Developing computational thinking via the visual programming tool lego education we do
- 1. Developing Computational Thinking via the Visual Programming Tool Lego Education WeDo Dra. Ana María Pinto Llorente Dra. Sonia Casillas Martín Dr. Marcos Cabezas González Dr. Francisco José García Peñalvo Salamanca, November 2016
- 2. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 Introduction The present study is conducted in the framework of Science, Primary Education and Computational Thinking. New Curricula in STEM subjects challenges of current and future society current digital world → Digital language and all the necessary skills Teaching practice must change Ability to program solve problems Computational thinking working paradigm → → Abstract, logical, modeling & constructive thinking
- 3. Objectives The aim of the present study was to know the students’ perception about the use of the software Lego Education WeDo in the subject of natural sciences to promote the computational thinking. We tried to test these hypotheses H1. Students will learn to build and program 3D models with Lego WeDo. H2. Students will think creatively to solve the problems. H3. Lego WeDo will help pupils to know the relationship between cause and effect. H4. The tasks developed will allow pupils to reflect about the possibilities they have, and to find the correct answer. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016
- 4. Method TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 The study focused on an innovative project of computational thinking, carried out in the state-funded school Santísima Trinidad in Salamanca, in Castilla-León, during the academic year 2015-2016. Natural Sciences Unit. Forces and machines 1. To understand the importance of machines, and classify them as simple and complex machines. 2. To list the most important simple machines and know how they work. 3. To know the three types of lever. 4. To understand the contribution of technological progress to meet people’s needs. 5. To become familiar with some mechanical movements. →
- 5. Method TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 Lego Education WeDo (Lego Group in collaboration with MIT). To build and program two 3D models Dancing Birds Smart Spinner → Lego Education materials support a process of learning that includes four phases: Connect, Construct, Contemplate, and Continue.
- 6. Method We have employed a Quantitative Research Ex-post-facto, non-experimental design. Semantic differential and test. Descriptive and inferential analysis. Research Phases 1. We established the objectives and hypothesis of our research. 2. We selected the sample and instruments. 3. We carried out the register coding and data analysis to obtain the results and conclusions of our study. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016
- 7. Sample • 52 Spanish pupils from the 4th grade of Primary education of the compulsory subject natural sciences with ages between 9 (53.8%, n=28) and 10 (46.2%, n=24). • 48.1% were boys (n=25) and 51.9% were girls (n=27). • All of them had knowledge of the use of computers, tablets and interactive whiteboard. • The fifty-two pupils had participated in previous projects in which they had the opportunity to work with the visual programming tool: Scratch. • 34.6% (n=18) were enrolled in the Robotics workshop, and had experience in the use of the 3D modeling software, Sketch Up. Sample TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016
- 8. Instrument Instrument Semantic differential & Test (adapted from the research led by García-Valcárcel) Types of questions → open, close, short answers & 7-point Likert scale (1 is the most negative answer, and 7 is the most positive one). Internal consistency → Cronbach’s alpha, α=0.870. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016
- 10. Results Students’ Perceptions about the Development of the Project TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 The participants assessed very positively the project carried out about natural sciences and computational thinking. The students considered that the project had been funny; they had loved this way of working; and wanted to learn more about the subject. Semantic differential It has been boring 6.77 It has been funny I do not like this way of working 6.77 I love this way of working I am no longer interested in this topic 6.77 I want to learn more about this topic
- 11. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 They emphasized that the teacher had explained clearly what they had to do; they considered that her help had been important; and emphasized her role as a guide, showing them what was right or wrong. Semantic differential The teacher has not given us clear instructions 6.71 The teacher has explained clearly what we had to do The teacher has not helped us 5.88 The teacher has helped us The teacher has not indicated what was right or wrong in our work. 5.81 The teacher has indicated what was right or wrong in our work.
- 12. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 The pupils also stated that the project had been useful and interesting; they had understood the activities, they had maximized time, they had learned more things than usual, and they had done them working in groups. Semantic differential It has been useless 6.69 It has been useful It has not been interesting 6.63 It has been interesting I have not understood what we have done 6.65 I have understood what we have done I have lost time 6.17 I have maximized time I have learned less things than usual 6.52 I have learned more things than usual We have not done the exercises well, working in group 6.46 We have done the activities well, working in group
- 13. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 Regarding the items that referred to the computational thinking, we emphasized the positive results of the students’ perceptions about the possibilities offered by Lego WeDo to build models in 3D and program them, as well as to learn to think creatively to make the 3D models, to reflect about the activities, to solve problems in a logical way, and to know the results of their decisions. Semantic differential I have not learned to build models in 3D 6.31 I have learned to build models in 3D I have not learned to program 6.50 I have learned to program I have not learned to think creatively to make the 3D models. 6.37 I have learned to think creatively to make the 3D models The activities done with Lego WeDo have not allowed us to reflect 6.42 The activities done with Lego WeDo have allowed us to reflect The project has not allowed us to solve problems in a logical way 6.29 The project has allowed us to solve problems in a logical way Lego WeDo has not allowed us to know the results of our decisions 6.38 Lego WeDo has allowed us to know the results of our decisions
- 14. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 We calculated the Mann-Whitney U test to determine whether there were statistically significant differences (CI 95%) between boys and girls in their assessments of the items of the semantic differential. The data analysis indicated that there were statistically significant differences in the items that referred to: • I have learned to program (item 15). • The activities done with Lego WeDo have allowed us to reflect (item 18). • I have learned to build models in 3D (item 24). • The project has allowed us to solve problems in a logical way (item 26). • I have learned to think creatively to make the 3D models (item 27). • Lego WeDo has allowed us to know the results of our decisions (item 28).
- 15. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test Gender Mean Rank Sum of Ranks Mann-Whitney U Sig. Z Item 15 Boy Girl 35.58 18.09 889.5 488.5 110.50 .000 -4.813 Item 18 Boy Girl 14.42 37.69 360.5 1017.5 639.50 .000 -6.228 Item 24 Boy Girl 39.04 14.89 976.0 402.0 24.000 .000 -6.465 Item 26 Boy Girl 13.80 38.26 345.0 1033.0 655.00 .000 -6.448 Item 27 Boy Girl 13.42 38.61 335.5 1042.5 664.50 .000 -6.698 Item 28 Boy Girl 13.98 38.09 349.5 1028.5 650.50 .000 -6.472
- 16. Results Students’ Perceptions about the Strong and Weak Aspects of the Project TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 61.50% to build & program 3D models 23.10% to work as a team 15.40% to work playing Students’ Perceptions about the aspects they liked most
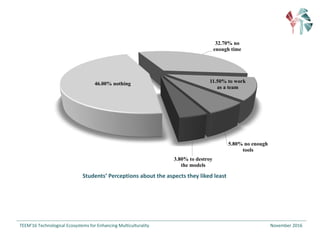
- 17. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 Students’ Perceptions about the aspects they liked least 46.00% nothing 32.70% no enough time 11.50% to work as a team 5.80% no enough tools 3.80% to destroy the models
- 18. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 Students’ Perceptions about the problems they had 51.90% no problems 15.40% to program the models 13.50% problems with the resources 11.50% to work as a team7.70% no enough time to finish
- 19. Conclusions The results from the semantic differential suggested the effectiveness of the project carried out in the subject natural sciences to increase the participants’ awareness of the computational thinking. There were evidences of the possibilities offered to: • reflect and think creatively about the opportunities they had to fulfill the activities correctly • know the results of their personal or group decisions • solve the problems in a logical way TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016 The students assessed very positively the teacher’s role in the project → guide, and thought that her help was essential for the success of the project.
- 20. Conclusions There were evidences of the students’ satisfaction towards the project, considering it useful and interesting, considering it a perfect way of learning which motivated them to learn more about the discipline of natural sciences. The use of Lego Education WeDo have allowed them to: • understand better the activities • work in groups • learn more things than usual. Our study and its results have proved the potential of the software Lego Education WeDo in the subject of natural sciences to: • promote the computational thinking • engage primary education students in programming, and problem solving. TEEM'16 Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality November 2016