Introduction To Data Structures.
- 1. Definitions What is Data Structure? “It is set of procedures to define, store, access and manipulate data” or “The organized collection of data is called data structure” or “The logical or mathematical model of a particular organization of data is called data structure”
- 2. Types of Data Structure • Physical Data Structures – The data structures that have actually or physically same space in memory are called physical data structures – For example, one dimensional array • Logical Data Structures – The data structures which are treated, defined and stored in their logical picture – For example, Boolean data type
- 3. Types of Data • Primitive • Non-primitive • Records and Files • Primitive(Elementary Data Types) – The data types which are processed or manipulated as a single whole(i.e, alone) – Example, integer, real, charater etc. – They are also called built-in data types
- 4. Types of Data • Non-Primitive(Structure Data Types) – The items which are collection of other data structures are called non-primitive items. – If more than one values are combined in the single name is called non-primitive data structures – Example, Arrays, Stack, Queues etc. • Types of non-Primitive Data Structures – Linear – Non-Linear
- 5. Linear Data Structures The DS in which there is concept of linearity b/w the components is called linear data structure. The components exists in a certain sequence one after another. They have some successor or predecessor Example, Arrays, Stack, Queues etc.
- 6. Types of Linear Data Structures • Physical Linear Data Structures – The linear data structures whose successive components occupy consecutive memory locations are called physical linear DS. – Example, Array • Logical Linear Data Structures – The linear DS whose components are accessed in certain sequence but they are not necessarily stored in consecutive memory locations. – Example, Linked Lists Queues and Stacks are both logical and physical linear data structures
- 7. Non-Linear • The data structure in which the order of data structure does not matter and is not fixed – Example Tree, Graph • Record The collection of fields is called record. What is Domain? – Set of possible values of an item is called its domain – For example, set of possible values of Boolean type is 2
- 8. Arrays • A collection of consecutive locations having same type that can be accessed randomly. They are physical linear data structure • Types of Arrays – One Dimensional Array – Two Dimensional Array – Multidimensional Array
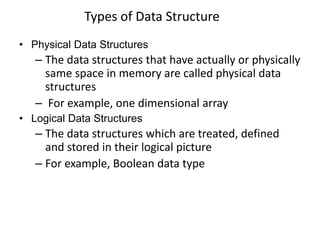
- 9. One Dimensional Arrays • 1-dimensional Arrays are also called vectors – Example, Int A[20]; – The elements of 1-d array are stored in consecutive memory locations – The start of array is called its base address – Let BA denotes the base address of the array and S denotes the size for each location, then the address of ith location can be accessed as: A(i)= BA + (i-1)* S Generally A(i)= BA + (i-lb)* S
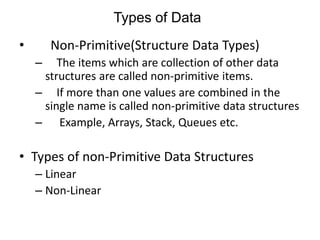
- 10. 2-d Array • Two dimensional array are used to store matrices • There are two methods for storing 2-d Arrays Row Major Order Column Major Order For Example int A[3][2]; Row Major Order 1 2 3 4 5 6 Column Major Order 1 3 5 2 4 6
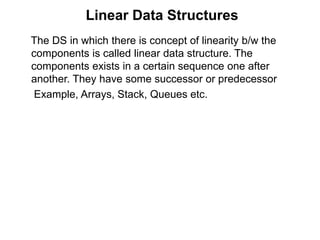
- 11. Row-Major and Column-Major Order • Consider 2-d array – int A[M][N]; – To reach an element in ith row and jth column will have to pass (i-1) rows and (j-1) columns. So address formula will be as: A(i,j)= BA+ [(i-1)*N + (j-1)]*S • In column Major Order A(i,j)= BA+ [(j-1)*M + (i-1)]*S – If lower and upper bounds are given then A(i,j)= BA+ [(i-L1)*(u2-L2+1) + (j-L2)]*S A(i,j)= BA+ [(j-L2)*(u1-L1+1) + (i-L1)]*S
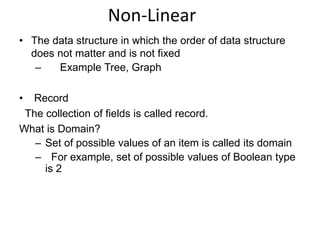
- 12. 3-d arrays • The storage for 3-d array has two types – Row- major order – Column – major order • In Row-Major order, first subscript varies more slowly than second which varies more slowly than 3rd element • In Column-Major order, 3rd subscript varies more slowly than 2nd which does more slowly than first one. – Example Int A[L][M][N] • Row-major order A(I,j,k)= BA+ [(i-1)*M*N +(j-1)*N+(k-1)]*S • Column-major order A(I,j,k)= BA+ [(k-1)L*M+(j-1)*M+(i]-1)]*S
- 13. N-Dimensional Array • Consider n-dimensional array variable as A[U1][U2]…….[Un] • Row-major order A(S1,S2,……Sn)= BA+ [(S1-1)U2*U3….Un+(S2-1)U3*U4….Un+(Sn- 1 -1)Un+(Sn-1)]*S • Column-major order ???





![One Dimensional Arrays
• 1-dimensional Arrays are also called vectors
– Example, Int A[20];
– The elements of 1-d array are stored in consecutive
memory locations
– The start of array is called its base address
– Let BA denotes the base address of the array and
S denotes the size for each location, then the address
of ith location can be accessed as:
A(i)= BA + (i-1)* S
Generally
A(i)= BA + (i-lb)* S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure-140904093950-phpapp02/85/Introduction-To-Data-Structures-9-320.jpg)
![2-d Array
• Two dimensional array are used to store matrices
• There are two methods for storing 2-d Arrays
Row Major Order
Column Major Order
For Example int A[3][2];
Row Major Order
1 2 3 4 5 6
Column Major Order
1 3 5 2 4 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure-140904093950-phpapp02/85/Introduction-To-Data-Structures-10-320.jpg)
![Row-Major and Column-Major Order
• Consider 2-d array
– int A[M][N];
– To reach an element in ith row and jth column will
have to pass (i-1) rows and (j-1) columns. So address
formula will be as:
A(i,j)= BA+ [(i-1)*N + (j-1)]*S
• In column Major Order
A(i,j)= BA+ [(j-1)*M + (i-1)]*S
– If lower and upper bounds are given then
A(i,j)= BA+ [(i-L1)*(u2-L2+1) + (j-L2)]*S
A(i,j)= BA+ [(j-L2)*(u1-L1+1) + (i-L1)]*S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure-140904093950-phpapp02/85/Introduction-To-Data-Structures-11-320.jpg)
![3-d arrays
• The storage for 3-d array has two types
– Row- major order
– Column – major order
• In Row-Major order, first subscript varies more slowly
than second which varies more slowly than 3rd element
• In Column-Major order, 3rd subscript varies more
slowly than 2nd which does more slowly than first one.
– Example Int A[L][M][N]
• Row-major order
A(I,j,k)= BA+ [(i-1)*M*N +(j-1)*N+(k-1)]*S
• Column-major order
A(I,j,k)= BA+ [(k-1)L*M+(j-1)*M+(i]-1)]*S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure-140904093950-phpapp02/85/Introduction-To-Data-Structures-12-320.jpg)
![N-Dimensional Array
• Consider n-dimensional array variable as
A[U1][U2]…….[Un]
• Row-major order
A(S1,S2,……Sn)= BA+ [(S1-1)U2*U3….Un+(S2-1)U3*U4….Un+(Sn-
1 -1)Un+(Sn-1)]*S
• Column-major order
???](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure-140904093950-phpapp02/85/Introduction-To-Data-Structures-13-320.jpg)