Assay of Carbidopa • Assay of Clonidine Hydrochloride • Assay of - Bendrofluazide,cimetidin,Ethinyloestradiol, Lomustine etc. • Compexometric titrations.






















![• Inert or Redox Electrodes:-
• These electrodes such as gold,platinum,or
carbon, immersed in a solution containing
both the oxidized & reduced states of
homogenous & reversible
• Eg.pt electrodes in the solution of iron(III) &
iron(ii) ions.
• Half cell reaction-
• Fe+3+ e - Fe+2
• Ecell=E0 Fe+3 / Fe+2 −(0.0592/n)log[Fe+2 /Fe+3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2potentiometry-190503133845/85/2-potentiometry-23-320.jpg)













![Liquid Membrane Electrodes
Ca2+ (aqueous) + 2(RO)2PO2- (organic) ⇋
[(RO)2PO2]2Ca (organic)
used for calcium determination](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2potentiometry-190503133845/85/2-potentiometry-38-320.jpg)










![• C6H4O2+ 2H++ 2e- C6H4(OH)2
• Quinone(Q) hydroquinone(QH2)
• E =E0-2.303RT log[QH2] (:.n=2)
2F [Q] [H+] 2
=E0-2.303RT log[QH2]+ E0- 2.303RT log[H+] 2
2F [Q] 2F
[QH2]=[Q] in aqueous solution of quinhydrone
log[QH2]
[Q] =log1=0 = E0-2.303RT x log[H+]
2F
=0.591pH at 250 C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2potentiometry-190503133845/85/2-potentiometry-50-320.jpg)









