Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming & Design Principles (TCF 2014)
- 1. 1 Introduction to OOP & Design Principles Trenton Computer Festival March 15, 2014 Michael P. Redlich @mpredli about.me/mpredli/ Sunday, March 16, 14
- 2. Who’s Mike? • BS in CS from • “Petrochemical Research Organization” • Ai-Logix, Inc. (now AudioCodes) • Amateur Computer Group of New Jersey • Publications • Presentations 2 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 3. Objectives (2) • Object-Oriented Programming • Object-Oriented Design Principles • Live Demos (yea!) 3 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 5. Some OOP Languages • Ada • C++ • Eiffel • Java • Modula-3 • Objective C • OO-Cobol • Python • Simula • Smalltalk • Theta 5 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 6. What is OOP? • A programming paradigm that is focused on objects and data • as opposed to actions and logic • Objects are identified to model a system • Objects are designed to interact with each other 6 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 7. OOP Basics (1) • Procedure-Oriented • Top Down/Bottom Up • Structured programming • Centered around an algorithm • Identify tasks; how something is done • Object-Oriented • Identify objects to be modeled • Concentrate on what an object does • Hide how an object performs its task • Identify behavior 7 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 8. OOP Basics (2) • Abstract Data Type (ADT) • user-defined data type • use of objects through functions (methods) without knowing the internal representation 8 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 9. OOP Basics (3) • Interface • functions (methods) provided in the ADT that allow access to data • Implementation • underlying data structure(s) and business logic within the ADT 9 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 10. OOP Basics (4) • Class • Defines a model • Declares attributes • Declares behavior • Is an ADT • Object • Is an instance of a class • Has state • Has behavior • May have many unique objects of the same class 10 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 11. OOP Attributes • Four (4) Main Attributes: • data encapsulation • data abstraction • inheritance • polymorphism 11 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 12. Data Encapsulation • Separates the implementation from the interface • A public view of an object, but implementation is private • access to data is only allowed through a defined interface 12 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 13. Data Abstraction • A model of an entity • Defines a data type by its functionality as opposed to its implementation 13 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 14. Inheritance • A means for defining a new class as an extension of a previously defined class • The derived class inherits all attributes and behavior of the base class • “IS-A” relationship • Baseball is a Sport 14 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 15. Polymorphism • The ability of different objects to respond differently to the same function • From the Greek meaning “many forms” • A mechanism provided by an OOP language as opposed to a programmer- provided workaround 15 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 16. Advantages of OOP • Interface can (and should) remain unchanged when improving implementation • Encourages modularity in application development • Better maintainability of code • Code reuse • Emphasis on what, not how 16 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 17. Classes (1) • A user-defined abstract data type • Extension of C structs • Contain: • constructor • destructor • data members and member functions (methods) 17 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 18. Classes (2) • Static/Dynamic object instantiation • Multiple Constructors: • Sports(void); • Sports(char *,int,int); • Sports(float,char *,int); 18 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 19. Classes (3) • Class scope (C++) • scope resolution operator (::) • Abstract Classes • contain at least one pure virtual member function (C++) • contain at least one abstract method (Java) 19 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 20. Classes (3) • Abstract Classes • contain at least one pure virtual member function (C++) • contain at least one abstract method (Java) 20 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 21. Abstract Classes • Pure virtual member function (C++) • virtual void draw() = 0; • Abstract method (Java) • public abstract void draw(); 21 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 22. Class Inheritance 22 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 23. Static Instantiation (C++) • Object creation: • Baseball mets(“Mets”,97,65); • Access to public member functions: • mets.getWin(); // returns 97 23 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 24. Dynamic Instantiation (C++) • Object creation: • Baseball *mets = new Baseball(“Mets”,97,65); • Access to public member functions: • mets->getWin(); // returns 97 24 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 25. Dynamic Instantiation (Java) • Object creation: • Baseball mets = new Baseball(“Mets”,97,65); • Access to public member functions: • mets.getWin(); // returns 97 25 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 26. Deleting Objects (C++) Baseball mets(“Mets”,97,65); // object deleted when out of scope Baseball *mets = new Baseball(“Mets”,97,65); delete mets; // required call 26 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 27. Deleting Objects (Java) Baseball mets = new Baseball(“Mets”,97,65); // automatic garbage collection or: System.gc(); // explicit call 27 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 29. What are OO Design Principles? • A set of underlying principles for creating flexible designs that are easy to maintain and adaptable to change • Understanding the basics of OOP isn’t enough 29 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 30. Some OO Design Principles (1) • Encapsulate WhatVaries • Program to Interfaces, Not Implementations • Favor Composition Over Inheritance • Classes Should Be Open for Extension, But Closed for Modification 30 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 31. Some OO Design Principles (2) • Strive for Loosely Coupled Designs Between Objects That Interact • A Class Should Have Only One Reason to Change 31 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 32. Encapsulate What Varies • Identify and encapsulate areas of code that vary • Encapsulated code can be altered without affecting code that doesn’t vary • Forms the basis for almost all of the original Design Patterns 32 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 33. 33 // OrderCars class public class OrderCars { public Car orderCar(String model) { Car car; if(model.equals(“Charger”)) car = new Dodge(model); else if(model.equals(“Corvette”)) car = new Chevrolet(model); else if(model.equals(“Mustang”)) car = new Ford(model); car.buildCar(); car.testCar(); car.shipCar(); } } Sunday, March 16, 14
- 34. Program to Interfaces, Not Implementations • Eliminates being locked-in to a specific implementation • An interface declares generic behavior • Concrete class(es) implement methods defined in an interface 34 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 35. 35 // Dog class public class Dog { public void bark() { System.out.println(“woof”); } // Cat class public class Cat { public void meow() { System.out.println(“meow”); } } Sunday, March 16, 14
- 36. 36 // Animals class - main application public class Animals { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog dog = new Dog(); dog.bark(); Cat cat = new Cat(); cat.meow(); } } // output woof meow Sunday, March 16, 14
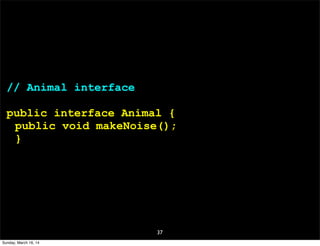
- 37. 37 // Animal interface public interface Animal { public void makeNoise(); } Sunday, March 16, 14
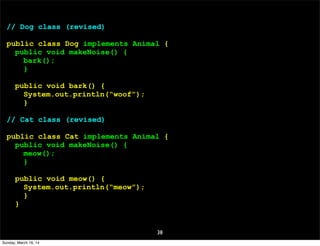
- 38. 38 // Dog class (revised) public class Dog implements Animal { public void makeNoise() { bark(); } public void bark() { System.out.println(“woof”); } // Cat class (revised) public class Cat implements Animal { public void makeNoise() { meow(); } public void meow() { System.out.println(“meow”); } } Sunday, March 16, 14
- 39. 39 // Animals class - main application (revised) public class Animals { public static void main(String[] args) { Animal dog = new Dog(); dog.makeNoise(); Animal cat = new Cat(); cat.makeNoise(); } } // output woof meow Sunday, March 16, 14
- 40. Favor Composition Over Inheritance • “HAS-A” can be better than “IS-A” • Eliminates excessive use of subclassing • An object’s behavior can be modified through composition as opposed through inheritance • Allows change in object behavior at run- time 40 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 41. Classes Should Be Open for Extension... • ...But Closed for Modification • “Come in,We’re Open” • extend the class to add new behavior • “Sorry,We’re Closed” • the code must remain closed to modification 41 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 42. A Simple Hierarchy... 42 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 43. ...That Quickly Becomes Complex! 43 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 44. Refactored Design 44 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 45. Live Demo! 45 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 46. Strive for Loosely Coupled Designs... • ...Between Objects That Interact • Allows you to build flexible OO systems that can handle change • interdependency is minimized • Changes to one object won’t affect another object • Objects can be used independently 46 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 47. Live Demo! 47 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 48. A Class Should Have... • ...Only One Reason to Change • Classes can inadvertently assume too many responsibilities • interdependency is minimized • cross-cutting concerns • Assign a responsibility to one class, and only one class 48 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 49. Local C++ User Groups • ACGNJ C++ Users Group • facilitated by Bruce Arnold • acgnj.barnold.us 49 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 50. Local Java User Groups (1) • ACGNJ Java Users Group • facilitated by Mike Redlich • javasig.org • Princeton Java Users Group • facilitated byYakov Fain • meetup.com/NJFlex 50 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 51. Local Java User Groups (2) • NewYork Java SIG • facilitated by Frank Greco • javasig.com • Capital District Java Developers Network • facilitated by Dan Patsey • cdjdn.com 51 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 52. Further Reading 52 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 54. Upcoming Events (1) • Trenton Computer Festival • March 14-15, 2014 • tcf-nj.org • Emerging Technologies for the Enterprise • April 22-23, 2014 • phillyemergingtech.com 54 Sunday, March 16, 14
- 55. 55 Upcoming Events (2) Sunday, March 16, 14




































![36
// Animals class - main application
public class Animals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.bark();
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.meow();
}
}
// output
woof
meow
Sunday, March 16, 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobject-orientedprogrammingdesignprinciples-140316163617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Design-Principles-TCF-2014-36-320.jpg)
![39
// Animals class - main application (revised)
public class Animals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.makeNoise();
Animal cat = new Cat();
cat.makeNoise();
}
}
// output
woof
meow
Sunday, March 16, 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobject-orientedprogrammingdesignprinciples-140316163617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Design-Principles-TCF-2014-39-320.jpg)
















