Ecommerce(2)
- 1. Quantifying e-Commerce Risk David Fishbaum, FSA Chuck McClenahan, FCAS MMC ENTERPRISE RISK CAS Seminar on Ratemaking - March, 2001
- 2. The Problem You’re the risk manager of a financial institution with a new web site Your insurance broker has provided you a quote for new e-commerce risk insurance coverage: $350,000 - $450,000 with low limits Your not exactly sure what the risks of the web site are What to do?
- 3. Background The financial institution provides community banks with a product portfolio of ancillary products such as: investments (mutual funds and stock trading) insurance other banking services You provide web sites for these community banks for investments, insurance and lending
- 4. What are the risks? Failure of the web site problems with the surroundings, power failure, fire or flooding failure of the hardware failure of the software attack through virus or computer hacker
- 5. Resultant damages are also varied Delay in performing a service Loss of brand value due to unreliability of service or transmission of computer virus loss of value through failure to deliver for example, an uncompleted stock trade
- 6. Background: E-commerce insurance coverage There is an intensive application the problem is that you can’t figure out how complex or risky a web site you are running A system audit is part of the insurance coverage there is a bias to find fault
- 7. How do you insure the high P/E ratio Its 1999 and the price/earnings ratio of the e-commerce function seems to have broken down The unspoken issue is how do you insure the value lost if something happens to the web site? Not sure this is an issue today
- 8. Why bring in Actuaries? Looking for someone to quantify the risk We brought a multidisciplinary team of actuaries, economists and policy expert The actuaries provided the quantification and modeling skill sets
- 9. Methodology Model the web site Stochastic testing Scenario testing
- 10. Model MMC ER developed a computer program to model the economic performance of the e-commerce infrastructure Used company’s performance statistics Used a Monte Carlo simulation to produce expected revenue and branding values Based on this quantification, valued the potential losses of a series of scenarios
- 11. Application Server/Firewall/Proxy Layer ISP Provider In our estimation of the probability of failure at the application host level, elements such as software outage, hardware outage, data base performance etc were considered. Flow of Information and quantification of failure probabilities
- 12. Assumptions Visits per week Usage over the week Revenue Customer value Application acceptance Downtime
- 14. The Scenarios Denial of service Physical damage to hardware location New virus brings down complete system Malicious employee Threats/extortion Theft of credit card numbers
- 15. The Scenarios Attack causes a degradation of performance or loss of service to web site Not covered under current coverage Modeling assumption: site down for 3 hours Income loss/Customer value loss Denial of service
- 16. The Scenarios Location of where hardware is kept is disabled Covered under current insurance Modeling assumption: site down for 10 days Income loss/Customer value loss Client bank’s lost revenue Physical damage to hardware location
- 17. The Scenarios Not covered under current coverage Model assumption: system down for 2 days Income loss/Customer loss New virus brings down complete system
- 18. The Scenarios Destruction of important data or programs Cost of recovery process covered under current coverage Not modeled Theft of policyholder info or other intangible property Not covered under current coverage Malicious Employee
- 19. The Scenarios Threat to commit a computer crime or to use information gained from a computer crime in exchange for money, personal gain or to embarrass the company Would be covered under current kidnap and ransom policies Threats/extortion
- 20. The Scenarios CD universe and Salesgate (e-mall) No credit card numbers are stored Theft of credit card numbers
- 21. Results of analysis Biggest risk business interruption Third party loss is minimal at this time though in time the Internet will affect its client relationship
- 22. Conclusions Better quantification of risks Better able to make a purchase decision Other risk management decisions What isn’t at risk is also important
- 23. Postscript The website is still in operation Strategy has been proven successful
- 24. e-Commerce Risk Bruce Schneier - Secrets and Lies (Wiley Computer Publishing, 2000) “ The insurance industry does this kind of thing all the time; it’s how they calculate premiums. They figure out the annual loss expectancy for a given risk, tack on some extra for their operational costs plus some profit and use the result”
- 25. e-Commerce Risk Bruce Schneier - Secrets and Lies (Wiley Computer Publishing, 2000) “ Of course there’s going to be a lot of guesswork in any of these; the particular risks we’re talking about are just too new and too poorly understood to be better quantized (sic).”
- 26. e-Commerce Risk Pricing e-Commerce Risk Determine Strategy Identify the Risks Collect Available Data Develop Model Price According to Strategy
- 27. e-Commerce Risk Determine Strategy “Guess and Confess” Loss Leader Self-Supporting Franklin Approach
- 28. e-Commerce Risk Determine Strategy - “Guess and Confess” Insurer uses best available judgment (usually discovered deep in the bowels of the marketing department) as to the proper rate Alternatively, rely on advice of career agents
- 29. e-Commerce Risk Determine Strategy - Loss Leader Aptly named, this strategy is based upon the assumption that the best way to develop experience and expertise is to write a lot of exposure
- 30. e-Commerce Risk Determine Strategy - Self-Supporting Goal is to cover losses and expenses, including start-up expenses, over some reasonable period of time. This is a radical strategy and has rarely been adopted in the property-casualty industry.
- 31. e-Commerce Risk Determine Strategy - Franklin Approach Focuses on loss avoidance Underwrites against “undesirable” hazards, e.g. large user base large asset base high public profile
- 32. e-Commerce Risk Identify the Risks We have a good track record here Medical Malpractice Computer Leasing Asbestos and Environmental
- 33. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon Data mining Digital wallet Extranet Luhn formula Smart card Thin client
- 34. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process
- 35. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process Data mining - looking for hidden data patterns
- 36. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process Data mining - looking for hidden data patterns Digital wallet - encryption software, user ID
- 37. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process Data mining - looking for hidden data patterns Digital wallet - encryption software, user ID Extranet - authorized outsider-available intranet
- 38. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process Data mining - looking for hidden data patterns Digital wallet - encryption software, user ID Extranet - authorized outsider-available intranet Luhn formula - credit card verifying algorithm
- 39. e-Commerce Risk Luhn formula (1) Start with penultimate digit and, moving left, double the value of each alternating digit. If you get a two digit number, add the two digits. (2) Add up all digits. Result must be zero mod 10
- 40. e-Commerce Risk Luhn formula 1234 567890 12347 1 4 3 8 5 3 7 7 9 0 1 4 3 8 7 1+4+3+8+5+3+7+7+9+0+1+4+3+8+7=70
- 41. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process Data mining - looking for hidden data patterns Digital wallet - encryption software, user ID Extranet - authorized outsider-available intranet Luhn formula - credit card verifying algorithm Smart card - personal electronic memory card
- 42. e-Commerce Risk How many do you recognize? Daemon - a structured background process Data mining - looking for hidden data patterns Digital wallet - encryption software, user ID Extranet - authorized outsider-available intranet Luhn formula - credit card verifying algorithm Smart card - personal electronic memory card Thin client - network computer w/o hard drive
- 43. e-Commerce Risk Ingram Micro Inc. vs. American Guarantee & Liability Insurance Company “ The court finds that ‘physical damage’ is not restricted to the physical destruction or harm of computer circuitry, but includes loss of access, loss of use and loss of functionality .”
- 44. e-Commerce Risk Ingram Micro Inc. vs. American Guarantee & Liability Insurance Company “ Restricting the policy’s language to that proposed by American [i.e.that contained in the policy] would be archaic .”
- 45. e-Commerce Risk TD Waterhouse fined $225,000 for repeated outages which left customers unable to trade 11 online brokers reported 88 outages for 1st 9 months 1999 (12th firm reported so many outages it didn’t keep track).
- 46. e-Commerce Risk Collect Available Data Exposure base not well-defined Economic costs of losses not disclosed Industry is young and evolving Threat base is also evolving
- 47. e-Commerce Risk Collect Available Data Remember, “Lloyd’s List” was started in 1696 but it wasn’t until 75 years later that the Society of Lloyd’s was formed
- 48. e-Commerce Risk Develop Model Identify major processes Identify major threats Relate threats to processes Determine (or guess at) parameters
- 49. e-Commerce Risk Example - Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
- 50. e-Commerce Risk “ Attack of the Zombies” - February,2000 Monday, February 7 Yahoo! portal rendered inaccessible for 3 hours Tuesday, February 8 Buy.com 90% inaccessible eBay incapacitated CNN 95% inaccessible Amazon.com slowed to 5 minute access time Wednesday, February 9 ZDNet.com unreachable E*Trade slowed “to a crawl” Excite 60% inaccessible
- 51. e-Commerce Risk How DDoS Works Goal is to render system inoperable One attacker controls multiple servers Method: Break into numerous sites, install “attack script” and orchestrate coordinated attack
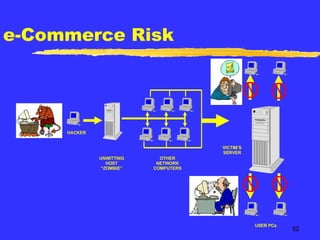
- 52. e-Commerce Risk USER PCs HACKER UNWITTING HOST “ ZOMBIE” OTHER NETWORK COMPUTERS VICTIM’S SERVER
- 55. e-Commerce Risk Price According to Strategy Frequency will vary with Popularity Profile Potential
- 56. e-Commerce Risk Price According to Strategy Severity will vary eToys v. E*Trade
- 57. e-Commerce Risk “ You gotta be careful if you don’t know where you’re going ‘cause you might not get there. ” - Yogi Berra











































![e-Commerce Risk Ingram Micro Inc. vs. American Guarantee & Liability Insurance Company “ Restricting the policy’s language to that proposed by American [i.e.that contained in the policy] would be archaic .”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecommerce2-1226683146789375-8/85/Ecommerce-2-44-320.jpg)