Domain Driven Design Tactical Patterns
- 1. Domain Driven Design – Tactical Patterns Cristian Zamfir & Robert Alexe 1
- 2. About us Robert Alexe Application Developer Working for IBM (DDD Projects :) ) Design Patterns Domain-Driven Design DevOps Robert Alexe Mail: robert.alexe@ro.ibm.com Cristian Zamfir Application Developer IBM DDD projects Clean code Object oriented not transaction script oriented Test Driven Design Cristi Zamfir Mail: cristian.zamfir@ro.ibm.com 2
- 4. 4
- 5. Plan ● Introduction ● Architecture ● Domain Layer: Entity, VO, Domain Services ● Application Layer: App Services ● Infrastructure Layer: Repositories, Infra Services ● Exposition Layer: Web API #3860 for questions 5
- 6. Introduction ●DDD ●Software development style ●Focus on building domain in tight collaboration with domain experts ●Ubiquitous Language – shared language between developers and business ●DDD – Tactical Patterns ●Low-level coding patterns => DDD mindset ●Class/module level ●Guidelines, workflows towards DDD R #3860 for questions 6
- 7. Onion Architecture Source: Patterns, Principles and Practices of DDD C #3860 for questions 7
- 8. Domain layer ●Main module ●Self-contained <=> Maven-independent ●“The Holy Grail” ●Only business concepts (no technical implementation) <=> Framework-agnostic ● => Freedom of mind ●Business logic expressed through Ubiquitous Language C #3860 for questions 8
- 9. Domain layer - Tactical patterns ●Value Objects ●Entities ●Aggregates ●Domain Repositories ●Domain services ●Domain events R #3860 for questions 9
- 10. Value Objects ●Immutable objects: cannot change their state!! ● Essential blocks in building entities and aggregates ● Equality done by VO’s fields, not by id or == ● Can encapsulate bits of basic business logic ● Validation at instantiation time (check domain constraints) ● Avoids “Primitive Obsession” final R #3860 for questions 10
- 11. Value Objects - schema Source: Patterns, Principles and Practices of DDD R #3860 for questions 11
- 12. Value Objects vs Primitive Obsession Map<Long, List<Long>> Map<CustomerId, List<OrderId>> List<CustomerOrderIds> R #3860 for questions 12
- 13. Value Objects vs Primitive Obsession void method(long a, long b, String s, int sn) void method(OrderId orderId, UserId userId, StreetAddress streetAddress) vs C #3860 for questions 13
- 14. Value Objects – bad example public class BadVo { } private List<String> someValues; public BadVo(List<String> someValues) { this.someValues = someValues; } public List<String> getSomeValues() { return someValues; } C #3860 for questions 14
- 15. public class GoodVo { } Good VO @NotNull private final List<String> someValues; public GoodVo(List<String> someValues) { this.someValues = new ArrayList<>(someValues); } public List<String> getSomeValues() { return Collections.unmodifiableList(someValues); } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if(this == o) return true; if(o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; GoodVo goodVo = (GoodVo)o; return Objects.equals(someValues, goodVo.someValues); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(someValues);} C #3860 for questions 15
- 16. public class GoodVo implements Validable<GoodVo> { } Even Better VO (our code) @NotNull private final List<String> someValues; public GoodVo(List<String> someValues) { this.someValues = new ArrayList<>(someValues); validate(this); } public List<String> getSomeValues() { return Collections.unmodifiableList(someValues); } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if(this == o) return true; if(o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; GoodVo goodVo = (GoodVo)o; return Objects.equals(someValues, goodVo.someValues); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(someValues);} C #3860 for questions 16
- 17. Entities ●Entities encapsulate domain concepts that change in time ●DDD blocks that have an identity (think PK) ●Compared only by their identity (id) ● Not by their state at a given time! (vs. VO) ●Can contain VOs and other entities ●Preserves internal consistency in constructors or state changing methods C #3860 for questions 17
- 18. DDD Entity vs @Entity ●DDD Entity is a concept, realising a set of principles ●Directly mapped to a business concept ●@Entity is an implementation detail ●Directly mapped to a DB table ●Sometimes can overlap ●Don’t be afraid to separate them, when useful (?) C #3860 for questions 18
- 19. Entities - schema Source: Patterns, Principles and Practices of DDD R #3860 for questions 19
- 20. Entitiespublic class DomainEntity implements Validable<DomainEntity> { } @NotNull private DomainEntityId id; @NotNull private ShortLabel title; @NotNull private Description description; public DomainEntity(DomainEntityId id, ShortLabel title, Description desc) { this.id = id; this.title = title; this.description = desc; validate(this); } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if(this == o) return true; if(o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; DomainEntity that = (DomainEntity)o; return Objects.equals(id, that.id); } @Override public int hashCode() { return id.hashCode(); } R #3860 for questions 20
- 21. Aggregates ●Conglomerates of VOs and Entities ●Ampler business concept ●Enforce/Guard business constraints(invariants) ●Access to aggregate’s state is made only through the aggregate root C #3860 for questions 21
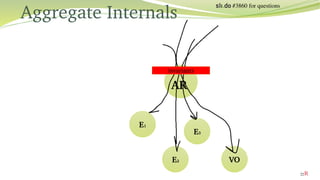
- 22. Aggregate Internals AR E1 E3 E2 VO invariants R #3860 for questions 22
- 23. Aggregate Transactions ●Each aggregate operation should be atomic ●Transaction Boundaries ●Modification of multiple aggregates through 1 client HTTP request? ➔ Ideal: two transactions (?) ~~~~> μ… => in the future will be easier to split into microservices => eventual consistency ➔ Engineering: … ☺ (1 transaction) R #3860 for questions 23
- 24. Aggregates public class Order extends BaseAggregateRoot<Order, UniqueId> { } @NotEmpty private List<Line> orderLines; //collection of VOs @NotNull private OrderStatus status; //VO @NotNull private UniqueId customerId; //VO public Order(List<Line> orderLines, OrderStatus status, UniqueId customerId) { super(Order.class, new UniqueId()); this.orderLines = new ArrayList<>(orderLines); this.status = status; this.customerId = customerId; validate(this); } public Set<Line> orderLines() { return unmodifiableSet(orderLines);} C #3860 for questions 24
- 25. Aggregates - interaction ID ID Object Links C #3860 for questions 25
- 26. Sli.do #3858 for questions 26
- 27. Domain repositories ●Interfaces for persistence abstraction ●Collection like methods (get, findAll, add) ●Interface – in domain module ●Implementation - in infrastructure module ● Connected through dependency inversion (wait for code…:) ) R #3860 for questions 27
- 28. Domain repositories ●Domain repositories only for aggregate roots ●Not for any internal entities ⇒Modification of an Aggregate is made only through the Aggregate Root. ●Personal experience example: 3 Aggregates, each containing 6-8 entities R #3860 for questions 28
- 29. Domain services ●Logic ∉ to a single Entity/Aggregate Root or too complex ●Implements business logic between: ● Aggregates ● Entities ● VOs ● Domain Repositories ● Other Domain Services ! DDD encourages distributing logic in data objects (Agg, Ent, VO) Against DDD! R #3860 for questions 29
- 30. Domain services - types 1) Implemented in domain module: ● Internal domain logic 2) Implemented in infrastructure module ● = infrastructure services ● They need infrastructure dependencies for executing operations ● Their interface is still in domain module (Dependency Inversion) ● Depend on external resources (DB, REST, JMS) R #3860 for questions 30
- 31. Domain Layer - tests ●Only fast, isolated, in-memory unit tests ●Tests only business rules ●No external dependencies ●Junit ●Mockito ●Stub implementation (InMemoryRepositories) R #3860 for questions 31
- 32. Application Services (AS) ●Handles Use Cases ●Orchestrates multiple domain services ●Do NOT depend on another AS ●Logic of one AS needs to be used in another AS ➔ refactored into a domain service (shared logic) ●Our approach: ●One AS class per User Story ●Command Pattern C #3860 for questions 32
- 33. Application Layer ●Use case / User story module ●Depends only on Domain Layer ●Hosts: ●Application Services ●Value Objects of type Command Pattern ●Application repositories for cross-aggregate consult operation ● “Light CQRS” <=> think “search results” C Sli.do #3858 for questions #3860 for questions 33
- 34. Application layer - testing ●Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) ●Cucumber framework ●.feature files that describe the user story in natural language ●.feature file steps are implemented via Java classes ● A contract agreed by both business team and developer team ● Isolation ≈ C Sli.do #3858 for questions #3860 for questions 34
- 35. Application layer – testing - feature @order Feature: Simple order of a product As a customer I want to order a product So that I can get the desired product Scenario: Customer places an order Given there are no orders for a customer When that customer buys a phone with a price of "1000" Then there is "1" "INITIATED" phone order for that customer C #3860 for questions 35
- 36. Application layer – testing ●Based on the principle: ●Given initial state of the system ● mockRepo.when() or inMemRepo.add() ●When triggering the user story ●Then check the expected state of the system ● assert ● mock.verify() C #3860 for questions 36
- 37. Infrastructure layer ●Technical module, depending on Application and Domain Layer ●Implements: ●persistence mechanism ●Repositories ●Infrastructure services ●Other technical aspects: ●Security ●Filesystem I/O ●Schedulers ●Caching ●Message R #3860 for questions 37
- 38. Infrastructure - testing ●Integration tests with in memory database ●Mock external systems ●Spring Boot’s @MockBean ●Special tests that require infrastructure ●Only a certain user role can invoke a method (@Secured) ●Transactional boundaries ●Caching R #3860 for questions 38
- 39. Exposition Layer ●Presentation level ●Exposes Rest API (HTTP Endpoints) ●Depends on application and domain layers ●Packed as project-exposition.war ●@SpringBootApplication was here C Sli.do #3858 for questions #3860 for questions 39
- 40. Exposition Layer ●Serialisation/Deserialisation of DTOs ●DTO conversion into application commands ●Our approach: ● Command Pattern™: encapsulates only input parameters ● We did not propagate DTOs in ApplicationServices (JSON is a detail) ●Calls to ApplicationService ●Surface Validation (@Valid) C #3860 for questions 40
- 41. Exposition - testing ●Test the correct serialisation/deserialisation of DTOs ●Test “Surface Validation” constraints ●Test exception handler ●Test the expected response is sent (200 OK) with the good format (JSON) ●MockMvc tests ●Don’t start the whole server only for request/response handler ●Mock Application Service C #3860 for questions 41
- 42. Sli.do #3858 for questions 42
- 44. ●Domain-Driven Design: Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software, by Eric Evans (horror) ●Implementing Domain-Driven Design, by Vaughn Vernon ●Patterns, Principles and Practices of Domain-Driven Design, by Sock Millet with Nick Tune References #3860 for questions 44
- 45. Thank you! #3860 for questions 45