Grasshopper optimization algorithm
- 1. Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm DR. AHMED FOUAD ALI FACULTY OF COMPUTERS AND INFORMATICS SUEZ CANAL UNIVERSITY
- 2. Outline Grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA) (History and main idea) Nature behavior of grasshopper. The main characteristic of the grasshopper swarm. Grasshopper optimization algorithm References
- 3. Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm (GOA) (History and main idea) Grasshopper optimization algorithm is a recent swarm intelligence algorithm developed by Mirjalili at. el GOA is a population based method GOA mimicking the behavior of grasshopper swarms and their social interaction.
- 4. Nature behavior of grasshopper Grasshoppers are destructive insects according to their damage to agriculture. They life has two phases, nymph and adulthood. The nymph grasshoppers have no wings so they move slowly and eat all vegetation on their path. After period of time they grow up and become adult with wings to form a swarm in the air and move fast to large scale region.
- 5. Nature behavior of grasshopper (Cont.) Although grasshoppers are usually seen individually in nature, they join in one of the largest swarm of all creatures. The size of the swarm may be of continental scale and a nightmare for farmers. The unique aspect of the grasshopper swarm is that the swarming behavior is found in both nymph and adulthood.
- 6. The main characteristic of the grasshopper swarm. The main characteristic of the swarm in the larval phase is slow movement and small steps of the grasshoppers. Long-range and abrupt movement is the essential feature of the swarm in adulthood. Food source seeking is another important characteristic of the swarming of grasshoppers by dividing the search process into two tendencies: exploration and exploitation.
- 7. Grasshopper optimization algorithm Grasshopper optimization algorithm is a recent population based algorithm, each grasshopper represents a solution in the population. The position of each grasshopper in the swarm is based on three forces. The social interaction between it and the other grasshoppers Si, the gravity force on it Gi and the wind advection Ai.
- 8. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) The final form of the three affected forces on each grasshopper can defined as follow. The social interaction force between each grasshopper and the other grasshopper can be defined as follow. Where dij is the distance between the grasshopper i and grasshopper j
- 9. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) s is a function represents the strength of two social force, attraction and repulsion between grasshoppers, it can be defined as follow. Where f, l are the intensity of the attraction and the attractive length scale. The social behavior is affected by the changing of the parameters f, l.
- 10. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) The repulsion force happen when the distance between two grasshoppers is in the interval [0, 2.079], and if the distance between two grasshoppers is 2.079, there is neither attraction nor repulsion which form a comfortable zone. If the distance greater than 2.079 the attraction force increases then it decreases gradually when it reach to 4. When the distance between two grasshopper greater than 10, the function s fails to apply forces between grasshoppers. In order to solve this problem, the distance of grasshoppers is mapped in the interval [1,4].
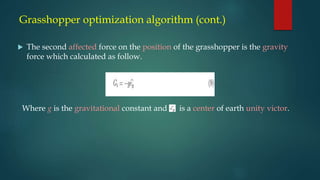
- 11. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) The second affected force on the position of the grasshopper is the gravity force which calculated as follow. Where g is the gravitational constant and is a center of earth unity victor.
- 12. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) The nymph grasshoppers movements correlated with wind direction because they have no wings. The wind direction can be calculated as follow. Where u is a constant drift and is a wind direction unity vector.
- 13. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) The position of the grasshopper can be calculated as follow. In order to solve optimization problems and prevent the grasshoppers to reach the comfort zone quickly and the swarm does not converge to the target (global optimum), the previous equation can be proposed as follow.
- 14. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) Where ubd, lbd are the upper and lower bound in the dth dimension. is the target value in the dth dimension. The parameter c is called a decreasing coefficient and it is responsible for reducing the comfort zone, repulsion zone and the attraction zone. The coefficient c is decreased proportional to the iterations number to balance exploration and exploitation in the grasshopper algorithm and it can be calculated as follow.
- 15. Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.) where cmax, cmin are the maximum and minimum values, l is the current iteration and L is the maximum number of iterations. The flowchart of the grasshopper optimization algorithm are shown in the following slide.
- 17. • Initialization. The algorithm starts by setting the initial values of the maximum and minimum values of the decreasing coefficient parameter, cmax, cmin respectively, the parameters l, f and the maximum number of iterations maxitr. •Initial population and evaluation. The initial population is generated randomly and each solution in the population is evaluated by calculating its value by using the objective function. •Assigning the overall best solution. After evaluating all the solutions in the initial population, the overall (global) best solution is assigned according to its value. •Updating the decreasing coefficient parameter. At each iteration, the coefficient parameter c is updating in order to shrink the comfort, repulsion and attraction zones as shown in Equation 13. Steps of the grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.)
- 18. Mapping the distance of grasshoppers. The function s as shown in Equation 8 is responsible for dividing the search space into comfort, repulsion and attraction zones, however its ability decreases to zero when the distance between two grasshoppers is greater than 10. In order to solve this problem the distance between the grasshopper mapped to the interval [1,4]. Updating solution. Each solution in the population is updated based on the distance between it and the other solutions, the decreasing coefficient parameter c and the global best solution in the population as shown in Equation 12. Steps of the grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.)
- 19. • Solution boundaries violation. After updating the solution, if it violates its upper and lower boundaries, it rests to its domain. •Visiting all the solutions in population. The previous three steps are repeated for all the solutions in the populations. •Solutions evaluations. The solutions in the population are updated and evaluated and the best global solution is assigned. •Termination criteria. The overall operations are repeated until reaching to the maximum number of iterations maxitr which is the termination criterion in our work. •Returning the best solution. The best globe solution T is returned when the algorithm reaches to its maximum number of iteration. Steps of the grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.)
- 20. References S. Saremi, S. Mirjalili, and A. Lewis. “Grasshopper optimisation algorithm: Theory and application”. Advances in Engineering Software, 105, 30-47, 2017










![Grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.)
The repulsion force happen when the distance between two grasshoppers is
in the interval [0, 2.079], and if the distance between two grasshoppers is
2.079, there is neither attraction nor repulsion which form a comfortable zone.
If the distance greater than 2.079 the attraction force increases then it
decreases gradually when it reach to 4.
When the distance between two grasshopper greater than 10, the function s
fails to apply forces between grasshoppers.
In order to solve this problem, the distance of grasshoppers is mapped in the
interval [1,4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grasshopperoptimizationalgorithm-180420115552/85/Grasshopper-optimization-algorithm-10-320.jpg)






![Mapping the distance of grasshoppers. The function s as shown in Equation 8 is
responsible for dividing the search space into comfort, repulsion and attraction
zones, however its ability decreases to zero when the distance between two
grasshoppers is greater than 10.
In order to solve this problem the distance between the grasshopper mapped to
the interval [1,4].
Updating solution. Each solution in the population is updated based on the
distance between it and the other solutions, the decreasing coefficient parameter
c and the global best solution in the population as shown in Equation 12.
Steps of the grasshopper optimization algorithm (cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grasshopperoptimizationalgorithm-180420115552/85/Grasshopper-optimization-algorithm-18-320.jpg)

