electrical steel.docx
- 1. Electrical steel is most important f unctional material which is used in generators,cores,transf ormers, and other power supply and conv ersion sy stems. In particular, low iron loss has been required in recent y ears as a means of contributing to a reduction in CO2 emissions into the atmosphere by achiev ing higher ef f iciency, and hence, energy sav ings in these dev ices. Electrical steel is a kind of special steel which is tailored to show certain specif ic magnetic properties such as small hy st eresis area (small energy dissipation per cy cle or low core loss) and high permeability . It is also called lamination steel, silicon (Si) steel, Si-electrical steel, or transf ormer steel. The steel contains specif ic percentage of Si in it which is responsible f or its unique property . In mild steel there is much loss in electrical energy due to hy steresis and eddy current and hence use of mild steel is uneconomical when it is used in the electrical dev ices. The hy steresis loss is shown in Fig 1. The hy steresis loss is proportional to the area of the respectiv e loops shown in the f igure.
- 2. Fig 1 Magnetic hysteresis loop of electric steel and mild steel Electrical steels hav e special phy sical properties which make them suitable f or application in the production of electric equipments and appliances with rotating magnetic f ields. The utilization of the f ully processed steels is also widespread f or construction of electrical static dev ices. Electrical st eels are used in the stacked cores of transf ormers and motors, which are rarely seen by the ordinary people. First silicon-iron alloy s designed f or the application in the electrical transf ormers were produced in the early 1900s. Si content of the f irst commercial products has been in the range of 1 % to 4 %, and since this beginning, a maximum amount of around 3 % Si was recognized as the best compromise between magnetic and mechanical perf ormances of the electrical steels. Ferro-magnetic materials are classif ied as hard magnetic materials, such as permanent magnets, which externally supply magnetic f lux semi- permanently once being magnetized, and sof t magnetic materials, such as those used in electromagnet cores, which cease to supply f lux when the electric current passing through the coil is stopped. Iron-based sof t magnetic materials are used in the cores of electrical equipments such as transf ormers, generators, and motors. Reducing losses generated f rom materials of these applications contributes directly to the improv ing of the energy conv ersion ef f iciency. Further, since electrical steels are essentially a metallic material with electrical conductiv ity , the application f requency range is at the most 100 kHz f rom the direct current range, ev en when their thickness is reduced to 0.1 mm. Electrical steel is a poly -cry stalline material, and these cry stals or grains show a strong magnetic anisotropy . They dev elop an entirely dif f erent magnetic behav iour depending on the direction of the magnetic f ield. In the 1930s Norman Goss inv ented a process of cold-rolling and heat-treatment f or electrical steels which improv ed the magnetic properties signif icantly along the rolling direction of the sheet. This process orders the grains in the direction of the best magnetic characteristics and achiev es a high degree of pref erred cry stal orientations. The ordered direction of cry stals or grains is termed ‘Goss texture’ characterizing cold-rolled-grain-oriented (CRGO) electrical steel. Power transf ormer cores are made of this product which is called electrical steel. In electrical steels, the iron loss under alternating magnetic f ields is reduced to the absolute minimum by apply ing adv anced metallurgical treatments. Ty pes of electrical steel are either non oriented electrical steel (NOES) or grain oriented electrical steel (GOES). The NOES can be f ully processed or semi processed. Non-oriented, f ully processed electrical steel has v ary ing Si lev els which range f rom 0.5 % to 3.25 % Si. It has unif orm magnetic properties in all directions. This ty pe of electrical steel does not need recry stallization processes to dev elop its properties. The low Si alloy grades prov ide better magnetic permeability and thermal conductiv ity . For high alloy grades, better perf ormance is expected in high f requencies, with v ery low losses. This ty pe of steel is good f or the magnetic circuits in motors, transf ormers, and electrical sy stem housing. This f ully processed ty pe prov ides difficulty in punchability due to a completed annealing process. Organic coatings are added to improv e lubrication in the punching process. Non-oriented semi-processed electrical steels are largely non-Si alloy ed steel and are annealed at low temperatures af ter the f inal cold rolling. The end-user, howev er, has to prov ide the f inal stress-relief annealing according to the intended application of the steel. The punchability of this ty pe of the
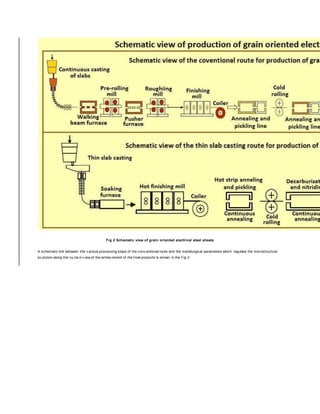
- 3. electrical steel is better than the non-oriented f ully processed ty pe, so organic coatings are not needed. Non-oriented semi-processed grades are good core materials f or small rotors, stators, and small power transf ormers. The NOES is the mostly used material among all sof t magnetic materials. The NOES is f unctional material f or the generation of energy as well as f or the use of electrical energy in electrical machines and components. There is no alternativ e material f or the NOES which constitutes around 75 % to 80 % of the demand of electrical steels. The relev ant magnetic properties (magnetization behav iour and magnetic losses) of the NOES are determined by the intensities of the texture components and the inhomogeneity of the micro-structure of the f inally processed material (grain size distribution, precipitations, and internal stresses). The number of the processing steps and the process parameters dif f er remarkably f or the NOES compared to GOES. The processing steps af ter casting comprises of hot rolling, cold rolling and f inal annealing. Product and process dev elopment in the f ield of NOES is c haracterized, like f or the GOES, by optimization of the magnetic properties and other phy sical properties f or special application areas as well as by the dev elopments. GOES is composed of iron with 3 % Si content with grains oriented to deliv er high permeability and low energy loss. Grain-oriented grades hav e strong cry stallographic properties. This ty pe undergoes a recry stallization process resulting in an enhanced grain structure which shows better magnetic properties in the rolling direction of the sheet. Grain-oriented steels are mostly used f or non-rotating applications, such as transf ormers. The thickness of GOES is mainly in the range of 0.23 mm to 0.35 mm, while that of NOES is 0.2 mm to 0.65 mm. With both steel ty pes, a thin insulation coating is painted and baked on the sheet surf ace to reduce the eddy currents generated under alternating magnetic f ields. A distinctiv e characteristic of GOES is the f act that a component, called inhibitor, which inhibits grain growth in the steel sheet, is introduced in the steel. Specif ically , with this technology , products with excellent magnetic properties are obtained by strongly suppressing grain growth by f ine dispersion of the inhibitor in the steel, perf orming high temperature, long sustained annealing (termed f inal annealing) in a condition which maintains a f ine grain structure, and selectiv ely promoting rapid growth of grains in this grain structure, and selectiv ely promoting rapid growth of grains in this f ine structure which possess a specif ic orientation f av ourable to magnetic properties, in a process termed secondary recry stallization. Accordingly the important points f or manuf acturing process are (i) a technique which causes a f ine dispersiv e precipitation of the inhibitor in steel, (ii) a technique which enables f ine control of the grain structure, and (iii) a technique f or selectiv ely promoting the growth of grains with the specif ied orientation. Production of electrical steels The dev elopment of the production routes in the last century has been amazing f ollowing the target of continuous cost reduction and y ield improv ing, reduction in energy consumption and production time, shortening and compaction of the processing cy cles. The old conv entional cy cle to produce GOES products is shown in Fig 2. The cy cle, based on the ‘Inherent Inhibition’ strategy , is v ery long and complex and the process parameters along all cy cle are to be v ery strictly controlled to achiev e the desired quality of the product.
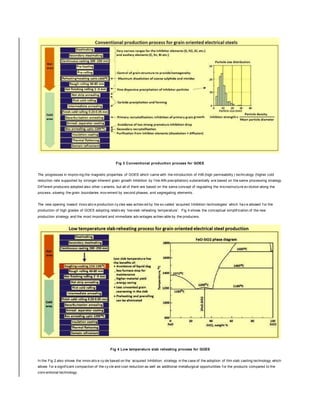
- 4. Fig 2 Schematic view of grain oriented electrical steel sheets A schematic link between the v arious processing steps of the conv entional route and the metallurgical parameters which regulate the microstructure ev olution along the cy cle in v iew of the achiev ement of the f inal products is shown in the Fig 3.
- 5. Fig 3 Conventional production process for GOES The progresses in improv ing the magnetic properties of GOES which came with the introduction of HiB (high permeability ) technology (higher cold reduction rate supported by stronger inherent grain growth inhibition by f ine AlN precipitation) substantially are based on the same processing strategy. Dif f erent producers adopted also other v ariants, but all of them are based on the same concept of regulating the microstructure ev olution along the process, slowing the grain boundaries mov ement by second phases, and segregating elements. The new opening toward innov ativ e production cy cles was achiev ed by the so called ‘acquired Inhibition technologies’ which hav e allowed f or the production of high grades of GOES adopting relativ ely ‘low slab reheating temperature’. Fig 4 shows the conceptual simplif ication of the new production strategy and the most important and immediate adv antages achiev able by the producers. Fig 4 Low temperature slab reheating process for GOES In the Fig 2 also shows the innov ativ e cy cle based on the ‘acquired Inhibition; strategy in the case of the adoption of thin slab casting technology which allows f or a signif icant compaction of the cy cle and cost reduction as well as additional metallurgical opportunities f or the products compared to the conv entional technology .
- 6. Looking at the f uture dev elopment trend of the GOES production technologies the driv ing f orce towards cy cle compaction and rationalization in v iew of cost and time. GOES is the material used as magnetically activ e media in the core of electric transf ormers, due to its high magnetic permeability and its low ‘core losses’ (power lost as heat due to dissipativ e phenomena activ e in the material during the magnetization process). The main parameters which characterize the perf ormance of the material in the application are polarization at f ixed v alue of maximum magnetizing f ield and the lost power due to dissipativ e phenomena occurring during magnetization process, f or a f ixed maximum induction. Characterizations are perf ormed at a f ixed f requency depending on the geographical area of the f inal application. The material grades nowaday s av ailable are classif ied in two large classes (standard grain oriented (CGO) and high permeability grain oriented (HGO), which are historically produced with two dif f erent technologies. The magnetic characteristics are strongly anisotropic if measured at dif f erent angles respect the rolling direction. Such a magnetic behav iour is related to a highly an-isotropous distribution of grains orientations in the material, which f rom the metallurgical point of v iew, is constituted by large grains (much larger than thickness v alue) ranging f rom f ew mm to f ew cm and cry stallograpically oriented with the easy magnetization direction of the lattice aligned within f ew angular degrees less than 10 deg in ‘standard grain oriented’ (CGO) and less than 5 degree in ‘super oriented’(HGO)) with the rolling direction (Goss orientation {110} <001>) as shown in Fig 5. Fig 5 Cubic cry stal with {110}<001> orientation and ty pical HGO grain structure The metallurgical and technological innov ations in the f ield of GOES in the recent y ears hav e been of tremendous impact on the industrial production of these materials. Due to the rationalization of the production cy cles (especially in hot area) GOES manuf acturing has become more f easible, allowing new steel organizations to produce this product. By the new methods based on the acquired inhibition strategy especially associated with thin slab casting technologies it is now possible to produce all the grades (CGO and HGO) by adopting practically the same processing route and chemical composition with great adv antages in terms of production costs. One important result of the innov ativ e production strategies is that, dif f erently f rom the past, the magnetic properties of the products can be tailored f or the specif ic application in a continuous mode ranging f rom the old conv entional CGO to the top grades of HGO products. The new production routes giv e f urther improv e chances f or enlargement of the range of product grades which can be now of f ered to transf ormer manuf acturers as giv en below. In the direction of lower dynamic core losses making feasible the production of higher Si content and lower strip thicknesses, mainly due to (i) improved capacity to handle higher ‘grain growth Inhibition’ level necessary to control the microstructure evolution after very high cold rolling rates, in view of the regulation of the oriented secondary recrystallization, and (ii) improved capacity to control the parameters influencing the brittleness of silicon-iron coils (hot band microstructure, surface and edges defects etc.). This allows the production of grades with 0.18 mm of thickness and lower. In the direction of grades having excellent magnetic properties (HGO) at higher thickness in respect to conventional products. This is mainly possible by the metallurgical chance to regulate texture and grain structure after primary recrystallization at final thickness with very low C content in the alloy. Such a condition avoids the need for decarburization, which represent the production bottle-neck in case of high thickness strips increasing the cost of production. The negative influence of high thickness on core losses is balanced by sharp texture achievable. 6.5 % silicon steel
- 7. Si is added to electrical steel sheets in order to increase their resistiv ity . In particular, because the eddy current loss in iron cores rises rapidly as the f requency increases, Si addition is extremely ef f ective in improv ing the high f requency magnetic properties of electrical steel sheets. It is also known that the magnetostriction of steel sheets is changed by adding Si to Fe, and reaches zero at a Si content of 6.5 %. Thus, high Si electrical steel sheets, and particularly 6.5 % Si steel sheets, display extremely good high f requency magnetic properties. Howev er, the ductility of steel sheets decreases as the Si content increases and the material shows remarkable embrittlement when the Si c ontent exceeds 3.5 %, making cold rolling dif f icult. For this reason, production of high Si electrical steel sheet with added Si contents exceeding 3.5 % at the industrial lev el had been dif f icult. Electrical steel is an iron alloy of iron which can hav e f rom zero percent to 6.5 % silicon but normally has Si content upto 3.2 % (higher concentrations normally prov oke brittleness during cold rolling). Manganese and aluminum can be added upto 0.5 %. Si signif icantly increases the electrical resistiv ity of the steel, which decreases the induced eddy currents and narrows the hy steresis loop of the material, thus lowering the core loss. Howev er due to the Si, the grain structure hardens and embrittles the steel, which adv ersely af fects the workability of the steel, especially during rolling. When alloy ing, the concentration lev els of carbon, sulphur, oxy gen and nitrogen are to be kept low since these elements indicate the presence of carbides, sulphides, oxides and nitrides in the steel. These compounds, ev en in particles sizes as small as one micrometer in diameter, increase hy steresis losses and decrease magnetic permeability . The presence of carbon has a more detrimental ef f ect than sulphur or oxy gen. Carbon also caus es magnetic aging when it slowly leav es the solid solution and precipitates as carbides, thus resulting in an increase in power loss ov er time. For this reason, the carbon lev el is kept to 0.005 % or lower. The carbon lev el can be reduced by annealing the steel in a decarburizing atmosphere, such as hy drogen. To solv e this technical problem, JFE Steel established the world’s first continuous production technology for 6.5 % Si steel sheets using chemical vapour deposition (CVD). Fig 6 shows the principle of the manufacturing process for 6.5 % Si steel sheets by CVD. Fi rst, a low Si steel thin sheet, which is produced easily by cold rolling, is selected as the base material. This is heated to a high temperature in a non- oxidizing atmosphere. When SiCl4 is supplied to the high temperature sheet surface, the Fe in the steel sheet and the Si in the SiCl4 gas undergo mutual substitution, and Si penetrates into the steel sheet. A Si-enriched layer is formed in the surface layer of the sheet by this chemical reaction. The Si is then diffused to the interior of the steel sheet by high temperature soaki ng in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, finally resulting in a steel sheet with a uniform 6.5 % Si content. Fig 6 Production process for 6.5 % steel Magnetic gradient high Si steel sheet
- 8. Gradient f unction materials, which are characterized by a continuous change in composition in the thickness direction, hav e been dev eloped mainly in the f ields of heat-resistant and thermo-electrical materials. The authors discov ered that electrical steel sheets hav ing a Si content distribution (gradient) in the sheet thickness direction display unique magnetic properties. A magnetic gradient high Si steel sheet with new magnetic properties, which cannot be realized in conv entional electrical steel sheets, has been successf ully developed by controlling the concentration distribution pattern in the sheet thickness direction. In particular, in the high f requency region, the new sheet possesses a low core loss property exceeding that of 6.5 % Si steel sheets. As in the production of 6.5 % Si steel sheets, this new magnetic gradient high Si steel sheet is produced by a process of siliconizing by CVD, f ollowed by dif f usion treatment using the continuous siliconizing line. In the production of magnetic gradient high Si steel sheets, t he product with the desired Si concentration distribution is obtained by controlling the amount of siliconizing during f ormation of the Si-enriched lay er in the sheet surf ace lay er and the siliconizing rate, and then controlling the temperature and treatment time during high temperature soaking in the non-oxidizing atmosphere. As shown in Fig 6, the magnetic gradient high Si steel sheets obtained by this process hav e a concentration distribution pattern in which the Si concentration increases continuously f rom the sheet centre to the surf ace lay er, and hav e a 6.5 % Si composition in the sheet surf ace lay er with extremely high magnetic permeability . o