Intra-coding using non-linear prediction, KLT and Texture Synthesis: AV1 encoders open the door to seemingly unconstrained video coding complexity
- 1. Institut für Informationsverarbeitung Intra-coding using non-linear prediction, KLT and Texture Synthesis AV1 encoders open the door to seemingly unconstrained video coding complexity Jörn Ostermann, Thorsten Laude, Yiqun Liu, Bastian Wandt, Jan Voges, Holger Meuel
- 2. Decoder Runtimes 2 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Relative factors to HM, i.e. HM=1 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 JEM AV1 JEM AV1 All-intra Random Access Complexityincrease Class A1 Class A2 Class B Class C Class D Class E Class F Overall HM Better
- 3. Encoder Runtimes 3 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Relative factors to HM, i.e. HM=1 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 JEM AV1 JEM AV1 All-intra Random Access Complexityincrease Class A1 Class A2 Class B Class C Class D Class E Class F Overall HM Better e.g. 10 frames/dayTotal CPU time: ≈ 1 decade
- 5. Trade-off Coding Efficiency vs. Complexity 5 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Better Better
- 6. Institut für Informationsverarbeitung Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding for HEVC Thorsten Laude and Jörn Ostermann
- 7. Prediction process • 33 angular modes, DC, planar • Extrapolation base: right column of left block, bottom row of top block Limitations of HEVC intra prediction • Only one direction for angular modes • Only one adjacent sample column/row as extrapolation base Motivation 7 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de CurrentAlready coded Top image: Lainema et al., Intra Coding of the HEVC Standard, TCSVT, 2012
- 8. Limitations of HEVC intra prediction • Only one direction for angular modes • Only one adjacent sample column/row as extrapolation base Motivation 8 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de CurrentAlready coded
- 9. Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding (CoMIC) 9 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 10. Reconstructed samples • Available at encoder and decoder Contour extraction • Detection • Parameterization Contour extrapolation • Sample value continuation • Various extrapolation methods Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 10 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 11. Contour detection Contour parameterization Contour extrapolation Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 11 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 12. Contour detection Contour parameterization Contour extrapolation Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 12 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Canny edge detection Signal-adaptive thresholds following Otsu1, 2 1Otsu, A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms, SMC, 1979 2Fang et al., The Study on an Application of Otsu Method in Canny Operator, ISIP, 2009
- 13. Contour detection Contour parameterization Contour extrapolation Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 13 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Polynomial parameterization Linear regression problem least squares
- 14. Contour detection Contour parameterization Contour extrapolation Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 14 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Contour width by comparison of sample values from central pixel with neighboring pixels
- 15. Contour detection Contour parameterization Contour extrapolation Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 15 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Varying prediction certainty Diminishing towards mean sample value of reconstructed area 𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑒 = 𝑠𝑠𝑚𝑚 𝑑𝑑 + 𝑠𝑠𝑎𝑎(𝑑𝑑max − 𝑑𝑑) 𝑑𝑑max 𝑑𝑑 = (𝑥𝑥𝑎𝑎 − 𝑥𝑥𝑒𝑒)2+(𝑦𝑦𝑎𝑎 − 𝑦𝑦𝑒𝑒)2 𝑠𝑠𝑚𝑚 𝑠𝑠𝑎𝑎 𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑒
- 16. Contour detection Contour parameterization Contour extrapolation Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 16 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de Background prediction: continuation of sample values • horizontal and vertical fill • mean fill for shielded pixels 𝑠𝑠𝑚𝑚
- 17. Comparison with state-of-the art of Liu et al.1 Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 17 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de 1Liu et al., Image Compression with Edge-based Inpainting, TCSVT, 2007 CoMIC (Ours) Liu et al. Contour extrapolation solely based on reconstructed samples no signalling Signalling of side information for the contour shape Sample value continuation PDE-based inpainting Signalling of representative sample values for the inpainting
- 18. Stand alone codec: Comparison with state-of-the art of Liu et al.1 (anchor: JPEG) Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 18 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de 21% 20% 44% 21% 33% 32% 15% 26% 24% 28% 29% 31% 27% 33% 29% 37% 30% 26% 32% 22% 26% 26% 31% 34% 31% 30% 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% 45% 50% Bitratesavings Liu et al. CoMIC [ours] 1Liu et al., Image Compression with Edge-based Inpainting, TCSVT, 2007 better
- 19. Additional coding mode in HEVC (HM-16.3) Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding 19 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de -2,0% -1,8% -1,6% -1,4% -1,2% -1,0% -0,8% -0,6% -0,4% -0,2% 0,0% Bike 14 BVI Ball Under Water BVI Bubbles Clear BVI Sparkler Basketball Drive BQTerrace Kimono Mean WeightedaverageBD-rate All intra Low delay Random access Mean better
- 20. • Separation of structural and texture parts • Contour extrapolation • All information available at decoder no signalling except for mode usage • Coding gain: up to 1.9% over HEVC up to 36.5% over JPEG • Outperforms related work CoMIC Results Parameterization and extrapolation of structural information result in improved intra prediction Conclusion 20 Thorsten Laude laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 21. Institut für Informationsverarbeitung Scene-based KLT for Intra Coding in HEVC Yiqun Li and Jörn Ostermann
- 22. General Idea 22 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Transform Coding Original Luminance Prediction Error Input: Prediction errors Output: Data for quantization Desired: Content representable by few coefficients in zig-zag order 16 ×16 TU Logarithm of Energy after DCT
- 23. Outline General Idea HM / JEM Karhunen Loeve Transform Conclusion 23 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 24. HM / JEM 24 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de DCT / DST Benefit: Fixed coefficients Sensitivity of eyes Drawbacks: DCT / DST not data-based Computational complexity HM JEM General DCT-II DCT-II Special 4×4 DST-VII for intra Adaptive multiple Core transform (AMT) : (DST- VII, DCT-VIII, DST-I, DCT-V) Mode dependent non-separable secondary transform (MDNSST) : 33 matrices for directional 2 matrices for non-directional modes
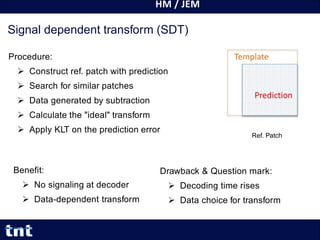
- 25. HM / JEM 25 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Signal dependent transform (SDT) Procedure: Construct ref. patch with prediction Search for similar patches Data generated by subtraction Calculate the "ideal" transform Apply KLT on the prediction error Ref. Patch Benefit: No signaling at decoder Data-dependent transform Drawback & Question mark: Decoding time rises Data choice for transform
- 26. Karhunen Loeve Transform 26 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de General Idea HM / JEM Karhunen Loeve Transform Conclusion
- 27. Karhunen Loeve Transform Desired Transform Energy compaction Data dependent ⇒ Karhunen Loeve Transform (KLT) Efficiency No re-generation at decoder ⇒ One off-line-trained transform for each case 27 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 28. Karhunen Loeve Transform Desired Transform: Indicator Prediction Mode (PM) (a) PM26 (b) PM18 Average absolute error of 8×8 TU, BQMall Direction-based KLT for intra ⇒ One transform matrix for each direction mode 28 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 29. Karhunen Loeve Transform Desired Transform: QP Dependency Average absolute error of 8×8 TUs (PM 10) from PartyScene QP-based KLT ⇒ Each sequence uses own KLT Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 10 QP 20 QP 37
- 30. Karhunen Loeve Transform Desired Transform: TU size TU Size Coverage Complexity TU size Distribution of TUs in Class B seqs. TU-based KLT ⇒ Aiming at 8×8 & 16×16 TUsYiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 11
- 31. Karhunen Loeve Transform Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Desired Transform: Scene (a) Basketball PM26 (b) BQMall PM 26 Average absolute error of 8×8 TU Scene-based KLT ⇒ Each sequence uses own KLT 12
- 32. Karhunen Loeve Transform Structure Block diagram of the hybrid encoder with KLT Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 13
- 33. Karhunen Loeve Transform Simulation Test sequences: JCT-VC 1920×1080: BasketballDrive, Kimono, Cactus, ParkScene, BQTerrace 832×480: BasketballDrill, BQMall, PartyScene, RaceHorses BVI Texture1 1920×1080: PondDragonflies, Sparkler, Bookcase, SmokeClear, Bricks Test Condition: Common Test Condition2 QP: 22 27 32 37 All-Intra (AI) Training Data: Class B & Class C 100 Frames TU size 8×8, 16×16 Evaluation: BD-Rate3 1 M. A. Papadopoulos, F. Zhang, D. Agrafiotis and D. Bull, A Video Texture Database for Perceptual Compression and Quality Assessment, ICIP 2015 2 F. Bossen, Common Test Conditions and Software Reference Configurations 3 G. Bjøntegaard, Improvements of the BD-PSNR Model, VCEG-AI11 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 14
- 34. Karhunen Loeve Transform 34 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Simulation Result 0 5 10 15 Scene−based 20 25 Kimono Cactus BQTerrace BallUnderWater BQMall BasketballDrill Plasma BricksBushes BricksLeaves Gain [%] BDBR. vs. HM−16.15 Average gain: 5.49%
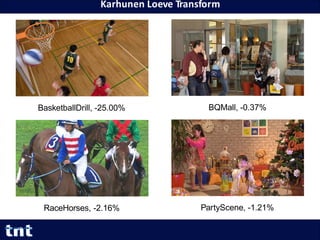
- 35. Karhunen Loeve Transform 35 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de BasketballDrill, -25.00% RaceHorses, -2.16% BQMall, -0.37% PartyScene, -1.21%
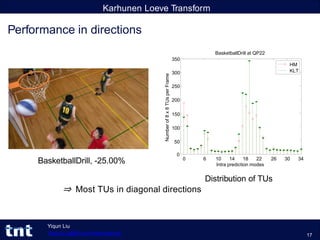
- 36. Karhunen Loeve Transform Performance in directions BasketballDrill, -25.00% 0 6 10 14 18 22 Intra prediction modes 26 30 34 0 250 200 150 100 50 300 350 Numberof8x8TUsperFrame BasketballDrill at QP22 HM KLT Distribution of TUs ⇒ Most TUs in diagonal directions Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 17
- 37. Karhunen Loeve Transform Performance in directions BQMall, -0.37% 0 6 10 14 18 22 Intra prediction modes 26 30 34 0 250 200 150 100 50 300 350 Numberof8x8TUsperFrame BQMall at QP22 HM KLT Distribution of TUs ⇒ Most TUs in horizontal and vertical directions Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 17
- 38. Karhunen Loeve Transform Performance in directions BQMall, -0.37% 0 6 10 14 18 22 Intra prediction modes 26 30 34 0 250 200 150 100 50 300 350 Numberof8x8TUsperFrame BQMall at QP22 HM KLT Distribution of TUs ⇒ Most TUs in horizontal and vertical directions Most gain comes from diagonal directions ⇒ Only diagonal prediction modes (2-5, 15-21, 30-34) Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de 17
- 39. Karhunen Loeve Transform Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Simulation Result Kimono 0 5 10 15 Scene−based 20 25 Cactus BQTerrace BallUnderWater BQMall BasketballDrill Plasma BricksBushes BricksLeaves Gain [%] BDBR. vs. HM−16.15 Average gain: Scene-based 5.49% Generic ~3% 18
- 40. Karhunen Loeve Transform Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Kimono 0 5 10 15 20 25 Simulation Result Diagonal BDBR. vs. HM−16.15 BricksLeaves BricksBushes Plasma BallUnderWater BQMall BasketballDrill BQTerrace Cactus Gain [%] Average gain: 5.49% vs. 4.14% Scene−based Scene−based diag. 18
- 41. Karhunen Loeve Transform Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Distribution of TUs on frame BasketballDrill, 1st frame, QP 32, HM-16.15 19
- 42. Karhunen Loeve Transform Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de Distribution of TUs on frame BasketballDrill, 1st frame, QP 32, scene-based KLT 19
- 43. Conclusion Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de General Idea HM / JEM Karhunen Loeve Transform Conclusion 20
- 44. Scene-based KLT Based on QP, TU-size, PM and scenes Average gain 5.49%, maximum at 25.00% Diagonal direction brings about 70% of all the gain Conclusion 21 Yiqun Liu Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 45. Institut für Informationsverarbeitung Texture Synthesis Bastain Wandt, Thorsten Laude, Bodo Rosenhahn, Jörn Ostermann pdf
- 46. Goal1 Penalty1 Penalty3 Penalty4 Texture Synthesis 46 Dipl.-Ing. Bastian Wandt wandt@tnt.uni-hannover.de
- 47. Zusammenfassung • AV1 has unseen level of encoder complexity • Scene-based KLT 5% • Non-linear intra prediction 0.5% • Texture synthesis for severely bandlimited channels Jörn Ostermann ostermann@tnt.uni-hannover.de


















![Stand alone codec: Comparison with state-of-the art of Liu et al.1
(anchor: JPEG)
Contour-based Multidirectional Intra Coding
18
Thorsten Laude
laude@tnt.uni-hannover.de
21%
20%
44%
21%
33%
32%
15%
26%
24%
28%
29%
31%
27%
33%
29%
37%
30%
26%
32%
22%
26%
26%
31%
34%
31%
30%
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
35%
40%
45%
50%
Bitratesavings Liu et al. CoMIC [ours]
1Liu et al., Image Compression with Edge-based Inpainting, TCSVT, 2007
better](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/180712klagenfurt-180720145443/85/Intra-coding-using-non-linear-prediction-KLT-and-Texture-Synthesis-AV1-encoders-open-the-door-to-seemingly-unconstrained-video-coding-complexity-18-320.jpg)














![Karhunen Loeve Transform
34
Yiqun Liu
Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
Simulation Result
0 5 10 15
Scene−based
20 25
Kimono
Cactus
BQTerrace
BallUnderWater
BQMall
BasketballDrill
Plasma
BricksBushes
BricksLeaves
Gain [%]
BDBR. vs. HM−16.15
Average gain: 5.49%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/180712klagenfurt-180720145443/85/Intra-coding-using-non-linear-prediction-KLT-and-Texture-Synthesis-AV1-encoders-open-the-door-to-seemingly-unconstrained-video-coding-complexity-34-320.jpg)


![Karhunen Loeve Transform
Yiqun Liu
Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
Simulation Result
Kimono
0 5 10 15
Scene−based
20 25
Cactus
BQTerrace
BallUnderWater
BQMall
BasketballDrill
Plasma
BricksBushes
BricksLeaves
Gain [%]
BDBR. vs. HM−16.15
Average gain: Scene-based 5.49%
Generic ~3%
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/180712klagenfurt-180720145443/85/Intra-coding-using-non-linear-prediction-KLT-and-Texture-Synthesis-AV1-encoders-open-the-door-to-seemingly-unconstrained-video-coding-complexity-39-320.jpg)
![Karhunen Loeve Transform
Yiqun Liu
Yiqun.Liu@tnt.uni-hannover.de
Kimono
0 5 10 15 20 25
Simulation Result Diagonal
BDBR. vs. HM−16.15
BricksLeaves
BricksBushes
Plasma
BallUnderWater
BQMall
BasketballDrill
BQTerrace
Cactus
Gain [%]
Average gain: 5.49% vs. 4.14%
Scene−based
Scene−based diag.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/180712klagenfurt-180720145443/85/Intra-coding-using-non-linear-prediction-KLT-and-Texture-Synthesis-AV1-encoders-open-the-door-to-seemingly-unconstrained-video-coding-complexity-40-320.jpg)






