Java Programming and J2ME: The Basics
- 1. Mobile Programming with J2ME By Oluwatosin Adesanya
- 2. Lesson 01: Basic Java Programming
- 3. Java is ... • A Pure OOP Language • A Hybrid Programming Language • First Compiled and Interpreted • Runs on a JVM (Java Virtual Machine) Byte Code Source Object Code Code
- 4. Getting Started • JDK (Java Development Kit) • Editor (Notepad) OR ... • Integrated Development Environment (Netbeans, Eclipse, JCreator etc.)
- 5. Setting Up Java • Install the JDK • The JDK Sits in C:Program FilesJavajdk1.6.0 • Set the PATH Environmental Variable (How?)
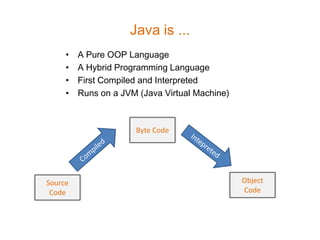
- 6. Setting the PATH Environmental Variable Open your Systems Property: choose Advanced System Settings, Click the Environmental Variable Button on the Dialog that shows Up
- 7. Setting the PATH Environmental Variable Scroll and Select Path , Click Edit Button
- 8. Setting the PATH Environmental Variable Append the current path with the path to the Java bin folder
- 9. Running Java • Save your Java source code as a .java file • Use the javac Command to compile your source codes (.java files) e.g javac Result.java • A .class file is generated called a bytecode • Use java Command to run the .class file e.g java Result • Do not add .class when compiling Source Object javac Byte Code java Code Code
- 10. The Structure of a Java Program • Java Programs are made up of classes • Classes are made up of methods • Java existing (ready-made) classes are found in the Java Class Libraries (Also Called Java APIs) • Execution of Java programs begin at the main method
- 11. A Simple Java Program public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); } }
- 12. Classes and Objects • A Class is like a factory from which Objects are churned Out. Example Class Car could produce objects Volkswagen bettles, Toyota Camri, Peugeout 306 An Object is a model of the Real World and has States (Or Properties) and Behaviours (Or Actions) Example Object Car States are Color, Speed, Size, Plate Licence No, Cost Behaviours are Start, Stop, Accelerate, Fuel, Open Door, etc.
- 13. Creating a Class Use the class Keyword Example public class HelloWorld { . . . } Do NOT Forget! Name your java file ClassName.java
- 14. Adding States (Properties) • States in Java are simply variables (Otherwise called fields) Example public class PaySlip { int numdone; String name; } Observe?! Every Line of Java code ends with a semicolon (;) int,float, double, boolean, char … are Java Primitive Types
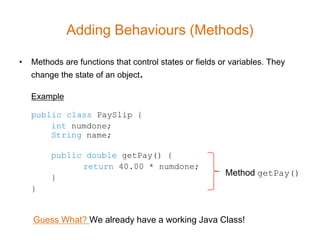
- 15. Adding Behaviours (Methods) • Methods are functions that control states or fields or variables. They change the state of an object. Example public class PaySlip { int numdone; String name; public double getPay() { return 40.00 * numdone; } Method getPay() } Guess What? We already have a working Java Class!
- 16. Using Our Class PaySlip We implement another tester class which contains the main method. public class TestPaySlip { public static void main(String[] args){ PaySlip opay=new PaySlip(); System.out.println("n"+opay.getPay()); } }
- 17. Constructors • Initializes the Object after memory allocation • Takes the same name as the Class • May accept parameters OR... may not • Every Class has a default constructor that accepts no parameter • Has No Return Type • Can be Overloaded (there can be multiple Constructors)
- 18. Constructors public class PaySlip { int numdone; String name; public PaySlip(int numdone, String name) { this.numdone=numdone; this.name=name; } public PaySlip(){ name=“Nobody”; numdone=0; } public double getPay() { return 40.00 * numdone; } }
- 20. Lesson 02: Java 2 Micro Edition(J2ME)
- 21. J2ME is ... • Java for small devices • Divided into Configurations, Profiles and Optional APIs Configurations, Profiles and Optional APIs combined together make up a stack Configurations: Specifies a JVM. We have CDC and CLDC CLDC (Connected Limited Device Configuration) is designed for devices with limited memory, displays, battery power and inputs. Profiles: Layered on top of CLDC and adds APIs for specific devices. We have MIDP, PDAP and Personal Profiles MIDP (Mobile Information Device Profile) has characteristics that makes most low end phones and PDAs fit in. J2ME is covered by MIDPs
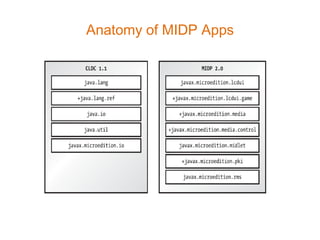
- 22. Anatomy of MIDP Apps
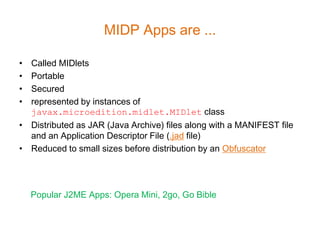
- 23. MIDP Apps are ... • Called MIDlets • Portable • Secured • represented by instances of javax.microedition.midlet.MIDlet class • Distributed as JAR (Java Archive) files along with a MANIFEST file and an Application Descriptor File (.jad file) • Reduced to small sizes before distribution by an Obfuscator Popular J2ME Apps: Opera Mini, 2go, Go Bible
- 24. The MIDlet Life Cycle
- 25. Shall We Create a MIDlet? package com.thinkit2ru; import javax.microedition.midlet.*; public class Metric extends MIDlet { public void startApp() { } public void pauseApp() { } public void destroyApp(boolean unconditional) { } }
- 26. Remember the Constructor? package com.thinkit2ru; import javax.microedition.midlet.*; public class Metric extends MIDlet { public Metric() { The Contructor: } Build Components Here public void startApp() { } public void pauseApp() { } public void destroyApp(boolean unconditional) { } }
- 27. You need to Know... • Primitive data types • String Manipulation • Control Statements • Arrays and other data structures • GUI Design • Database Connectivity • Multithreading • Ethics and Conventions








![A Simple Java Program
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j2metutorial-130125020927-phpapp02/85/Java-Programming-and-J2ME-The-Basics-11-320.jpg)



![Using Our Class PaySlip
We implement another tester class which
contains the main method.
public class TestPaySlip {
public static void main(String[] args){
PaySlip opay=new PaySlip();
System.out.println("n"+opay.getPay());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j2metutorial-130125020927-phpapp02/85/Java-Programming-and-J2ME-The-Basics-16-320.jpg)