Ast
- 2. AIMS To measure susceptibility of an isolate to range of antibiotics. To select the most appropriate antibiotic for patients. To assess emerging bacterial resistance patterns.
- 3. Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) Develop standards, methods, QC parameters, and interpretive criteria for sensitivity testing If necessary, can alter the breakpoints based on emerging resistance
- 4. Definition • Minimum Inhibition Concentration (MIC) The lowest concentration of antimicrobial agent that inhibits visible growth/ multiplication of a microorganism. • Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) The MBC is the lowest concentration of the antibiotic that will kill a bacterial strain.
- 5. CHOICE OF ANTIBIOTIC Follow CLSI recommendations Each laboratory should have a battery of antibiotics ordinarily used for testing Use the least toxic, most cost-effective, and most clinically appropriate agents Refrain from more costly, broader-spectrum agents Selection of antimicrobial is based on the type of organism being tested and source of the isolate
- 6. METHODS Disk diffusion method • Kirby Bauer disk diffusion method • Stoke’s method Broth macrodilution / Tube dilution Broth microdilution Agar dilution method Gradient diffusion method (E-Test) Automated methods (VITEK) Molecular methods (PCR detecting drug resistant genes)
- 7. DISK DIFFUSION METHODS • Put a filter disc containing measured quantity of drugs on a solid medium that has been seeded with test bacteria • Two types - 1. Kirby Bauer disk diffusion method 2. Stoke’s method
- 8. DISK DIFFUSION METHODS • Disk diffusion tests are the most widely used method. • They are suitable for rapidly growing pathogenic bacteria • They are unsuitable for slow growing bacteria.
- 9. PRINCIPLE • Antimicrobial disk placed on agar media. • Antimicrobial begins to diffuse into surrounding agar. • A logarithmic reduction in concentration occurs as the distance from the disk increases. • The rate of diffusion of antimicrobial through the agar is dependent upon the diffusion and solubility properties of the drug in agar and the molecular weight of the antimicrobial compound.
- 10. • The antimicrobial inhibits the growth of bacteria. • The zone size of inhibition of growth is influenced by the depth of the agar medium pH presence of divalent cations inoculum density and temperature of incubation.
- 11. REQUIREMENTS • Sterile liquid medium (peptone water broth) in 2ml tubes • 0.5 McFarland standard and Wickerham card • Mueller-Hinton agar plates • Caliper or ruler • Antibiotic disks • Forceps, Antibiotic disk dispenser (optional) • 18 to 24 hour old pure culture of the organism to be tested • Vortex • Sterile swabs/Inoculating loop • 35°C to 37°C non-CO2 incubator.
- 12. PROCEDURE- Kirby-Bauer Disc diffusion method • Preparation of inoculum Using a sterile inoculating loop, touch 4 or 5 isolated colonies of the organism to be tested. Suspend the organism in 2 ml of suitable liquid medium (peptone water broth) Vortex the broth tube to create a smooth suspension. Adjust the turbidity of this suspension to a 0.5 McFarland standard (1.5 x 108 cfu/mL) • by adding more organism if the suspension is too light or • diluting with sterile saline if the suspension is too heavy. Use this suspension within 15 minutes of preparation
- 13. Inoculation of the MH plate Dip a sterile swab into the inoculum tube. Rotate the swab against the side of the tube (above the fluid level) using firm pressure, to remove excess fluid. Inoculate the dried surface of a MH agar plate by streaking the swab three times over the entire agar surface; rotate the plate approximately 60 degrees each time to ensure an even distribution of the inoculum. Rim the plate with the swab to pick up any excess liquid Dry the plate for least 3 to 5 minutes, but no more than 15 minutes.
- 14. Placement of the antibiotic disks Place the appropriate antimicrobial impregnated disks on the surface of the agar, using forceps to dispense each antimicrobial disk one at a time. When all disks are in place, replace the lid, invert the plates, and place them in a 35°C air incubator for 16 to 18 hours.
- 15. The Kirby-Bauer Disc diffusion method 15 Transmitted Light
- 17. Interpretation and Reporting • By comparing with the diameters with “standard tables” - zone size is determined. • Based on standard chart zone size is susceptible (S), intermediate (I), or resistant (R). Susceptible ‘S’ - Interpretive category that indicates an organism is inhibited by the recommended dose, at the infection site. Intermediate “I” - Interpretive category that represents an organism that may require a higher dose of antibiotic for a longer period of time to be inhibited Resistant “R” - Interpretive category that indicates an organism is not inhibited by the recommended dose, at the infection site.
- 18. Commonly used disk concentrations and interpretation of disk diffusion test
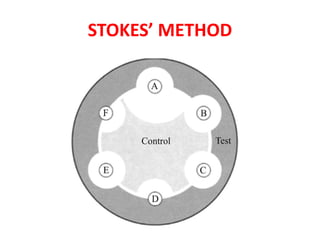
- 19. STOKES METHOD • The comparative disk test • Uses both a test organism and a control organism on the same plate. • The control organism is of defined sensitivity to the antibiotics being tested. • Allows a direct comparison of the diameter of the zones of inhibition between the test and control organisms.
- 20. STOKES METHOD • The MHA plate is divided into 3 parts. • Test organism is inoculated on the central one third and control strain on upper and lower thirds of the plate. In modified Stokes disk diffusion method- the test bacterium is inoculated over the upper and lower thirds of the plate and control on central one third. • An Uninoculated gap of 2-3 mm wide should separate, the test and the control area on which the antibiotic disks are applied. • The plates are then incubated at 370C for 16-18 hours.
- 21. Reporting in Stokes Method • The sensitivity report is prepared by comparing the zones of inhibition of control and test bacterium. • The radius of the inhibition zone from the edge of the disk to the edge of the zone is measured. Result is interpreted as: • Sensitive (S): Zone radius is wider than or equal to, or not >3 mm smaller than the control. • Intermediate ( I): Zone radius is >2 mm but smaller than the control by >3 mm. • Resistant (R): No zone of inhibition or zone radius measures 2 mm or less.
- 23. STOKES’ METHOD
- 24. BROTH DILUTION METHOD • Procedure • Making serial dilutions (2-fold) of antibiotic in broth Mueller-Hinton, Tryptic Soy Broth Inoculation of fix bacterial inoculum, incubate overnight Controls: • no inoculum • no antibiotic Turbidity visualization MIC MBC can be obtained by subculturing from each tube to a nutrient agar plate without any antimicrobial agent
- 26. BROTH DILUTION METHOD 26 Day 1 Add 1 ml of test bacteria (1*106 CFU/ml) to tubes containing 1 ml broth and concentration of antibiotic (mg/l) Controls: C1 = No antibiotic, check viability on agar plates immediately C2 = No test bacteria Bacterial conc.= 5*105 CFU/ml Incubate 35 oC, o/n 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 C1 C2 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 C1 C2
- 27. 27 BROTH DILUTION METHOD Day 2 Record visual turbidity Subculture non-turbid tubes to agar plates (use 0.01 ml standard loop) MIC = 16 mg/l 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 C1 C2 0.01 ml (spread plate), Incubate 35 oC, o/n 64 32 16 Day 3 Determine CFU on plates: At 16 mg/ = 700 CFU/ml > 0.1% of 5*105 CFU/ml MBC = 32 mg/l
- 28. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing using micro-broth dilutions • • • • • • • • • • • • • 96 well microtiter plate ug/ml 64 32 16 8 4 2
- 29. Epsilometer /E test • This is a quantitative method of detecting MIC by using the principles of both dilution and diffusion of antibiotic into the medium • The Etest technique comprises a predefined gradient (serial dilution) of antibiotic concentrations on a plastic absorbent strip. • applied to a lawn inoculum of a bacterium. following incubation of the test organism, an elliptical zone of inhibition is produced surrounding the strip • The antibiotic conc. at which the ellipse edge intersect the strip is taken as MIC value. 29
- 30. The gradient technique, Etest
- 31. AUTOMATED SYSTEMS • Systems are computer assisted and have sophisticated software to analyse the growth rate and determine the antibiotic susceptibility report. • Detect growth in microvolumes of broth with various dilutions of antimicrobials • Detection via photometric, turbidimetric, or fluorometric methods • Types BD Phoenix system (Becton Dickinson) Vitek 1 and 2 (bioMerieLLx) Micro Scan Walk Away system TREK Sensititre
- 32. AUTOMATED SYSTEMS • Advantages Increased reproducibility Decreased labor costs Rapid results Software • Detects multi-drug resistances • ESBLs • Correlates bacterial ID with sensitivity • Disadvantages – Cost
- 34. THANK YOU