Java - Inheritance Concepts
- 1. Inheritance Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 2. 2 Inheritance Inheritance can be defined as the process where one class acquires the properties (methods and fields) of another. The class which inherits the properties of other is known as subclass (derived class, child class) and the class whose properties are inherited is known as superclass (base class, parent class). Therefore, a subclass is a specialized version of a superclass. It inherits all of the instance variables and methods defined by the superclass and adds its own, unique elements. Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 3. 3 Important terminologies Super Class: The class whose features are inherited. Sub Class: The class that inherits the other class. The subclass can add its own fields and methods in addition to the superclass fields and methods. Reusability: Inheritance supports the concept of “reusability”, i.e. when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing class. To inherit from a class, use the extends keyword. Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
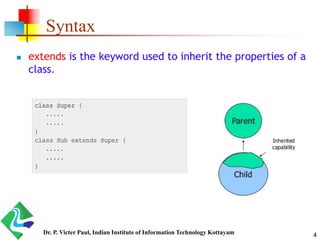
- 4. 4 Syntax extends is the keyword used to inherit the properties of a class. Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 5. 5 Syntax Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 6. 6 Inheritance Demo Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 7. 7 Inheritance Demo Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 8. Try it!! Although a subclass includes all of the members of its superclass, it cannot access those members of the superclass that have been declared as private. The final Keyword If you don't want other classes to inherit from a class, use the final keyword. 8Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 9. Using super to Call Superclass A subclass can call a constructor defined by its superclass by use of the following form of super: arg-list specifies any arguments needed by the constructor in the superclass. super() must always be the first statement executed inside a subclass’ constructor. 9Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 10. Using super to Call Superclass 10Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 11. Using super to access members A subclass can access the data members and methods of superclass by use of the following form of super: member can be either a method or an instance variable. This second form of super is most applicable to situations in which member names of a subclass hide (same name) members by the same name in the superclass 11Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 12. Using super to access members 12Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
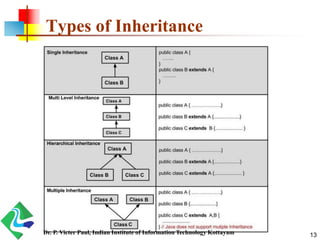
- 13. Types of Inheritance 13Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 14. Single Inheritance When a class inherits another class, it is known as a single inheritance. 14Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 15. Multi level Inheritance When there is a chain of inheritance, it is known as multilevel inheritance. 15Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 16. Hierarchical Inheritance When two or more classes inherits a single class, it is hierarchical inheritance 16Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 17. Multiple Inheritance To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java. Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class. In java, we can achieve multiple inheritance only through Interfaces. 17Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 18. Method Overriding In a class hierarchy, when a method in a subclass has the same name and type signature as a method in its superclass, then the method in the subclass is said to override the method in the superclass. When an overridden method is called from within a subclass, it will always refer to the version of that method defined by the subclass. The version of the method defined by the superclass will be hidden. 18Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 19. Method Overriding How to call the show() method of Class A???? Two possible ways!!!!! 19Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 20. Final Keyword The keyword final has three uses. First, it can be used to create the equivalent of a named constant. The other two uses of final apply to inheritance. Using final to Prevent Overriding Using final to Prevent Inheritance 20Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 21. Final Keyword 21Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 22. Important facts about inheritance Default superclass: Except Object class, which has no superclass, every class has one and only one direct superclass (single inheritance). In the absence of any other explicit superclass, every class is implicitly a subclass of Object class. Superclass can only be one: A superclass can have any number of subclasses. But a subclass can have only one superclass. This is because Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes. Inheriting Constructors: A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass. Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass. Private member inheritance: A subclass does not inherit the private members of its parent class. However, if the superclass has public or protected methods for accessing its private fields, these can also be used by the subclass. 22Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 23. The instanceof Keyword The java instanceof operator is used to test whether the object is an instance of the specified type (class or subclass or interface). The instanceof in java is also known as type comparison operator because it compares the instance with type. It returns either true or false. 23Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 24. The Object Class There is one special class, Object, defined by Java. All other classes are subclasses of Object. That is, Object is a superclass of all other classes. This means that a reference variable of type Object can refer to an object of any other class. Check what are the methods associated with Object class!!!! 24Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam
- 25. The End… 25Dr. P. Victer Paul, Indian Institute of Information Technology Kottayam