Chapter_6_Prescriptive_Analytics_Optimization_and_Simulation.pptx.pdf
- 2. • Understand the applications of prescriptive analytics techniques in combination with reporting and predictive analytics • Understand the basic concepts of analytical decision modeling • Understand the concepts of analytical models for selected decision problems, including linear programming and simulation models for decision support • Describe how spreadsheets can be used for analytical modeling and solutions • Explain the basic concepts of optimization and when to use them • Describe how to structure a linear programming model • Explain what is meant by sensitivity analysis, what-if analysis, and goal seeking • Understand the concepts and applications of different types of simulation • Understand potential applications of discrete event simulation
- 3. School District of Philadelphia Uses Prescriptive Analytics to Find Optimal Solution for Awarding Bus Route Contracts • The School District of Philadelphia was in search of private bus vendors to outsource some of their bus routes. • The vendors were evaluated based on five variables: cost, capabilities, reliance, financial stability, and business acumen.
- 4. School District of Philadelphia Uses Prescriptive Analytics to Find Optimal Solution for Awarding Bus Route Contracts • Solution: The school created an optimization model (using Solver analytic tool in Excel) that took into account the aforementioned variables associated with each vendor. • Benefits: In addition to determining how many of the vendors should be awarded contracts, the model helped develop the size of each of the contracts. • The size of the contracts varied from one vendor getting 4 routes to another receiving 97 routes.
- 5. What can We Learn from this Case? Most organizations face the problem of making decisions where one has to select from multiple options. Each option has a cost and capability associated with it. The goal is to select the combination of options that meet all the requirements and yet optimizes the costs. Most organizations face the problem of making decisions where one has to select from multiple options. Each option has a cost and capability associated with it. The goal is to select the combination of options that meet all the requirements and yet optimizes the costs.
- 6. Model-Based Decision Making • Prescriptive analytics – making decision using some kind of analytical model – Descriptive and predictive analytics creates the foundation (i.e., choice alternatives) for prescriptive analytics (i.e., making best possible decision) • Descriptive and Predictive leads to Prescriptive – Descriptive, Predictive Prescriptive
- 7. Model-Based Decision Making • Example – Profit maximization based on product/service pricing. – Which customers should receive certain promotional offers to maximize overall response (while staying within a pre-specified budget).
- 9. Case 6.1: Optimal Transport for ExxonMobil Downstream through a Decision Support System (DSS) ExxonMobil provides several ranges of petroleum products, including clean fuels, lubricants, and high-value products and feedstock to several customers. Challenge: The manual process could not determine the actual routes of vessels, the timing of each vessel, and the quantity of vacuum gas oil loaded and discharged. Solution: the company used mathematical programming language, GAMS, to make strategic business decisions in terms of the type of ships it uses, the types of cargo it carries, the volume of cargo it carries, and the ports that it works with most frequently. https://www.google.ca/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwi6qK_eqNPZAhVV_WMKHYr0CVQQjRx6BAgAEAY&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.offshoreenergytoday.com%2F
- 10. Identification of the Problem • Environmental analysis (information collection) • Variable identification • Forecasting (predictive analytics) – More information leads to better forecast/prediction Mathematical modeling is a key element to prescriptive analytics
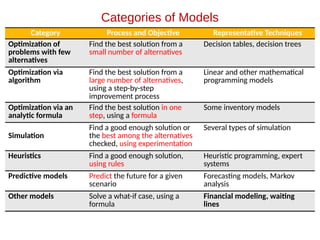
- 11. Category Process and Objective Representative Techniques Optimization of problems with few alternatives Find the best solution from a small number of alternatives Decision tables, decision trees Optimization via algorithm Find the best solution from a large number of alternatives, using a step-by-step improvement process Linear and other mathematical programming models Optimization via an analytic formula Find the best solution in one step, using a formula Some inventory models Simulation Find a good enough solution or the best among the alternatives checked, using experimentation Several types of simulation Heuristics Find a good enough solution, using rules Heuristic programming, expert systems Predictive models Predict the future for a given scenario Forecasting models, Markov analysis Other models Solve a what-if case, using a formula Financial modeling, waiting lines Categories of Models
- 12. • Quantitative Models: Mathematically links decision variables, uncontrollable variables, and result variables Structure of Mathematical Models for Decision Support Independent Variables Dependent Variable
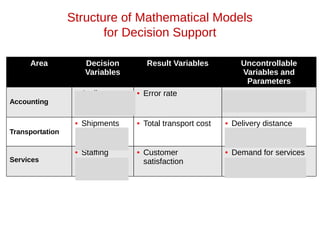
- 13. Area Decision Variables Result Variables Uncontrollable Variables and Parameters Financial investment • Investment alternatives and amounts • Total profit • Rate of return on investment • Liquidity level • Inflation rate • Prime interest rate • Competition Marketing • Advertising budget • Where to advertise • Market share • Customer satisfaction • Customer’s income • Competitor’s actions Manufacturing • What and how much to produce • Inventory levels • Compensation programs • Total cost • Quality level • Employee satisfaction • Machine capacity • Materials prices Structure of Mathematical Models for Decision Support
- 14. Area Decision Variables Result Variables Uncontrollable Variables and Parameters Accounting • Audit schedule • Error rate • Tax rates • Legal requirements Transportation • Shipments schedule • Total transport cost • Delivery distance • Regulations Services • Staffing levels • Customer satisfaction • Demand for services Structure of Mathematical Models for Decision Support
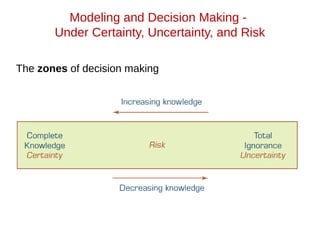
- 15. Modeling and Decision Making - Under Certainty, Uncertainty, and Risk • Assume complete knowledge • All potential outcomes are known • May yield optimal solution • Assume complete knowledge • All potential outcomes are known • May yield optimal solution Certainty Certainty •Several outcomes for each decision •Probability of each outcome is unknown •Knowledge would lead to less uncertainty •Several outcomes for each decision •Probability of each outcome is unknown •Knowledge would lead to less uncertainty Uncertainty Uncertainty • Considering several possible outcomes for each alternative • The long-run probabilities that the given outcomes will occur are assumed to be known. • Considering several possible outcomes for each alternative • The long-run probabilities that the given outcomes will occur are assumed to be known. Under Risk Under Risk
- 16. Modeling and Decision Making - Under Certainty, Uncertainty, and Risk The zones of decision making
- 17. Decision Modeling with Spreadsheets • Spreadsheet – Most popular end-user modeling tool – Flexible and easy to use – Powerful functions (add-in functions) – Programmability – What-if analysis and goal seeking – Simple database management – Seamless integration of model and data – Example: Microsoft Excel
- 18. Case 6.4: Pennsylvania Adoption Exchange Uses Spreadsheet Model to Better Match Children with Families • Challenge: PAE had a system that was complex and antiquated, and did not provide good match information for adoptions. • Solution: The new spreadsheet-based tool allows for greater customization of the results and search methodology. It allows for a weighted model based on the importance of different attributes, and also allows weight to be given based on the location of the family and child.
- 19. Case 6.5: Metro Meals on Wheels Treasure Valley Uses Excel to Find Optimal Delivery Routes • Meals on Wheels is a not-for-profit organization that delivers approximately one million meals to homes of older people in need across the United States. • A team of volunteer drivers that drive their personal vehicles each day to deliver meals to 800 clients along 21 routes and cover an area of 2,745 square kilometers. http://www.startribune.com/less-money-more-meals-twin-cities-meals-on-wheels-opens-dedicated-kitchen-in-minneapolis/421238373/ Challenge: The organization was dealing with a very complex process due to the large volume of meals delivered and the time sensitivity of delivering those meals. Existing procedures are very time intensive in order to meet the organization's needs.
- 20. Case 6.5: Metro Meals on Wheels Treasure Valley Uses Excel to Find Optimal Delivery Routes • Solution: The spreadsheet managed each client’s information, particularly their address. The spreadsheet then used an application programming interface (API) to connect to a map service. This allowed for the calculation of the most efficient routes based on the actual location of each client. As a result of using this tool, the total annual driving distance decreased by 10,000 miles, while travel time was reduced by 530 hours.
- 21. • Decision Modeling with Spreadsheets • Mathematical Programming Optimization • Multiple Goals, Sensitivity Analysis, What-If Analysis and Goal Seeking
- 22. Decision Analysis with Decision Tables and Decision Trees • Decision situations that involve a finite and usually not too large number of alternatives are modeled through an approach called decision analysis. • Alternatives are listed in a table or a graph
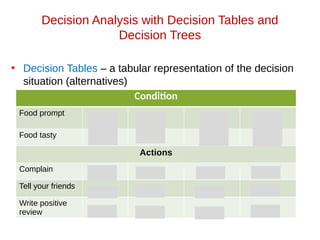
- 23. Decision Analysis with Decision Tables and Decision Trees • Decision Tables – a tabular representation of the decision situation (alternatives) Condition Food prompt Food tasty Actions Complain Tell your friends Write positive review
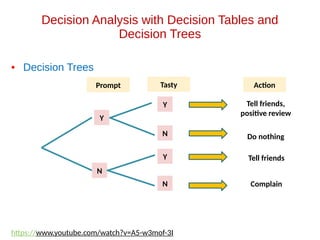
- 24. Decision Analysis with Decision Tables and Decision Trees • Decision Trees Prompt Tasty Y N Y N Y N Action Tell friends, positive review Do nothing Tell friends Complain https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A5-w3mof-3I
- 25. Decision Trees • Graphical representation of relationships • Demonstrates complex relationships • Cumbersome, if many alternatives exist • Many tools exist: o Mind Tools Ltd., mindtools.com o TreeAge Software Inc., treeage.com o Palisade Corp., palisade.com
- 26. Decision Table - Investment Example: Possible Situations 1. If solid growth in the economy, bonds yield 12%; stocks 15%; time deposits 6.5% 2. If stagnation, bonds yield 6%; stocks 3%; time deposits 6.5% 3. If inflation, bonds yield 3%; stocks lose 2%; time deposits yield 6.5% Investment example: Goal: maximize the yield after one year Yield depends on the status of the economy • Solid growth • Stagnation • Inflation
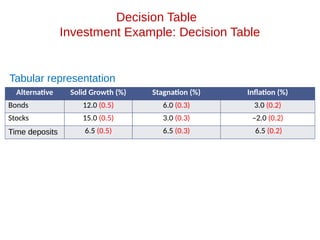
- 27. Decision Table Investment Example: Decision Table Tabular representation Alternative Solid Growth (%) Stagnation (%) Inflation (%) Bonds 12.0 6.0 3.0 Stocks 15.0 3.0 –2.0 Time deposits 6.5 6.5 6.5 Treating Uncertainty: Optimistic approach vs. pessimistic approach
- 28. Decision Table • Treating Risk: – Use known probabilities (expected values) – E.g., the chance of solid growth at 50%, the chance of stagnation at 30%, and the chance of inflation at 20%.
- 29. Decision Table Investment Example: Decision Table Tabular representation Alternative Solid Growth (%) Stagnation (%) Inflation (%) Bonds 12.0 (0.5) 6.0 (0.3) 3.0 (0.2) Stocks 15.0 (0.5) 3.0 (0.3) –2.0 (0.2) Time deposits 6.5 (0.5) 6.5 (0.3) 6.5 (0.2)
- 30. Simulation • Simulation is the “appearance” of reality • It is often used to conduct what-if analysis on the model of the actual system • It is a popular DSS technique for conducting experiments with a computer • Often used when the system is too complex for other DSS techniques
- 32. • Imitates reality and captures its richness both in shape and behavior – “Represent” versus “Imitate” • Technique for conducting experiments • Often to “solve” [i.e., analyze] very complex systems/problems • Simulation should be used only when a numerical optimization is not possible Major Characteristics of Simulation
- 33. Advantages of Simulation • It is fairly straightforward • Experiment with different alternatives • Can handle wide variety of problem types • Can include the real complexities of problems • Produces important performance measures • Often it is the only DSS modeling tool for non-structured problems
- 34. Disadvantages of Simulation • Cannot guarantee an optimal solution, but relatively good ones are generally found • Time-demanding and costly construction process • Cannot transfer solutions and inferences to solve other problems (models are problem specific) • So easy to explain/sell to managers, may lead to overlooking analytical/optimal solutions • Software may require special skills/experience
- 35. Simulation Methodology Model Development Steps: 1. Define problem 5. Conduct experiments 2. Construct the model 6. Evaluate results 3. Test and validate model 7. Implement solution 4. Design experiments
- 36. • Visual interactive modeling (VIM), also called Visual Interactive Simulation or Visual Interactive Problem Solving • Goal is to address conventional simulation modeling inadequacies • Uses computer graphics and animation • Virtual reality Visual Interactive Simulation (VIS)
- 37. Visual Interactive Simulation (VIS) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HBNH8tzsfVM
- 38. Simulation Software • A comprehensive list can be found at – orms-today.org/surveys/Simulation/Simulation.html • Simio LLC, simio.com • SAS Simulation [SAS OR], sas.com • Lumina Decision Systems, lumina.com • Oracle Crystal Ball, oracle.com • Palisade Corp., palisade.com • Rockwell Software, arenasimulation.com …
- 40. BSI: Teradata Episode: The Sad Case of StagnoBank Business Scenario Investigations: • A large international Bank is in trouble as customer service is lousy, most marketing offers are rejected by customers, and the bank has lost its appeal to younger households. BSI is engaged to work on new ideas for investments in Better Marketing, Better Customer Service, and New Mobile Apps.
- 41. BSI: Teradata Episode: The Sad Case of StagnoBank https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MScwTqhM3TI
- 42. BSI: Teradata Episode: The Sad Case of StagnoBank
- 44. Chapter 6- Review Prescriptive Analytics: Optimization and Simulation























![• Imitates reality and captures its richness both in
shape and behavior
– “Represent” versus “Imitate”
• Technique for conducting experiments
• Often to “solve” [i.e., analyze] very complex
systems/problems
• Simulation should be used only when a numerical
optimization is not possible
Major Characteristics of Simulation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6prescriptiveanalyticsoptimizationandsimulation-220714181547-80be2bf5/85/Chapter_6_Prescriptive_Analytics_Optimization_and_Simulation-pptx-pdf-32-320.jpg)





![Simulation Software
• A comprehensive list can be found at
– orms-today.org/surveys/Simulation/Simulation.html
• Simio LLC, simio.com
• SAS Simulation [SAS OR], sas.com
• Lumina Decision Systems, lumina.com
• Oracle Crystal Ball, oracle.com
• Palisade Corp., palisade.com
• Rockwell Software, arenasimulation.com …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6prescriptiveanalyticsoptimizationandsimulation-220714181547-80be2bf5/85/Chapter_6_Prescriptive_Analytics_Optimization_and_Simulation-pptx-pdf-38-320.jpg)