Input and output basic of c++ programming and escape sequences
- 1. Lecture#18
- 2. Every program takes some data as input and generates processed data as output. • C++ supports set of I/O functions. C++ uses the concepts of stream and stream classes to implement its I/O operations with console and disk files. In this chapter we will discuss how stream classes support the console-oriented I/O operations.
- 3. Stream is a sequence of bytes. If data is received from input devices in sequence then it is called as source stream. When data is passed to output devices then it is called destination. The data is received from keyboard or disk and can be passed on to monitor or to the disk.
- 5. Data in source stream can be used as input data by program . Source stream is called as input stream. Destination stream that collects output data from the program is known as output stream.
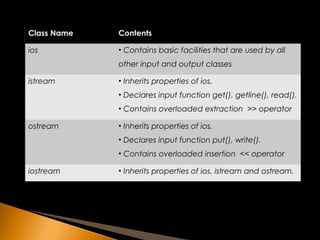
- 7. C++ streams based are based on class and object theory. C++ has a number of stream classes that are used to work with console and file operations. These classes are known as streams classes. All these classes are declared in the header file <iostream>.
- 8. Classes istream and ostream are derived classes of base class ios. • streambuf handles the buffer by providing the facilities to flush and pour the buffer. • iostream is derived from classes istream and ostream by using multiple inheritance. • ios class is a virtual class which avoid ambiguity • ios class has an ability to handle formatted and unformatted I/O operations.
- 10. Input stream uses cin object to read data. Output stream uses cout object to display data on the screen. Data type is identified by these functions using operator overloading << (insertion) and >> (extraction). The >> operator is overloaded in istream class The << operator is overloaded in ostream class
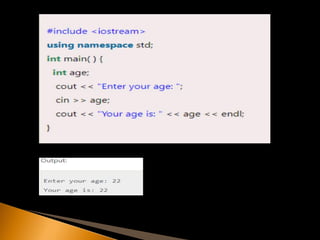
- 12. The cin is predefine object of istream class. It is connected with the standard input device. The operator used in cin is >> to read the input from the console. Example
- 14. The cout is predefined object of ostream class. It is connected with the standard output devices to show the result. The cout is used in conjunction with stream operator << to display the output on console.
- 18. cin object can be used with other member functions such as getline(), read() etc. cin.get(char & ch): reads an input character and store it in ch. cin.getline(char*buffer, int length): read a stream of characters into the string buffer, it stops when It has read length-1 character or When it finds an end of line character ‘n’ or the end of the file ‘eof’
- 19. cin.read(char*buffer, int n):read n bytes(or until the end of the file)from the stream into the buffer. cin.ignore(int n): ignore the next n characters from the input stream. cin.eof( ):returns a non-zero value if the end of file(eof) is reached.
- 20. In C++ programming, a manipulator is a function or object used with the input/output streams (e.g.cin, cout) to modify the formatting or behavior of the data being read from or written to the streams. Manipulators are typically used to control things like formatting, precision, alignment, and other aspects of input/output operations. Manipulators are often used with the insertion (<<) and extraction (>>) operators to modify the behavior of the streams. They can be applied directly to the stream or to individual data items.
- 21. endl: Inserts a newline character into the output stream and flushes the stream buffer. e.g. cout << "Hello, world!" <<endl; setw(int width): Sets the minimum field width for the next output value. e.g. cout << setw(10) << 42; // Output: " 42“; setprecision(int n): Sets the precision for floating-point values. double value = 3.14159; cout << setprecision(3) << value; // Output: "3.14“ fixed: Sets the floating-point output format to fixed-point notation. double value = 3.14159; cout << fixed << value; // Output: "3.141590“ scientific: Sets the floating-point output format to scientific notation. double value = 314159000000.0; std::cout << std::scientific << value; // Output: "3.141590e+11"
- 22. hex, oct, dec: Sets the base for integer output to hexadecimal, octal, or decimal respectively. int value = 42; cout <<hex << value; // Output: "2a" boolalpha: Outputs boolean values as "true" or "false" instead of 1 or 0. bool flag = true; std::cout << std::boolalpha << flag; // Output: "true“
- 23. The escape sequences are special non-printing character that are used to control the printing behavior of the output stream object(cout). These characters are not displayed in the output. An escape sequence is prefixed with the backslash () and used to control the printing behavior. The backslash() is called an escape character. These are written in single/double quotes.
- 24. The escape sequence can be inserted at any position of the string such as… ◦ At the beginning of the string ◦ In the middle of the string ◦ At the end of the string
- 25. ‘n’ is used to insert a new line. It insert a new line and the cursor moves to the beginning to the next line ‘t’ is used for tab. It moves the cursor one horizontal tab stop to next tab stop. ◦ cout<<“programmingtcode”; output is programming code ‘a’ stand for alarm. It causes a beep sound in the computer. ‘b’ stand for backspace. It moves the cursor one space back. e.g cout<<“welcomeb”; After execution of this statement the string welcome will be printed and cursor move one step back and delete ‘e’.
- 26. ‘r’ is used for return. It moves the cursor to the beginning of the current line. ‘’ is used to insert single quotation mark in the output Cout<<“’welcome’”; Output is ‘welcome’ “” is used to insert a double quotation mark in the output. Cout<<“”welcome””; Output is “welcome” ‘f’ is used for form feed. It causes the output to the feed one paper on the printer attached to the computer. ‘’ is used to insert a backslash character in the output. For example a statement is given below using ‘’ escape sequence. cout<<“programming”; Output is programming If single backslash is used there will be no effect on the output.