ATmega 16
- 1. 1
- 2. Contents • Introduction • History of AVR • AVR microcontroller • Types of AVR microcontrollers • AVR architecture • GPIO Registers • Interfacing • Timers • References • Conclusion 2
- 3. Introduction • AVR stand for ADVANCED VIRTUAL RISC. • AVR micro controllers is family of RISC microcontrollers from Atmel. • AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on- chip flash memory for program storage. • AVR microcontrollers are very popular, used in numerous applications, particularly in project prototyping and also in embedded devices. 3
- 4. History of AVR • AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed by Atmel beginning in 1996. • The Atmel AVR has 8-bit RISC microcontrollers. • The AVR architecture was conceived by two students at the Norwegian Institute of Technology, Alf-Egil Bogen and Vegard Wollan. 4
- 5. RISC microcontroller • RISC stands for Reduced Introduction Set Computer. • Till 1980 Trend was to build increasingly complex CPUs with complex set of instructions like (CISC). • Instruction execute in single cycle. • RISC architecture CPUs capable of executing only a very limited simple set of instructions. 5
- 6. AVR microcontroller • Devices range from 1 to 256KB. • Pin count range from 8 to 100. • Full code compatibility. • Pin/feature compatible families. • One set of development tools. 6
- 7. Types of AVR microcontrollers AVR microcontrollers are obtainable in three categories:- • Tiny AVR • Mega AVR • Xmega AVR 7
- 8. TINY AVR This microcontroller has Less memory, small in size, only for simpler applications. • 0.5–16 KB program memory. • 6–32-pin package. • Small in size. 8
- 9. MEGA AVR • This microcontroller is the most popular having a good amount of memory up to 256KB, higher no. of inbuilt peripherals and fit for modest to difficult applications. • 4–256 KB program memory • 28–100-pin package • Extended instruction set 9
- 10. ATMEGA16 PIN DIAGRAM • Atmega16 have total of 40 pins in which 32 are I/O pins. • VCC (PIN10) - Digital supply voltage. • GND (PIN11) - Ground • Port A (PA7..PA0) - Port A serves as the analog inputs to the A/D Converter Port A also serves as an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port, if the A/D Converter is not used. • 10
- 11. CONTINUE… • Port B (PB7..PB0) - Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors selected for each bit. • Port C (PC7..PC0) - Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors selected for each bit. • Port D (PD7..PD0) - Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors selected for each bit. • RESET - Reset Input a low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a reset • AVCC - AVCC is the supply voltage pin for Port A and the A/D Converter. • AREF - AREF is the analog reference pin for the A/D Converter. • XTAL 2 - Output to Inverting Oscillator Amplifier. 11
- 12. XMEGA AVR • This microcontroller is used commercially for compound applications, which need large program memory and also high speed. • 16–384 KB program memory • 44-100 pin • Extended performance features such as DMA, Event System. 12
- 13. AVR ARCHITECTURE • ALU • 32 General Purpose Registers • Static RAM • EEPROM • Flash • Timer/Counter • Comparator • Watch Dog timer • Protocols: UART, SPI, I2C • I/O Ports 13
- 14. Table 1: Basic registers of ATmega16 GPIO Registers 14
- 15. INTERFACING OF LED • A LED is an acronym for Light Emitting Diode and is basically an electronic device which emits light when an electric current flows through it. 15
- 16. 16
- 17. 17
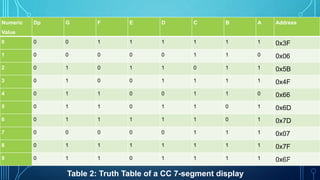
- 18. Numeric Value Dp G F E D C B A Address 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0x3F 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0x06 2 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0x5B 3 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0x4F 4 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0x66 5 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0x6D 6 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0x7D 7 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0x07 8 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0x7F 9 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0x6F18 Table 2: Truth Table of a CC 7-segment display
- 19. 7-SEGMENT DISPLAY INTERFACING 19 • The seven segment display is the most common display device used in many gadgets, and electronic appliances like digital meters, digital clocks, microwave oven and electric stove, etc. • Types of 7-Segment Displays: Common Anode Display Common Cathode Display
- 20. 20
- 21. 21
- 22. INTERFACING OF SWITCH • An electrical switch is any device used to interrupt the flow of electrons in a circuit. Switches are essentially binary devices they are either completely on (“closed”) or completely off (“open”). 22
- 23. DC MOTOR INTERFACING • An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. 23
- 24. 24
- 25. 25
- 26. LCD INTERFACING • LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen is an electronic display module and find a wide range of applications. A 16x2 LCD display is very basic module and is very commonly used in various devices and circuits. 26
- 27. 27
- 28. 28
- 29. TIMERS • Timer is totally independent of the CPU. • In AVR timers are of two types: 8-bit and 16-bit timers. TIMER0 – 8-bit timer TIMER1– 16-bit timer TIMER2 – 8-bit timer 29
- 30. INTERRUPTS • Interrupts are basically events that require immediate attention by the microcontroller. • Atmega16 in total has twenty one (21) interrupts available. • The available interrupts are categorized in two classes: External Interrupts Internal Interrupts 30
- 31. Conclusion • AVR is RISC architecture. • AVR microcontrollers are very popular, used in numerous applications, particularly in project prototyping and also in embedded devices. • Programming is easy. • AVR is Pipe lined processors resulting in faster execution. • A watchdog to handle hanging software states is added. 31
- 32. REFERENCES • Mazidi Ali Muhammad, Mazidi Gillispie Janice, “The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded System using Assembly and C”, Pearson 2 𝑛𝑑 Edition. • ATMega16 Datasheet. 32
- 33. 33