introduction to C programming (C)
- 2. What is a programming language? • Programming Language is • A tool for instructing machines. • A meansof communicating between programmers. • A meansof controlling computerized devices. • A notation for algorithms.
- 3. Programming Domains • Scientific applications • Businessapplications • Artificial intelligence • Systemsprogramming • Scripting languages • Special purposelanguages
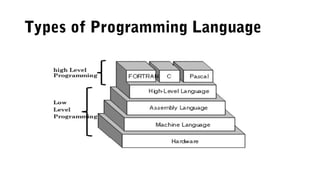
- 4. Machine Language • Machinelanguageisthelowest-level programming language. • Machine languages are the only languages understood by computers. • A computer programming language consisting of binary or hexadecimal instructions which a computer can respond to directly.
- 5. Why Humans Don't Use Machine Language
- 6. • Machine languages are almost impossible for humans to use becausethey consist entirely of numbers. • Programmers, therefore, use either a high-level programming languageor an assembly language. • An assembly language contains the same instructions as a machine language, but the instructions and variables have names instead of being just numbers.
- 7. Types of Programming Language
- 8. Assembly Language • A low-level symbolic codeconverted by an assembler. • Assembly language is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to asan assembler likeNASM, MASM, etc. • A processor understands only machine language instructions, which arestringsof 1'sand 0's. • However, machine language is too obscure and complex for using in software development. So, the low-level assembly language is designed for a specific family of processors that represents various instructionsin symbolic codeand amoreunderstandableform.
- 9. Advantages of Assembly Language Having an understanding of assembly languagemakesone awareof − •How programsinterfacewith OS, processor, and BIOS; •How dataisrepresented in memory and other external devices; •How theprocessor accessesand executesinstruction; •How instructionsaccessand processdata; •How aprogram accessesexternal devices.
- 10. High Level Language • A high-level language is a programming language such as C, FORTRAN, or Pascal that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of a particular typeof computer. • Such languages are considered high-level because they are closer to human languages.
- 11. Advantages of high-level languages • Better portability (program runson many CPUs) • Richer datatypesand memory management • Natural structuresfor expressing flow of control • Much better support for softwaremaintenance • Much better support for softwarereuse
- 12. Translation Process of HLL • Compiler: Translatesan entirehigh-level languageprogram into machinecodebeforeit isexecuted. • Interpreter: Simulatesahigh-level languageprogram, translating commandsto machinecodealong theway, only asneeded.
- 13. Compiler
- 14. Features of C language • It is a robust language with rich set of built-in functions and operators that can beused to writeany complex program. • The C compiler combines the capabilities of an assembly language with featuresof ahigh-level language. • Programs Written in C are efficient and fast. This is due to its variety of datatypeand powerful operators. • C is highly portable this means that programs once written can be run on another machineswith littleor no modification. • Another important featureof C program, isitsability to extend itself.
- 15. Features of C language
- 16. C - Program Structure A C program basically consistsof thefollowing parts− •Preprocessor Commands •Functions •Variables •Statements& Expressions •Comments
- 17. Sample Program
- 18. • Let ustakealook at thevariouspartsof theaboveprogram − • The first line of the program #include <stdio.h> is a preprocessor command, which tells a C compiler to include stdio.h file before going to actual compilation. • The next line int main() is the main function where the program execution begins. • The next line /*...*/will be ignored by the compiler and it has been put to add additional comments in the program. So such linesare called comments in theprogram. • The next line printf(...) is another function available in C which causes the message"Hello, World!" to bedisplayed on thescreen. • The next line return 0; terminates the main() function and returnsthevalue 0.
- 19. Character set of C • It denotesany alphabet, digit or special symbol used to represent information. 1. Source characterset a. Alphabets b. Digits c. Special Characters d. WhiteSpaces 2. Execution characterset a. EscapeSequence
- 20. Source character set • ALPHABETS Uppercase letters ---------- A-Z Lowercase letters ---------- a-z DIGITS -------------------------------- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
- 23. Execution Character Set • Certain ASCII characters are unprintable, which means they are not displayed on the screen or printer. Those characters perform other functions aside from displaying text. Examples are backspacing, moving to anewline, or ringing abell. • These are employed at the time of execution of the program. Execution characters set are always represented by a backslash () followed by a character. Note that each one of character constants represents one character, although they consist of two characters. Thesecharacterscombinationsarecalled asescape sequence
- 24. Identifiers • In C language identifiers are the names given to variables, constants, functionsand user-definedata. • Theseidentifier aredefined against aset of rules.
- 25. Keywords
- 26. C - Variables • A variable is nothing but a name given to a storage area that our programscan manipulate. • Each variable in C has a specific type, which determines the size and layout of thevariable'smemory; • The name of a variable can be composed of letters, digits, and the underscore character. It must begin with either a letter or an underscore. Upper and lowercase letters are distinct because C is case- sensitive.