E Commerce14a
- 1. CS155b: E-Commerce Lecture 14: March 1, 2001 Introduction to B2B E-Commerce
- 2. Assignments HW4 due in class March 27, 2001 Reading: “ How XML Enables Internet Trading Communities and Marketplaces,” by R. Glushko “ Entering the 21 st Century: Competition Policy in the World of B2B Electronic Marketplaces” Executive Summary, Chapters 1 and 2: Required Chapter 3: Optional
- 3. Electronic Commerce Definitions Electronic commerce is a set of technologies, applications, and business processes that link business, consumers, and communities. For buying, selling, and delivering products and services For integrating and optimizing processes within and between businesses.
- 4. Definitions, continued B2B Commerce : “Interactions relating to the purchase and sale of goods and services between businesses.” Estimated to be 70% of the US economy! B2B electronic marketplaces (“B2Bs”) : Systems of suppliers, distributors, customers and infrastructure and service providers that use the Internet for communications and transactions.
- 5. Business Models for Electronic Commerce Stores and malls Virtual communities Purchasing center Auctions and reverse auctions Value-chain service provider Value-chain integrator Collaboration and concurrent engineering Information brokerage
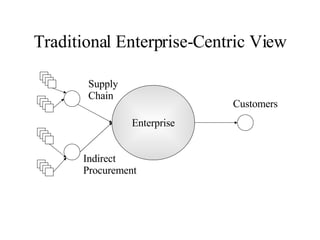
- 6. Traditional Enterprise-Centric View Enterprise Supply Chain Indirect Procurement Customers
- 7. Internet Business Models and Integration Requirements Internet enables new models for marketplaces, trading communities, outsourcing, open sourcing, buying consortia, supply chain integration and “virtual enterprises” that are fundamentally different
- 8. Networks of Commerce Communities Procurement Outsourcing Assembly Outsourcing Enterprise Distribution Markets Supply Chain Indirect Procurement Customers
- 9. Specific B2B Tasks Search Source Specify Negotiate and bid Order Receive goods and services
- 10. “Horizontal” B2Bs Serve many different industries. “ Product focus” is broad. Examples HotOffTheWire (consumer goods for small and midsized retailers) NTE (National Transportation Exchange, which sells unused trucking capacity to businesses) equalFooting (obtains volume discounts for small businesses through “virtual aggregation”)
- 11. “Vertical” B2Bs Serve a single industry Product focus is on “the supply chain of one product category” or on “expertise and in-depth content knowledge for one industry.” Examples Covisint (automotive) MetalSite BuyProduce
- 12. Revenue Models Transaction-related fees Per-transaction Flat ( e.g. , monthly, yearly) Value-based Membership/Subscription fees Value-added service fees Logistics ( e.g. , shipping) Financing Advertising and Marketing Sales of Data and Information
- 13. Participant Ownership Advantages Economies of scale Technical expertise and content knowledge Incentive to maintain high-volume participation Disadvantages Barriers to niche-player and new-player entry Anti-trust Issues Alternatives Ownership by technology firms Ownership by 3 rd party investors, e.g. , venture capitalists
- 14. COMMERCE ONE Full Name: Commerce One, Inc. Employees: 3500 Stock Price: $17.5 (Feb 27, 2001) Revenues in Q4, 99-00: $191,000,000 Business Area: E-Marketplace
- 15. PRODUCTS E-Market Solutions: MarketSet™, MarketSite™, and Net Market Maker Enterprise Buyer: Automates the procurement cycle Services: Strategy & technology consulting, Integration, Educational Services, etc. Customers: Companies (including CitiBank, Compaq, Nokia, and Staples) and Exchanges (including Covisint)
- 16. BRIEF HISTORY 1994 Founded as DistriVision Development Corporation 1997 Re-launched as Commerce One July 1999 IPO Mar 2000 Historic Peak of Stock Price ($135.625) Q3, 00-01 Starts earning money
- 18. REVENUE CHART
- 19. ARIBA Full Name: Ariba, Inc. Employees: 1680 Stock Price: $17.25 (Feb 27, 2001) Revenues in Q1, 00-01: $170,200,000 Business Area: integrated commerce solutions and web-based commerce services
- 20. PRODUCTS Procurement systems for managing buying, selling, and marketplace eCommerce processes Product series include Ariba Buyer, Ariba Marketplace, Ariba Dynamic Trade, etc. About 40% sales from technical support, training, and other related services Major clients: DuPont, Federal Express, Chevron, Hewlett-Packard, etc.
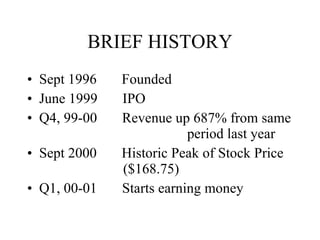
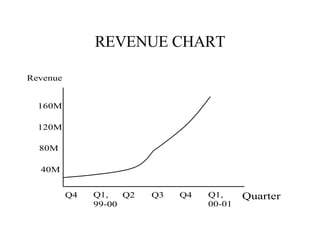
- 21. BRIEF HISTORY Sept 1996 Founded June 1999 IPO Q4, 99-00 Revenue up 687% from same period last year Sept 2000 Historic Peak of Stock Price ($168.75) Q1, 00-01 Starts earning money
- 23. REVENUE CHART
- 24. Covisint Founded officially Dec 11, 2000 by Ford, General Motors, Nissan and Renault. Started originally as a vision group 12 mo. earlier. B2B e-business exchange allowing automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers to speed the flow of material through the supply chain If Covisint lives up to its promise, consumers will eventually be able to custom-configure a car -- from engine size to upholstery color -- and drive it home a week after placing their order.
- 25. The Exchange Virtual Project Workspace Desktop application that allows members to buy and sell automotive parts, supplies, and services Procurement Auctions: Seller and Buyer auctions Catalogs: Custom and Community Supply SupplyConnect: Access to every step of the supply process
- 27. Revenue Model One-time licensing fees for members Flat transaction fees Variable-rate transaction fees Additional fees for auctions and catalogs Covisint hopes to tap into the $1.3 trillion of purchased goods and services in the global automotive industry (eventually).
- 28. Unresolved Issues Initially there won't be transparent, real-time, two-way supply-chain connections between the auto companies and all tiers of suppliers – no real improvement. Not all auto companies and suppliers will be signed up. Auto companies are the only ones to set the rules for the exchange. Rising tensions between software partners as Covisint delays final specs for application development. Other similar exchanges are planned by other automotive companies.