Channalging Cases in AHF Hypoperfusion
- 1. Hypoperfusion Adrian F. Hernandez, MD, MHS Associate Director Duke Clinical Research Institute 2015 Heart Failure
- 2. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 DECLARATION OF INTEREST • RESEARCH – AstraZeneca – BMS – GSK – Merck – Novartis • Honorarium – AstraZeneca – GSK – Merck – Novartis
- 3. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Agenda • Case Examples from the Duke Hospital • Diagnostic Considerations • Inotropic Options • Mechanical Support
- 4. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Cases from the halls of Duke North 7300: Sick or Not Sick? 35 yo man with non- ischemic CM • 3 weeks of worsening dyspnea, fatigue • BP 90/50 • 75 yo female with long history of ischemic CM • Progressive weight gain and edema • BP 110/60 44
- 5. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Cases from the halls of Duke North 7300: Sick or Not Sick? 60 yo man with long history of HF PE: JVP mildly elevated; Cold, trace edema • Labs: • BUN:70; • Creatinine: 2.1 • AST 1500; ALT 1200 • T.Bili 3.1 • 75 yo female with long history of HF, COPD • PE: JVP elevated Massive edema • Labs: • BUN:70; • Creatinine: 2.1 • AST 300; ALT 200 • T.Bili 1.8 45
- 6. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Yes Stevenson LW. Eur J Heart Failure 1999;1:251-257 No Warm and Dry PCW normal CI normal Cold and Wet PCW elevated CI decreased Cold and Dry PCW low/normal CI decreased Congestion at RestCongestion at Rest LowLow PerfusionPerfusion at Restat Rest No Yes Warm and Wet PCW elevated CI normal PatientPatient Classification andClassification and TreatmentTreatment
- 7. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Mechanisms Leading to 2 Types of Cardiogenic Liver Injury Samsky MD et al JACC 2013
- 8. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Biochemical Profile Acute Cardiogenic Liver Injury • Rapid elevation of ALT/LDH 10-20 X normal • 1-3 days after hemodynamic insult • Correction within 7-10 days after hemodynamics normalize • ALT: LDH <1.5 characteristic of acute cardiogenic liver injury • Prolonged PT/INR • Total bilirubin increase and delayed c/w ALT, LDH, AST Chronic Passive Congestion • LFTs commonly elevated but small in magnitude • Often characterized as cholestasis (increase alk phos, GGT, total bili) Samsky MD et al JACC 2013
- 9. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Suspected Acute Heart Failure Algorithm Authors/Task Force Members et al. Eur Heart J 2012;33:1787-1847 Shock: Do something!
- 10. All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Current Treatments of Acute Heart Failure Diuretics Reduce fluid volume Vasodilators Decrease preload and/or afterload Inotropes Augment contrac- tility
- 11. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Results Placebo Milrinone (n = 472) (n = 477) p-value Primary Endpoint (Days of CV hospitalization within 60 days) Median days 7.0 6.0 Mean days ( sd) 12.5 14 12.3 14 Discharge to Day 60 Mean CV days 5.9 13 5.7 13 0.594 ACE-I at Target Dose (%) 48 hrs 35.8 40.5 0.140 Discharge 40.9 43.8 0.362 0.714 4 Cuffe MS et al. JAMA 2002
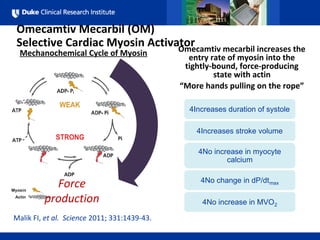
- 12. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Omecamtiv Mecarbil (OM) Selective Cardiac Myosin Activator Malik FI, et al. Science 2011; 331:1439-43. Mechanochemical Cycle of Myosin Force production 4Omecamtivmecarbil Omecamtiv mecarbil increases the entry rate of myosin into the tightly-bound, force-producing state with actin “More hands pulling on the rope” 4Increases duration of systole 4Increases stroke volume 4No increase in myocyte calcium 4No change in dP/dtmax 4No increase in MVO2
- 13. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Time-dependent Elastance [E(t)] 0 0.5 1.0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Time (sec) NormalizedE(t) Dobutamine Baseline TEmax TEmin 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Baseline Omecamtiv mecarbil TEmin TEmax Time (sec) 0 0.5 1.0 MVO2 Increased MVO2 Unchanged Malik FI, et al. Science 2011 Omecamtiv Mecarbil: Dog Heart Failure Model Increases the Duration but not the Velocity of Contraction
- 14. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Percutaneous Left Ventricular Support Devices Werdan et al, EHJ 2014
- 15. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Physiological Effects of IABP —Sheidt, NEJM 1973; Mueller, Circ 1972 Cardiac Index 40% (L/min/M2) Arterial Lactate 42% (mmol/L) Coronary 34% Blood Flow (M2/100g/min) CardiacOutput 500 ml/min Heart rate bts/min Systolic BP 29 mmHg Diastolic BP 30 mmHg
- 16. The Problem of Acute Cardiogenic Shock New Engl J Med 2012;367:1287-96 IABP SHOCK II Trial On the basis of the IABP-Shock II trial, we must move forward with the understanding that a cardiovascular condition with a 40% mortality at 30- days is unacceptable. New Eng J Med 2012;367:1349-50
- 17. IABP SHOCK-2 Trial: Predictors of Mortality Thiele et al, Lancet 2013 Univariate Multivariate The two strongest predictors (age and prior stroke) cannot be modified by any acute intervention The next three predictors (lactate, oliguria, and pH) suggest that the amount of LV support is important
- 18. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Impella Technology 2.5 – 12 Fr: 2.5 L/min CP – 14 Fr: 3.5 L/Min 5.0 – 21 Fr: 5.0 L/Min
- 19. Cardiac Index CardiacIndex (l/min/m2) Wedge Pressure 0 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 On Impella PCWP (mmHg) 0 20 24 28 22 26 30 Pre Impella* 1.9±0.7 pH pHLevel 0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.0 7.2±0.2 On Impella Pre Impella On Impella Pre Impella 2.8±0.7 32±12 20±11 p=0.0001 P<0.0001 p<0.0001 Mean Arterial Pressure 61±18 94±23p<0.0001 7.4±0.1 MAP (mmHg) 0 50 60 70 80 90 On Impella Pre Impella* 100 USPella Registry: Hemodynamic and Metabolic Changes O’Neill, TCT 2011
- 20. ISAR-SHOCK RANDOMIZED TRIAL Impella 0.49 0.15 0.60 Primary Endpoint: Increase in Cardiac Index From Baseline (measured after 30 min of support) CardiacIndex(L/min/m2) IABP P=0.02 0.45 0.30 0.75 0 0.11 1.10 0.20 0.25 1.25 CardiacOutput(L/min) 0.75 0.50 1.50 0 P<0.01 Seyfarth et al. JACC 2008;52:1584–8
- 21. Tandem Heart
- 22. Percutaneous VAD: TandemHeart Cardiac Index C. Venous Pressure CVP (mmHg) 0 9 10 11 12 13 14 Serum Lactate SerumLactate (mmol/L) 0 2.8 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.4 4.6 15 4.8 0 1.4 1.8 2.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 CardiacIndex (l/min/m2) IABP 1.5 1.7 PerVAD 1.7 2.3 Pre p=0.4 n=20 n=21 Post p=0.005 IABP PerVAD IABP 13 12 PerVAD 11 10 Pre p=0.3 n=20 n=21 Post p=0.06 IABP PerVAD IABP 3.8 3.3 PerVAD 4.5 2.8 Pre p=0.5 n=20 n=21 Post p=0.03 IABP PerVAD Wedge Pressure IABP 27 22 PerVAD 20 16 PCWP (mmHg) 0 Pre p=0.02 n=20 n=21 Post p=0.003 IABP PerVAD 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 Thiele and al. Eur. Heart Journal 2005:1276-83
- 23. Percutaneous VAD: TandemHeart 30-day Mortality 0 10 30 50 20 40 60 30-dayMortality(%) IABP 45% PerVAD 43% p=0.8 9/20 9/21 Thiele et al. Eur. Heart Journal 2005:1276-83 Limb Ischemia 0 10 30 50 20 40 60 LimbIschemia(%) IABP 0% PerVAD 33% p=0.009 0/20 7/21 Transfusion IABP 40% PerVAD 90% p=0.002 8/20 19/21 DIC* 0 10 30 50 20 40 60 LimbIschemia(%) IABP 20% PerVAD 62%p=0.001 4/20 13/21 0 40 60 80 50 70 90 RequiredTransfusion(%) 100
- 24. § Venous to arterial conduit with oxygenator § Can deliver 6 l/min CO § Generally 18-21 Fr venous and 14-16 Fr arterial catheters § No randomized trials § Observational data only Percutaneous Cardiopulmonary Bypass (ECMO or CPS) Lifebridge B2T Pump
- 25. Abrams, et al, JACC 2014
- 26. Percutaneous Cardiopulmonary Bypass (ECMO or CPS) in Cardiogenic Shock § 52 studies § 533 patients § Average 52% of pts discharged alive (all studies) § Range of survival: 0-100% Nichol et al, Rescuscitation 2006 Evidence of publication bias with most studies to the left of median
- 28. 4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007 Conclusions • Hypoperfusion in acute heart failure is a major challenge: – Diagnosis may be complex • Inotrope treatment to ‘rescue’ the patient • Mechanical circulatory support evolving – Technology improvement – Challenges for evidence-based medicine











![4All Rights Reserved, Duke Medicine 2007
Time-dependent Elastance [E(t)]
0
0.5
1.0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
Time (sec)
NormalizedE(t)
Dobutamine
Baseline
TEmax
TEmin
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
Baseline
Omecamtiv
mecarbil
TEmin
TEmax
Time (sec)
0
0.5
1.0
MVO2 Increased MVO2 Unchanged
Malik FI, et al. Science 2011
Omecamtiv Mecarbil: Dog Heart Failure Model
Increases the Duration but not the Velocity of Contraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypoperfusion-160202095811/85/Channalging-Cases-in-AHF-Hypoperfusion-13-320.jpg)














