Java - File Input Output Concepts
- 1. Java - File Input / Output Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 2. Topics Input/output File Directories The Stream Classes IO Stream Types Binary Versus Text Files Byte Streams - InputStreams Byte Streams - OutputStreams Character Streams - Reader Byte Streams - Writer 2Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 3. Input/output Java programs perform I/O through streams. A stream is an abstraction that either produces or consumes information. A stream is a sequence of bytes (or data or objects) that flow from a source to a destination. A stream is linked to a physical device by the Java I/O system. Stream: an object that either, sends data to its destination (screen, file, etc.) or accepts data from a source (keyboard, file, etc.) acts as a transmission/exchange buffer between source and destination Java implements streams (IO operations) within class hierarchies defined in the java.io package. https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/io/package-summary.html 3Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 4. File We begin our discussion with one of the most distinctive I/O classes: File. Although most of the classes defined by java.io operate on streams, the File class does not. It deals directly with files and the file system. That is, the File class does not specify how information is retrieved from or stored in files; it describes the properties of a file itself. A File object is used to obtain or manipulate the information associated with a disk file, such as the permissions, time, date, and directory path, and to navigate subdirectory hierarchies. Files are a primary source and destination for data within many programs. 4Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 5. File A directory in Java is treated simply as a File with one additional property — a list of filenames that can be examined by the list( ) method. The following constructors can be used to create File objects: File(String directoryPath) File(String directoryPath, String filename) where, directoryPath is the path name of the file, filename is the name of the file or subdirectory, File defines many methods that obtain the standard properties of a File object. For example, getName( ) returns the name of the file, getParent( ) returns the name of the parent directory, and exists( ) returns true if the file exists, false if it does not. 5Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 6. File Properties 6Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 7. Directories A directory is a File that contains a list of other files and directories. When you create a File object and it is a directory, the isDirectory( ) method will return true. In this case, you can call list( ) on that object to extract the list of other files and directories inside. 7Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 8. Directory Properties 8Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
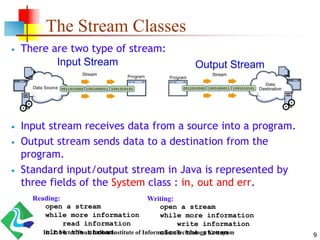
- 9. The Stream Classes There are two type of stream: Input stream receives data from a source into a program. Output stream sends data to a destination from the program. Standard input/output stream in Java is represented by three fields of the System class : in, out and err. Input Stream Output Stream Reading: open a stream while more information read information close the stream Writing: open a stream while more information write information close the stream 9Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 10. IO Stream Types Two main categories of streams in Java : Byte Streams – These provide a way to handle byte oriented input/output operations. InputStream and OutputStream classes are at the top of their hierarchy. Each of these abstract classes has several concrete subclasses that handle the differences between various devices, such as disk files, network connections, and even memory buffers. Two of the most important are read( ) and write( ), which, respectively, read and write bytes of data. 10Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 11. IO Stream Types Two main categories of streams in Java : Character Streams – These provide a way to handle character oriented input/output operations. At the top are two abstract classes, Reader and Writer They make use of Unicode and can be internationalized. Two of the most important methods are read( ) and write( ), which read and write characters of data, respectively. These methods are overridden by derived stream classes 11Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 12. Byte Stream Classes 12Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
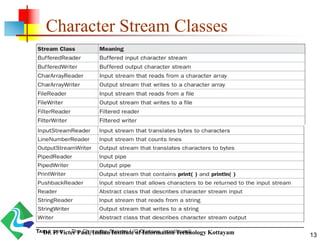
- 13. Character Stream Classes 13Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 14. Binary Versus Text Files Binary files: the bits represent other types of encoded information, such as executable instructions or numeric data these files are easily read by the computer but not humans they are not "printable" files actually, you can print them, but they will be unintelligible Text files: the bits represent printable characters one byte per character for ASCII, the most common code for example, Java source files are text files so is any file created with a "text editor" 14Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 15. Byte Streams - InputStreams InputStream is an abstract class that defines Java’s model of streaming byte input. Most of the methods in this class will throw an IOException on error conditions. Reading bytes: Used to read 8-bit bytes Classes of hierarchy of input stream classes Input Functions Reading bytes Closing streams Marking positions in stream Skipping in a stream Finding the number of bytes in a stream 15Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 16. Methods Defined by InputStream 16Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 17. InputStream – Subclass hierarchy InputStream AudioInputStream FileInputStream ObjectInputStream SequenceInputStream ByteArrayInputStream PipedInputStream FilterInputStream A FileInputStream obtains input bytes from a file in a file system. An AudioInputStream is an input stream with a specified audio format and length. A ByteArrayInputStream contains an internal buffer that contains bytes that may be read from the stream. A SequenceInputStream represents the logical concatenation of other input streams. 17Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 18. Byte Streams - OutputStreams OutputStream is an abstract class that defines streaming byte output. Most of the methods in this class return void and throw an IOException in the case of errors. Writing bytes: Classes of hierarchy of Outputstream classes Output Functions Writing bytes Closing streams Flushing streams 18Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 19. Methods Defined by OutputStream 19Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 20. OutputStream – Subclass hierarchy FileOtputStream is an output stream for writing data to a File. A ByteArrayInputStream is a output stream in which the data is written into a byte array. OutputStream FileOutputStream ObjectOutputStream ByteArrayOutputStream PipeOutputStream FilterOutputStream 20Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 21. FileInputStream 21Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 22. FileOutputStream 22Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 23. Character Streams - Reader Reader is an abstract class that defines Java’s model of streaming character input. All of the methods in this class will throw an IOException on error conditions. Reading character: Used to read characters from the files Classes of hierarchy of reader class Functions are similar to InputStream 23Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 24. Methods Defined by Reader 24Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
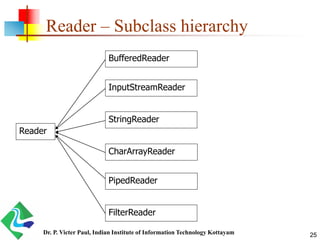
- 25. Reader – Subclass hierarchy Reader BufferedReader InputStreamReader StringReader CharArrayReader PipedReader FilterReader 25Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 26. Byte Streams - Writer Writer is an abstract class that defines streaming character output. All of the methods in this class throw an IOException in the case of errors. Writing characters: Classes of hierarchy of writer class Output Functions Writing bytes Closing streams Flushing streams 26Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 27. Methods Defined by Writer 27Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 28. Writer – Subclass hierarchy Writer BufferedWriter OutputStreamWriter StringWriter CharArrayWriter PipedWriter FilterWriter PrintWriter 28Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 29. FileReader 29Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 30. FileReader 30Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 31. 31 The End… Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam