2 sql - single-row functions
- 1. Chapter 3 Selected Single-Row Functions and Advanced DML & DDL
- 2. Chapter Objectives • Use the UPPER, LOWER, and INITCAP functions to change the case of field values and character strings • Extract a substring using the SUBSTR function • Determine the length of a character string using the LENGTH function
- 3. Chapter Objectives • Use the LPAD and RPAD functions to pad a string to a desired width • Use the LTRIM and RTRIM functions to remove specific characters strings • Round and truncate numeric data using the ROUND and TRUNC functions • Calculate the number of months between two dates using the MONTHS_BETWEEN function
- 4. Chapter Objectives • Identify and correct problems associated with calculations involving null values using the NVL function • Display dates and numbers in a specific format with the TO_CHAR function • Determine the current date setting using the SYSDATE keyword • Nest functions inside other functions • Identify when to use the DUAL table
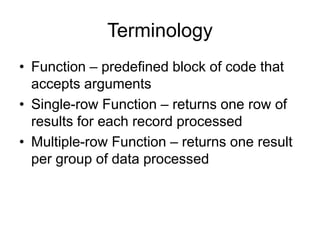
- 5. Terminology • Function – predefined block of code that accepts arguments • Single-row Function – returns one row of results for each record processed • Multiple-row Function – returns one result per group of data processed
- 7. Case Conversion Functions Alter the case of data stored in a column or character string
- 8. LOWER Function Used to convert characters to lower-case letters
- 9. UPPER Function Used to convert characters to upper-case letters
- 10. INITCAP Function Used to convert characters to mixed-case
- 11. Character Manipulation Functions Manipulates data by extracting substrings, counting number of characters, replacing strings, etc.
- 12. SUBSTR Function Used to return a substring, or portion of a string
- 13. LENGTH Function Used to determine the number of characters in a string
- 14. LPAD and RPAD Functions Used to pad, or fill in, a character string to a fixed width
- 15. LTRIM and RTRIM Functions Used to remove a specific string of characters
- 16. REPLACE Function Substitutes a string with another specified string
- 17. CONCAT Function Used to concatenate two character strings
- 18. Number Functions Allows for manipulation of numeric data
- 19. ROUND Function Used to round numeric columns to a stated precision
- 20. TRUNC Function Used to truncate a numeric value to a specific position
- 21. Date Functions Used to perform date calculations or format date values
- 22. MONTHS_BETWEEN Function Determines the number of months between two dates
- 23. ADD_MONTHS Function Adds a specified number of months to a date
- 24. NEXT_DAY Function Determines the next occurrence of a specified day of the week after a given date
- 25. TO_DATE Function Converts various date formats to the internal format (DD-MON-YYYY) used by Oracle9i
- 26. Format Model Elements - Dates
- 27. NVL Function Substitutes a value for a NULL value
- 28. NVL2 Function Allows different actions based on whether a value is NULL
- 29. TO_CHAR Function Converts dates and numbers to a formatted character string
- 30. Format Model Elements – Time and Number
- 31. Other Functions • NVL • NVL2 • TO_CHAR • DECODE • SOUNDEX
- 32. DECODE Function Determines action based upon values in a list
- 33. SOUNDEX Function References phonetic representation of words
- 34. Nesting Functions • One function is used as an argument inside another function • Must include all arguments for each function • Inner function is resolved first, then outer function
- 35. Summary of functions Single-Row Functions • Text Functions lpad, rpad, lower, upper, initcap, length, substr, instr, trim, concat • Arithmetic Functions abs, round, ceil, floor, mod, sign, sqrt, trunc, vsize • List Functions greatest, least, decode • Date Functions add_months, last_day, months_between, new_time, next_day, round, trunc • Conversion Functions to_char, to_number, to_date
- 36. DUAL Table • Dummy table • Consists of one column and one row • Can be used for table reference in the FROM clause Ex: select sysdate from dual
- 37. Advanced Data Selection in Oracle Using a Subquery Multiple-Row Subqueries SELECT ename, job, sal FROM emp WHERE sal = (SELECT MIN(sal) FROM emp); SELECT empno, ename, job, sal FROM emp WHERE sal < ANY (SELECT sa FROM emp WHERE job AND job <> 'SALESMAN'; multiple-row comparison operators – IN, ANY,ALL
- 38. Manipulating Oracle Data Inserting Rows with Null Values and Special Values Copying Rows from Another Table INSERT INTO emp (empno, ename, hiredate, jo sal,comm, mgr, deptno) VALUES (113,'Louis', SYSDATE, 'MANAGER', 69 NULL, NULL, 30); INSERT INTO sales_reps(id, name, salary, co SELECT empno, ename, sal, comm FROM emp WHERE job LIKE '%SALES%';
- 39. Creating and Managing Database Objects (Tables) Creating a Table by Using a Subquery CREATE TABLE dept30 AS SELECT empno, ename, sal*12 ANNSAL, hiredate FROM emp WHERE deptno = 30;
- 40. Creating and Managing Database Objects (Tables) Common Datatypes Datatype Description VARCHAR2(siz e) Variable-length character data, can up to 4,000 bytes. CHAR(size) Fixed-length character data, can up to 2,000 bytes. NUMBER(p.s) Variable-length numeric data, can up to 38 digits. E.g. Number(5.2) 999.99 DATE Date and time values, 7 bytes. Other data types included: LONG, CLOB, RAW, LONG RAW, BLOB, BFILE, ROWID … etc.
- 41. Creating and Managing Database Objects (Tables) The Drop Table Statement DROP TABLE table; Dropping a Table DROP TABLE dept30;
- 42. Other Database Objects (Views, Sequences)Views CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE|NOFORCE] VIEW view [(alias[, alias]...)] AS subquery [WITH CHECK OPTION [CONSTRAINT constraint]] [WITH READ ONLY [CONSTRAINT constraint]]; DROP VIEW view; To restrict data access To make complex queries easy To provide data independence To present different views of the same data You can retrieve data from a view as from a table.
- 43. Other Database Objects (Views, Sequences) Modifying a View CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW empv30 (id_no, name, salary) AS SELECT empno, ename, sal FROM emp WHERE deptno = 30; Drop a View DROP VIEW empv30 Creating a View CREATE VIEW empv30 AS SELECT empno, ename, sal FROM emp WHERE deptno = 30;
- 44. Other Database Objects (Views, Sequences) Sequences CREATE SEQUENCE sequence [INCREMENT BY n] [START WITH n] [{MAXVALUE n | NOMAXVALUE}] [{MINVALUE n | NOMINVALUE}] [{CYCLE | NOCYCLE}] [{CACHE n | NOCACHE}]; Automatically generates unique numbers Is typically used to create a primary key Replaces application code
- 45. Other Database Objects (Views, Sequences) Creating a Sequence NEXTVAL and CURRVAL Pseudocolumns CREATE SEQUENCE deptid_seq INCREMENT BY 10 START WITH 5 MAXVALUE 9999; NEXTVAL returns the next available sequence value. It returns a unique value every time it is referenced, even for different users CURRVAL obtains the current sequence value. NEXTVAL must be issued for that sequence before CURRVAL contains a value
- 46. Other Database Objects (Views, Sequences) Using a Sequence View the current value Removing a Sequence INSERT INTO dept(deptno, dname, loc) VALUES (deptid_seq.NEXTVAL,'Support', ' HONG KONG' ); SELECT deptid_seq.CURRVAL FROM dual; DROP SEQUENCE deptid_seq;
- 47. Appendix B: Useful link • Try these with SQL http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~csc3170/tutorial/index. html • http://db00.cse.cuhk.edu.hk • http://www.db.cs.ucdavis.edu/teaching/sqltutorial • http://www.w3schools.com/sql









































![Other Database Objects (Views,
Sequences)Views
CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE|NOFORCE] VIEW view
[(alias[, alias]...)]
AS subquery
[WITH CHECK OPTION [CONSTRAINT constraint]]
[WITH READ ONLY [CONSTRAINT constraint]];
DROP VIEW view;
To restrict data access
To make complex queries easy
To provide data independence
To present different views of the same data
You can retrieve data from a view as from a table.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-sql-single-rowfunctions-190916072603/85/2-sql-single-row-functions-42-320.jpg)

![Other Database Objects (Views,
Sequences)
Sequences
CREATE SEQUENCE sequence
[INCREMENT BY n]
[START WITH n]
[{MAXVALUE n | NOMAXVALUE}]
[{MINVALUE n | NOMINVALUE}]
[{CYCLE | NOCYCLE}]
[{CACHE n | NOCACHE}];
Automatically generates unique numbers
Is typically used to create a primary key
Replaces application code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-sql-single-rowfunctions-190916072603/85/2-sql-single-row-functions-44-320.jpg)


