An Integer Programming Representation for Data Center Power-Aware Management - slides
- 1. ILP model and Heuristic Authors: Josep Subirats Arinto Murdopo Ioanna Tsalouchidou
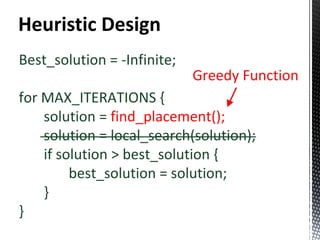
- 2. ContentResult Problem Description The ILP model Heuristic Design Data-Set Generation Results Conclusions
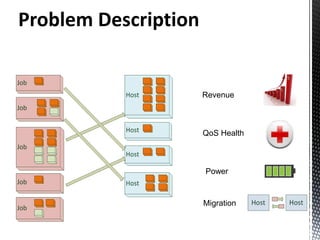
- 3. Problem Description Grid data-center scheduling problem Optimal solution economic revenue power saving QoS Set of elements machines processors jobs
- 5. Problem Description Revenue QoS Health Power Migration
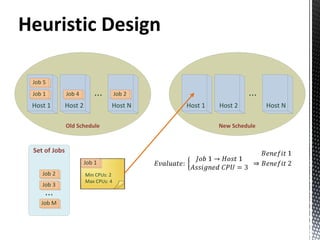
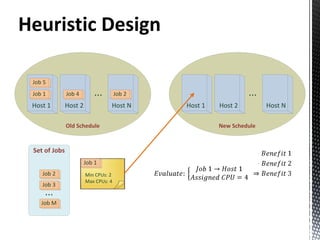
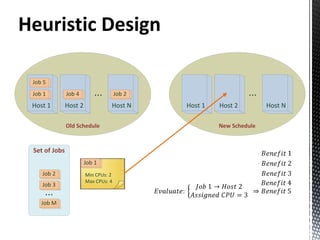
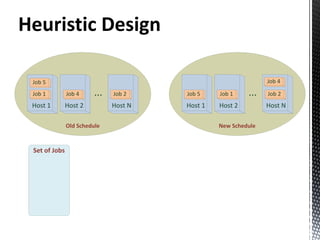
- 6. ILP Job allocation in data-grid • Power consumption based on used CPUs • CPUs in each host • Min CPUs required by each job • Max CPUs required by each job
- 7. ILP Objective Function Benefit of Max: Execution QoS Penalty Power Consumption Migration Cost
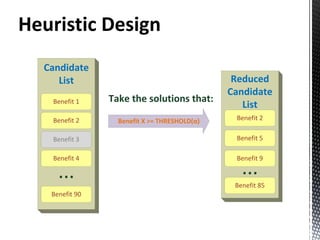
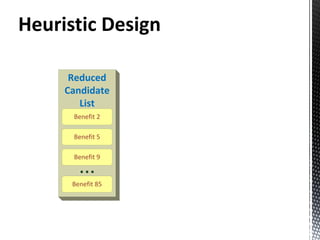
- 8. ILP S.T: Processor switched on/off in order: keep consistency Relaxation: job scheduled or not scheduled Available CPUs in each host not exceed Output: Max. Benefit Placement of each job in the infrastracture CPU assignment for each job CPUs used in each host
- 29. Data Generation Generate an array of numHosts components: cpus[]: CPUs in each host, each with 1, 2, 4 or 8 CPUs (random). Generate two arrays of numJobs components: consMin[]: minimum CPU required, between 1 and 10 (random). consMax[]: maximum CPU required, randomly between consMin[j] + 1 to 2 extra CPUs (random).
- 30. CPU : Intel i7 @ 2.8 GHz OS: Windows 7 RAM: 8 GB CPLEX: IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio 12.4 Heuristic: Java in JRE 1.6.0_24-b07
- 31. Multiple Alpha: 0, 0.1, 0.2 … 1 Multiple Problem Sizes: 5H10J, 15H30J, 20H40J, 30H40J, 40H80J, 100H200J Multiple Iterations: 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000
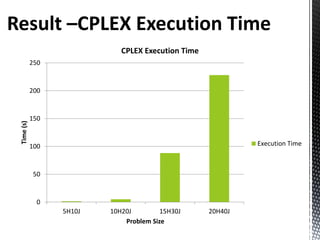
- 32. CPLEX Execution Time 250 200 150 Time (s) 100 Execution Time 50 0 5H10J 10H20J 15H30J 20H40J Problem Size
- 33. Heuristic Random 100H200J - Time (s) 350 300 250 200 Time (s) 150 Time (s) 100 50 0 10 100 1000 10000 100000 Number of Iteration
- 34. Alpha vs Benefit 20H40J NR Alpha vs Benefit 40H 80J NR 101 195 96 190 10 185 10 Benefit Benefit 91 100 180 100 1000 175 1000 86 10000 170 10000 81 165 100000 100000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.5 1 1.5 Alpha Alpha Alpha vs Benefit 30H60J NR Alpha vs Benefit 100H 200J NR 140 580 10 560 10 Benefit 130 Benefit 100 540 100 120 520 1000 1000 110 500 10000 10000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 480 100000 0 0.5 1 100000 Alpha Alpha
- 35. Alpha vs Benefit 20H40J NR 97 95 93 91 10 Benefit 89 100 1000 87 10000 85 100000 83 81 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Alpha
- 36. Alpha vs Benefit 100H 200J NR 570 560 550 540 10 Benefit 530 100 1000 520 10000 100000 510 500 490 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Alpha
- 37. Solution Quality - Alpha 0.1 - 100H - 200J - 100000 Iterations 100 12377 133566 683 99.5 69 Normalized Benefit (%) 99 24 98.5 Normalized 17 Benefit (%) 14 98 97.5 11 7 97 Time (mili seconds)
- 38. Solution Quality - Zoomed In - Alpha 0.1 - 100H - 200J - 100000 Iterations 100 99.5 69 Normalized Benefit (%) 99 24 98.5 Normalized 17 Benefit (%) 14 98 97.5 11 7 97 Time (mili-seconds)
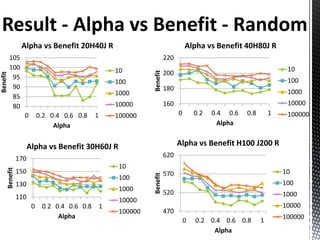
- 39. Alpha vs Benefit 20H40J R Alpha vs Benefit 40H80J R 105 220 100 10 10 200 Benefit Benefit 95 100 100 90 180 1000 1000 85 80 10000 160 10000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 100000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 100000 Alpha Alpha Alpha vs Benefit 30H60J R Alpha vs Benefit H100 J200 R 170 620 10 Benefit 150 570 10 Benefit 100 130 100 1000 520 1000 110 10000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 10000 100000 470 Alpha 100000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Alpha
- 40. Alpha vs Benefit 20H40J R 105 100 95 10 Benefit 100 90 1000 10000 100000 85 80 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Alpha
- 41. Alpha vs Benefit H100 J200 R 610 590 570 550 10 Benefit 100 530 1000 10000 510 100000 490 470 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Alpha
- 42. Solution Quality - Alpha 0.0 - 100H - 200J - 100000 Iterations 100 224536 98 8813 112341 96 Normalized Benefit (%) 2012 94 13 Normalized 92 Benefit (%) 90 9 88 3 86 Time (mili-seconds)
- 43. Solution Quality - Zoomed In -Alpha 0.0 - 100H - 200J - 100000 Iterations 99 97 Normalized Benefit (%) 95 93 292 617 693 13 91 Normalized 9 Benefit (%) 89 3 87 85 Time(mili-seconds)
- 44. Problem Size vs Methodology vs Benefit 700 CPLEX 600 500 Heuristic Non- Random Initial 400 Selection (NR) Benefit Heuristic Random 300 Initial Selection(R) - 10000 Iter 200 Heuristic Random Initial Selection(R) - 100 100000 Iter 0 Problem Size
- 45. Conclusions Datacenter job scheduling and management can be optimized using ILPs. Complex ILP restrictions can be translated into easy heuristic code. CPLEX does not scale well. Heuristics can cope with higher problem sizes.
- 46. Conclusions Lower alpha values achieve better results. Alpha of 0 is the best when using random node selection. Random node selection obtains the best results. More iterations achieve better benefits.
- 47. Reference J. L. Berral García, R. Gavaldà Mestre, J. Torres Viñals, and others, “An integer linear programming representation for data-center power-aware management,” 2011. http://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/11061
- 48. ILP model and Heuristic Authors: Josep Subirats Arinto Murdopo Ioanna Tsalouchidou



















![Data Generation
Generate an array of numHosts components:
cpus[]: CPUs in each host, each with 1, 2, 4 or 8 CPUs
(random).
Generate two arrays of numJobs components:
consMin[]: minimum CPU required, between 1 and
10 (random).
consMax[]: maximum CPU required, randomly
between consMin[j] + 1 to 2 extra CPUs (random).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-121122054558-phpapp02/85/An-Integer-Programming-Representation-for-Data-Center-Power-Aware-Management-slides-29-320.jpg)