Chapter 7 PPOINT
- 1. Human Populations By David Holland Da boss
- 2. Population Growth Every second Four children are born and two people die. 2005= 6.4 Billion People Living 75 Million per year Overpopulation
- 3. Human Population Before agriculture (10,000 years ago), scientists believe that the world’s population was only a few million. More food= more people (50 million by 5,000 b.c.) Time of Christ= only 300 million people (very slow growth) Until the Middle ages, population held in check by disease, famines, and war. After 1600 a.d., growth was rapid. More sailing, agricultural innovations, and better hygiene. We are now in an exponential or J curve pattern of growth.
- 5. Limits to Growth- Malthus and Marx 1798- Rev. Thomas Malthus- An Essay on the Principle of Population . Human populations tend to increase at an exponential or compound rate while food production either remains stable or increases only slowly. Thus, humans will eventually run out of food and descend into chaos.
- 6. Limits to Growth- Malthus and Marx Karl Marx was a critic of Malthus Population growth is a symptom rather than a root cause of chaos (poverty, resource depletion, pollution etc) He believed the real causes of chaos are exploitation and oppression Neo-Malthusians= David Pimentel a Cornell University entomologist claims the optimum human population is 2 billion, or the number living in 1950
- 7. Limits to Growth- Malthus and Marx
- 8. Benefits of more people More people= larger markets, more workers, more inventors, and efficiencies of scale in mass production of goods. More ideas leads more innovations and thus we can produce less waste and consume less. Going Green Economist Julian Simon= People are the “Ultimate Resource” and developing countries have advantage.
- 9. Human Demography Demography= Vital stats about people: births, marriages, deaths. The statistical study of human populations relating to growth rate, age, structure, geographic distribution and their effects on social, economic, and environmental conditions.
- 10. How many?
- 11. How many? Largest countries in 2004(in millions) China-1,300 India-1,087 U.S.-294 In 2050 India- 1,628 China- 1,437 U.S.- 420
- 12. How Many
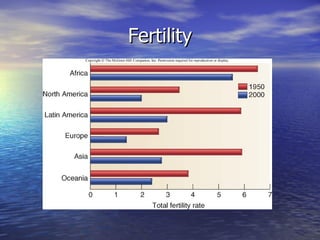
- 13. Fertility Crude birth rate= number of births in a year per thousand persons. (not adjusted for population characteristics such as the number of women in reproductive age. Total fertility rate- number of children born to an average woman in a population during her entire reproductive life. Fertility rates declined in all regions but Africa over past 50 years Due to birth control Zero Population Growth= when births plus immigration in a population just equals deaths plus emigration.
- 14. Fertility
- 15. Mortality Crude death rates= number of deaths per thousand persons in any given year. Natural increase of a population= crude birth rate-crude death rate Total growth rate= includes immigration and emigration as well as births and deaths. Rule of 70- years to double population= 70/ % change in population
- 16. Life Span Life expectancy= average age that a newborn infant can expect to attain in any given society. For most of history it was between 35-40. Declining mortality, not increasing fertility is the cause of population growth in the past 300 years. Globally, the number of people over the age of 60 years old is expected to triple increasing from 600 million to nearly 2 billion. Due to new medicine, better food, better sanitation and income (see graph)
- 18. Long Life Dependency ratio- the number of nonworking compared to working individuals in a population. Mexico has huge amounts of working supporting children, the U.S. has declining number of workers supporting the elderly.
- 20. Population Growth Opposing factors Pronatalist pressures- factors that increase a people’s desires to have babies. Enjoyment, source of income (jobs), help around the home etc. Discouraging factors= higher education for women and personal freedom for women, cost, careers etc.
- 21. Birth Dearth Birth Rates have been falling in the U.S. and other developed countries which may be because of problems with sperm (chapter 8)
- 22. Demographic Transition 1945- Demographer Frank Notestein pointed out that typical pattern of falling death rates and birth rates due to improved living conditions usually accompanies economic development. Transition from high birth and death rates to lower birth and death rates.
- 23. Demographic Transition This graph shows theoretical birth, death and population growth rates in a demographic transition accompanying economic and social development. In a predevelopment society, the birth and death rates are high and the total population growth rate is stable. During development, death rates all first, then birth rates after two generations.
- 24. Optimism vs. Pessimism Optimistic= improved standard of living, increased confidence that children will be able to survive until maturity, improved social status of women, increased availability and use of birth control. Pessimistic= poorer countries caught in demographic trap that prevents them from escaping the middle stage of a transition. Such rapid growth that many die because of lack of resources.
- 25. Social Justice Social Justice =fair share of benefits for everyone. The world has enough resources for everyone, but inequitable social and economic systems cause misdistribution of those resources Causes poverty etc.
- 26. Family Planning Family Planning= allows couples to determining the number and spacing of their children. Birth control= any method used to reduce births, including abstinence, delayed marriage, contraception, etc.
- 27. Family Planning
- 28. The Future of Human Populations The U.S. is isolated in our population policies. 1994- U.N. met to discuss women’s rights and population. Goal of universally available reproductive health services, including health planning by 2015. George Bush refused to reaffirm involvement because it could be read as promoting abortion…good job George
- 29. Growth
- 31. Case Study- A billion People and Growing India- adds more people to the world’s population every year than any other country. 2005- Added more than 185 million residents in the previous decade stood at 1.1 billion. 2050- over 1.63 billion. Problems= There is already poverty, lack of food, housing, education and employment. How do they decrease population growth? Birth Control vs. Time At 1994 conference, some said gov’t should be responsible for controlling birth rate Opponents argue that effort would waste a lot of resources they need for other things. Solution=
- 32. Case Study- A billion People and Growing Solution= 2000, decided to let each state approach the problem. Some focus on social justice, other are more direct. Kerala= education, affordable health care, and family planning= social justice Andra Pradesh= Most dramatic fertility decline because of monetary stimulus to be sterilized after one or two children. However aimed at women, bring up forced sterilizations of 1970s prime minister Indira Gandhi. Feminists are protesting Still some populations like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are increasing above 2.5 percent per year.
- 33. Case Study- A billion People and Growing