Influence of the population structure on the performance of an Agent-Based Evolutionary algorithm
- 1. Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Influence of the Population Structure on the Goals Methodology Analysis of Performance of an Agent-based Evolutionary Results Conclusions Algorithm Conclusions Future Works J.L.J. Laredo et al. Dpto. Arquitectura y Tecnolog´ de Computadores ıa Universidad de Granada 11-Sept-2010 1 / 18
- 2. Scope Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals • Status: Peer-to-Peer Evolutionary Computation (P2P EC) Methodology Analysis of Results represents a parallel solution for hard problems Conclusions optimization Conclusions Future Works • Modelling: Fine grained parallel EA using a P2P protocol as underlying population structure • Objective: Comparison of different population structures on the EA performance 2 / 18
- 3. Outline Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent 1 Introduction Experimental Analysis 2 Model Design Goals Methodology The Evolvable Agent Analysis of Results Conclusions 3 Experimental Analysis Conclusions Goals Future Works Methodology Analysis of Results 4 Conclusions Conclusions 5 Future Works 3 / 18
- 4. Introduction Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental P2P EC Analysis Goals • Virtualization: Methodology Analysis of Single view at Results Conclusions application level Conclusions • Decentralization: Future Works No central management • Massive Scalability: Up to thousands of computers 4 / 18
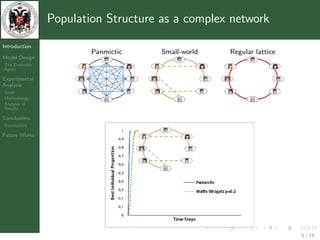
- 5. Population Structure as a complex network Introduction Panmictic Small-world Regular lattice Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals Methodology Analysis of Results Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 5 / 18
- 6. Population Structure as a complex network Introduction Panmictic Small-world Regular lattice Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals Methodology Analysis of Results Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 5 / 18
- 7. Population Structure as a complex network Introduction Panmictic Small-world Regular lattice Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals Methodology Analysis of Results Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 5 / 18
- 8. Population Structure as a complex network Introduction Panmictic Small-world Regular lattice Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals Methodology Analysis of Results n(n−1) 2 log(n) n Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 5 / 18
- 9. Outline Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent 1 Introduction Experimental Analysis 2 Model Design Goals Methodology The Evolvable Agent Analysis of Results Conclusions 3 Experimental Analysis Conclusions Goals Future Works Methodology Analysis of Results 4 Conclusions Conclusions 5 Future Works 6 / 18
- 10. The Evolvable Agent Model Introduction Model Design Design principles The Evolvable Agent • Agent based approach Experimental Analysis • Fine grain parallelization Goals • Spatially structured EA Methodology Analysis of • Local selection Results Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 7 / 18
- 11. The Evolvable Agent Model Introduction Model Design Design principles The Evolvable Agent • Agent based approach Experimental Analysis • Fine grain parallelization Goals • Spatially structured EA Methodology Analysis of • Local selection Results Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 7 / 18
- 12. Outline Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent 1 Introduction Experimental Analysis 2 Model Design Goals Methodology The Evolvable Agent Analysis of Results Conclusions 3 Experimental Analysis Conclusions Goals Future Works Methodology Analysis of Results 4 Conclusions Conclusions 5 Future Works 8 / 18
- 13. Goals and Test-Cases Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Goal Analysis Goals • Comparison of performances using different population Methodology Analysis of Results structures Conclusions Conclusions Ring Watts-Strogatz Newscast Future Works 9 / 18
- 14. Outline Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent 1 Introduction Experimental Analysis 2 Model Design Goals Methodology The Evolvable Agent Analysis of Results Conclusions 3 Experimental Analysis Conclusions Goals Future Works Methodology Analysis of Results 4 Conclusions Conclusions 5 Future Works 10 / 18
- 15. Experimental settings Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis • 2-Trap. L=12...60 Goals Methodology • Population size Analysis of Results • Estimated by bisection Conclusions • Selectorecombinative Conclusions Future Works GA (Mutation less) • Minimum population size able to reach 0.98 of SR • Uniform Crossover • Binary Tournament 11 / 18
- 16. Outline Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent 1 Introduction Experimental Analysis 2 Model Design Goals Methodology The Evolvable Agent Analysis of Results Conclusions 3 Experimental Analysis Conclusions Goals Future Works Methodology Analysis of Results 4 Conclusions Conclusions 5 Future Works 12 / 18
- 17. Population Structure Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Settings Analysis Goals Problem instance: 2-trap Methodology Analysis of Results Pop. Size: Tuning Algorithm Conclusions No Mutation Conclusions Future Works 13 / 18
- 18. Population Structure Introduction Model Design Settings The Evolvable Agent Problem instance: L=60 2-trap Experimental Analysis Pop. Size: 135 Goals Methodology Max. Eval: 5535 1 Analysis of Results Mutation: Bit-flip Pm = L Conclusions Conclusions Future Works 14 / 18
- 19. Conclusions Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals • Regular lattices require of smaller population sizes Methodology Analysis of Results ... BUT a bigger number of evaluations to find a solution. Conclusions • Different small-world methods produce an equivalent Conclusions Future Works performance ...That’s good! Many P2P protocol are designed to work as small-world networks (i.e. Interoperability/Migration between P2P platforms) 15 / 18
- 20. Future Works Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals Methodology Analysis of Results • Validation of the model in a real P2P infrastructure Conclusions Conclusions • Exploration of other P2P protocols as population Future Works structures • Extension of the P2P concept to other metaheuristics 16 / 18
- 21. Questions Introduction Model Design The Evolvable Agent Experimental Analysis Goals Methodology Analysis of Results Conclusions Conclusions Thanks for your attention! Future Works 17 / 18