Instructional ppt
- 1. Teach ME in a Different Way, I’m Different! Jessica N. Walker
- 2. Imagine… Mrs. Hightower: Good evening class, today we are going to finish our addition problems we started yesterday, so get out your problems and begin. (All students with the exception of 2 individuals understand the assignment, Michael-African-American, Neina- Hispanic) Michael: I don’t understand… Neina: Neither do I… Mrs. Hightower: Well, I explained how to do this yesterday, you should have been paying attention, everyone else understood why can’t you guys? Michael/ Neina: We did, we just don’t understand! Mrs. Hightower: Figure it out on your own. I read over it and we worked 1 problem out in our heads yesterday. Think about it.. How can we make this situation better?
- 3. How to make this situation better? There are 2 individual students from 2 different backgrounds. Michael is African-American, while Neina is Hispanic. The remainder of the student body in the classroom is Caucasian. The teacher stated that she taught the material one time and failed to realize that all of her students have not mastered the concept. She has failed to realize that some students learn best with an example. Some learn best visually, kinesthetically and auditorally. She could incorporate technology and use manipulatives to ensure the success of all students. She has also failed to realize that cultures and ethnicities play a major role in the learning of students. http://www.judithkleinfeld.com/ar_learningstyles.html
- 4. Research says… According to Guild, the emphasis on uniformity is a serious disadvantage for students whose culture has taught them behaviors and beliefs that are different from the norms of the majority culture most often emphasized in schools. Students whose families value collaboration are told to be independent. Students whose culture values spontaneity are told to exercise self- control. Students who are rewarded in their families for being social are told to work quietly and alone. (Guild, 1990).
- 5. Research says… “ A duality of socialization is required of Black people. Black children have to be prepared to imitate the "hip," "cool," behavior of the culture in which they live and at the same time to take on those behaviors that are necessary to be upwardly mobile." (Guild, 1990). This cultural clash often causes students to struggle in school, and yet their individual strengths, if valued, respected, and promoted, would bring them success and increase their self- confidence. (Guild, 1990). http://www.newhorizons.org/strategies/styles/guild.htm
- 6. Research says… According to Kleinfeld, Children from different cultural background as a group seem to have distinctive patterns of intellectual abilities. Native American children, for example, appear to have especially high levels of visual and spatial skills and do less well on tests of verbal ability in English. This does not mean that every Native American child will have this ability pattern, just that this pattern is more common among this cultural group than among certain other cultural groups, such as Caucasian or African-American children. (Kleinfeld, 1971).
- 7. Problem Statement Too often, educators continue to treat all learners alike neglecting their individual differences.
- 8. Problem Elaboration Cultural differences are connected to learning styles. The way a student grows and develops has a major impact on his or her learning. http://www.ssc.education.ed.ac.uk/courses/pictures/vjun0921.jpg
- 9. Problem Elaboration It is important to study why individual students should be taught differently depending on their individual differences. According to Guild, Many reports contend that African Americans or Hispanic Americans or girls learn in certain common ways. There are a variety of descriptions of typical learning patterns of African Americans (Hale- Benson, 1986; Shade, 1989; Hilliard, 1989) which report the students‘ desire for oral experiences, physical activity, and strong personal relationships (Shade, Hilliard). These patterns would call for classroom work that includes collaboration, discussion, and active projects.
- 10. “ If children can’t learn the way we teach, we should teach them the way they learn.”
- 11. Problem Elaboration Each individual learner has a specific culture, family background and socioeconomic level that can affect his or her learning. According to Merlino, knowing the nuances and customs of a particular culture in addition to the artifacts of the culture is key to developing cultural sensitivity. Hispanic adolescent girls view their mother's sister as a role model in their life, so getting to know "aunty" as well as the parents would be tantamount to understanding such a student. Asian cultures typically value a collectivist orientation which values family or group needs over individual ones so the Asian student who may appear shy to the uninformed teacher may be expressing a cultural mind set by not wanting to call attention to himself or otherwise diminish the abilities of classmates. This specific knowledge would help in modifying curriculum for these two student examples. Knowing the cultural background of my students and developing my cultural sensitivity will be a crucial part of teaching in the classroom. http://www.cmu.edu/teaching/designteach/design/yourstudents.html
- 12. Research Purpose The goal of this research is to discover how learners bring their own individual approach, talents and interests to their learning environment.
- 13. Significance of the Study It is important to learn about different cultures in the classroom because the success for our diverse student populations in schools calls for continual reexamination of educators' assumptions, expectations, and biases. Many of the educators today treat all learners the same neglecting their individual differences which causes many students to struggle in the classroom. http://www.stenhouse.com/shop/pc/viewprd.asp?idProduct=8998
- 14. Significance of the Study This study is important to educators and students and proves why we as educators should educate ourselves on the different cultures in our classrooms. Students can be diverse based on ethnicity, religion, gender, and socioeconomic backgrounds. Once this research is done, we will then be able to learn about our students in our classrooms and will be able to better accommodate them and not treat all learners the same.
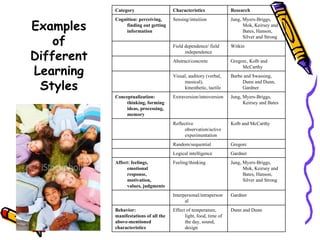
- 15. Examples of Different Learning Styles Dunn and Dunn Effect of temperature, light, food, time of the day, sound, design Behavior: manifestations of all the above-mentioned characteristics Gardner Interpersonal/intrapersonal Jung, Myers-Briggs, Mok, Keirsey and Bates, Hanson, Silver and Strong Feeling/thinking Affect: feelings, emotional response, motivation, values, judgments Gardner Logical intelligence Gregorc Random/sequential Kolb and McCarthy Reflective observation/active experimentation Jung, Myers-Briggs, Keirsey and Bates Extraversion/introversion Conceptualization: thinking, forming ideas, processing, memory Barbe and Swassing, Dunn and Dunn, Gardner Visual, auditory (verbal, musical), kinesthetic, tactile Gregorc, Kolb and McCarthy Abstract/concrete Witkin Field dependence/ field independence Jung, Myers-Briggs, Mok, Keirsey and Bates, Hanson, Silver and Strong Sensing/intuition Cognition: perceiving, finding out getting information Research Characteristics Category
- 17. Conclusion/ Summary Learning about cultures and learning style differences is important for all educators, and is something that needs to be addressed and assessed carefully. Where a child is currently living, or the child’s specific background roots, and the learning expectations and experiences in the classroom is directly related to the child's school success academically, socially, and emotionally. Understanding learning differences will help educators facilitate, structure, and validate successful learning for every student.
- 18. Bibliography Guild, P., McKinney, L., & Fouts, J. (1990). A study of the learning styles of elementary students: Low achievers, average achievers, high achievers. Seattle:WA: The Teaching Advisory. Hale-Benson, J.E. (1986). Black children: Their roots, culture, and learning styles. (Rev. ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. Hilliard, A.G., III (1989). Teachers and cultural styles in a pluralistic society. NEA Today (January), 65-69. Kleinfeld, JS. (1971). Visual memory in village Eskimo and urban Caucasian Children. Arctic, 24,132-138. Merlino, R., http://www.helium.com/items/169369-addressing-cultural-diversity-in-the-classroom Shade, B.J. (1989). The influence of perpetual development on cognitive style: Cross ethnic comparisons. Early Child Development and Care, 51, 137-155.
- 19. Bibliography http://www.istockphoto.com/stock-photo-7744823-elementary-school-classroom.php http://www.istockphoto.com/stock-photo-10617621-diverse-children.php http://www.istockphoto.com/stock-photo-3512017-circle-of-friends.php