Designing KM Architecture
- 1. Designing Knowledge Management Architecture CREATE BRAND MARKET www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal How to implement successful KM Programs
- 2. In an economy where the only certainty is uncertainty, the one sure source of competitive advantage is knowledge. Successful companies are those that consistently create new knowledge, disseminate it widely throughout the organization, and quickly embody it in technologies and products. Ability to manage “knowledge” within the organization adds value and contributes to competitive advantage. The Business environment forces are: Speed, Smart products and Service intensity, Globalization, Shortening product life cycle, and Network intensity Introduction www.creatingdemand.org Introduction Manage “knowledge” Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 3. INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Focus on recording and processing explicit information Takes information from multiple sources and organizes into database system designed for centralized information storage and control Emphasizes collaboration and sharing Difference b/w Information Management & KM www.creatingdemand.org Difference b/w Information Management & KM KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Focus on capturing tacit and explicit information takes information from one source and promotes reuse in other situations designed for distributed access, storage and control emphasises inquiries to highly structured repositories Dependent on well defined inquiries for retrieval, productivity for efficiency Employs technologies (e.g. visualization) for knowledge discovery, productivity for innovation Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 4. KM not only manages explicit knowledge but also tacit knowledge that is embedded in the systems, products, processes and in people’s minds. Capturing tacit knowledge through periodic meetings, apprenticeships, mentoring and a culture of sharing KM is around people and not around technology. KM program should relate to the organization’s purpose and strategy. KM architecture should be evolved with reference to the corporate strategy and the strategic intent. KM emphasizes on the creation and building of dynamic organizational/ personal capabilities to interact with the environment De-mystifying Knowledge Management www.creatingdemand.org De-mystifying Knowledge Management Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 5. Organizational Knowledge: what an organization knows, how it uses what it knows and how fast it can know something new Organizational Memory: An explicit , disembodied , persistent representation of knowledge and information in the organization Types of Knowledge: Tacit and explicit Tacit knowledge : highly personal “something not easily visible and expressible”. Subjective insights, intuitions, and hunches. Its two dimensions are : technical dimensions consisting of informal skills and crafts the cognitive dimension that encompasses schemata, mental models, beliefs and perceptions. Knowledge Management Conceptualization www.creatingdemand.org Knowledge Management Conceptualization Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 6. Knowledge Cycle: The progression is from events to data, information and knowledge Tacit Knowledge Cycle: The progression is from Functional to Phenomenal, Semantic and application Modes of Knowledge Conversion within Organizations: from tacit to tacit across individuals through socialization with peers, tacit to explicit by externalization process, explicit to tacit by internalization process and from explicit to explicit by combination . Internalization is closely related to organizational learning. In externalization Metaphors, analogies figures, models are used to communicate tacit kn. Knowledge Management Conceptualization www.creatingdemand.org Knowledge Management Conceptualization Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 7. Learning Cycle consists of : concrete experiences, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization and active experimentation Organizational Learning consists of : Organization picks up signals from the environment (Past , Present and Future) , The organization analyses and reflects upon these experiences in the form of a situation audit where SWOT are analyzed , The next stage is abstract conceptualization where the organization defines its purpose , vision / mission, goals/ objectives and generates strategic options. In the last stage , the organization implements the chosen strategy and monitors / evaluates the performance of the strategy. This feedback on performance provides the organization with a new set of experiences, leading to the next cycle Learning Cycle & Strategic Process of Learning www.creatingdemand.org Learning Cycle & Strategic Process of Learning Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
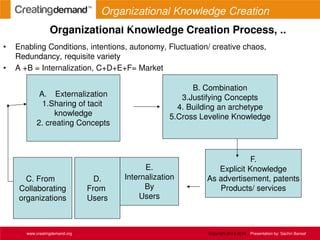
- 8. Organization knowledge creation is a continuous and a dynamic interaction between tacit and explicit knowledge Process of Knowledge Creation: Enabling conditions, intentions, autonomy, fluctuation/ creative chaos, redundancy, requisite variety . (A). Externalization 1. Sharing of Tacit Knowledge: we need to evolve norms and/ or systems of observation, documentation, reporting, and dissemination of practices, habits, working patterns, style and thought process 2. Creating Concepts means sharing of tacit knowledge that corresponds roughly roughly to socialization. Sharing is facilitated through the creation of a field of interaction, where members share their experiences and mental models Sharing Tacit Knowledge: The process starts with the ‘sharing of tacit knowledge’ that corresponds roughly to socialization. Creating Concepts: The shared tacit models , when expressed in words and phrases , give rise to explicit concepts or creating concepts and give rise to externalization process. Knowledge Creation Process www.creatingdemand.org Knowledge Creation Process Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 9. Justifying Concepts: Concepts created are justified in the light of whether they are worthwhile for the organization to expend effort , time and resources. Building an archetype: When justified concepts are put to test in the form of an archetype or prototype, the organization enters in this phase. Cross-leveling of knowledge: It kicks off a new cycle of knowledge –generation based on prototype created. This new knowledge creation can happen either within organization or outside the organization (amongst its customers, supplier, competitors, affiliates etc) through dynamic interaction. Three major imperatives in this transformation: Use of metaphors and analogies ; transforming personal knowledge in organizational knowledge; and an organizational climate of chaos and redundancy Metaphors are used in organizations to highlight certain distinctive people , behavior, products or processes Analogies are more structured ,and are used to highlight differences or similarities among concepts Knowledge Creation Process www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal Knowledge Creation Process
- 10. Dissemination of explicit individual knowledge among all in the organization To transform tacit knowledge with individual to organizational knowledge : create an organizational climate of chaos and redundancy. When directions from the top management are ambiguous , operational details are shifted to down to lower ranks of the hierarchy. This fosters lot of creativity within the organization Knowledge Creation Process www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal Knowledge Creation Process
- 11. Organizational Knowledge Creation Process, .. • Enabling Conditions, intentions, autonomy, Fluctuation/ creative chaos, Redundancy, requisite variety • A +B = Internalization, C+D+E+F= Market B. Combination 3.Justifying Concepts 4. Building an archetype 5.Cross Leveline Knowledge A. Externalization 1.Sharing of tacit knowledge 2. creating Concepts C. From Collaborating organizations D. From Users E. Internalization By Users F. Explicit Knowledge As advertisement, patents Products/ services www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal Organizational Knowledge Creation Process
- 12. Unloading burden of past experience, arising out of organizational history. It blinds people from critically analyzing and confronting new data. To break organizational defensive routines or norms of behavior To overcome tunnel vision in people : people view context from their own perspective and other reason is organizational structure, culture and norms. Bounded rationality : individuals enact and create their own world. Organizations are socially constructed mental models residing in the minds of the individuals. A systematic initiative is therefore required to break these obstacles The main issue that arises ‘who in the organization is responsible for creation of knowledge’? Yes-no individual or department Challenges in creating Organizational knowledge , out of Individual Knowledge www.creatingdemand.org Creating organizational knowledge Challenges Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 13. Stage 1: Capture-identify the required knowledge domains in alignment with KM strategy, locate the source of knowledge (internal/external), and acquire or generate the required knowledge Stage2: Collate – classify/ codify the knowledge objects (document and create knowledge bases), synthesize (seek patterns across different knowledge objects), identify the target groups for the different knowledge objects , represent (refine, organize and present the knowledge objects in a user friendly manner) , and adapt (translate the knowledge objects to the local context) Stage 3: Share- implement and maintain knowledge sharing systems (like groupware, email, bulletin boards, meetings, etc) and disseminate (to the relevant target groups) The Process of Managing Knowledge in Organizations. www.creatingdemand.org Process of Managing Knowledge Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 14. Stage 4: Capitalize-monitor usage, assess/ measure the benefits of knowledge management in terms of specified knowledge goals, get feedback, review and renew the knowledge bases (including identification of new knowledge to be captured), and embed knowledge into the organization’s value creation activities (products, services, and or information) Cycle of Knowledge Management Process: The stages are mutually exclusive ; they are often concurrent, overlapping and do not necessarily progress sequentially Capture Capitalize Collate Share The Process of Managing Knowledge in Organizations. www.creatingdemand.org Process of Managing Knowledge Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 15. As per Beckman(1999)Six perspectives of KM are: Conceptual, Process, Technology, Organizational, Management and Implementation The Conceptual perspective includes : storage media, accessibility, typology, hierarchy and development of principles and frameworks for managing knowledge The Process perspective : generating , formalizing, distributing, sharing and applying organizational knowledge The Technological perspective : use of I.T. for implementing a. creation of a IT infrastructure , representation of the knowledge objects within the systems, formation of knowledge repositories and databases, forming integrated Performance Support Systems (IPSS) and knowledge transformation by data mining etc A Framework for Implementing Knowledge Management Programs. www.creatingdemand.org Framework for Implementing Knowledge Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 16. The organizational perspective is concerned with with the internal organization that is created for spreading , evangelizing, and implementing KM. It deals with creating a culture of sharing, trust worthiness, collaboration and cooperation The management perspective deals with the measurement and evaluation of the benefits of implementing a KM program for business goals, emergent rewards / incentives/ motivational systems. The implementation perspective focuses on specific issues encountered in the implementation process- the building of IT infrastructure, identification of critical success factors for implementing KM understanding the prerequisites and challenges, integration of KM with business and corporate strategies A Framework for Implementing Knowledge Management Programs. www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal Framework for Implementing Knowledge
- 17. 1. Knowledge Architecture: decisions include knowledge mapping, i.e., ‘what knowledge is required for the business’ including objects required, their location, who needs, how to classify, and codify this knowledge in repositories, databases etc 2. Systems and Technology: includes implementation structures, systems for dissemination, access and usage; and technology used for accumulation , review, administration and access control of the knowledge base generated 3. People Issues: includes motivating people to participate in the KM program; creating a culture of knowledge sharing, institutionalizing awards,, incentives and peer recognition schemes, and aligning compensation and performance etc Decisions in designing a KM Process www.creatingdemand.org Designing a KM Process Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal
- 18. Reputation to overall gains www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal Strategically connected with clients, engaging and involving them: •How to get closer to customers? •To build brand awareness and enhance loyalty? •To position new products and services for the effective market penetration? •To fulfill what customers really desire? Specialties Brand Strategy, business entry & planning, product development, internet marketing, trade distribution, public private partnerships, sustainable tourism management and investment promotion. Crafting, Operationalizing and Implementing Growth Strategies to maximize opportunities in emerging geographies; experience as my strong resource and capability Sachin Bansal Enhancing business profitability
- 19. SACHIN BANSAL- Chief Explorer INDIA : +91 97111 90192 sb@creatingdemand.org www.creatingdemand.org facebook.com/creatingdemand DELHI LONDON MELBOURNE NEW YORK ITALY www.creatingdemand.org Copyright 2013-2014 Presentation by: Sachin Bansal Enhancing business profitability….