Leachate Management
- 1. Prof. M.R.Ezhilkumar Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology Coimbatore ezhilkumar@skcet.ac.in I only feel angry when I see waste. When I see people throwing away things we could use. – Mother Teresa 1 17CE413 SOLID AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT 3.5 – Leachate Management
- 2. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 2 Learning Outcomes ☼ Leachate production ☼ Leachate Collection ☼ Leachate Treatment ☼ Leachate Management 3.5 – Leachate Management
- 3. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 3 Video Session
- 4. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 4 Leachate Infiltrative water percolates through waste materials, results in the leaching of organic and inorganic compounds (McBean et al. 1995). A complex organic waste that changes with time Problematic components – Degradable & nondegradable organics – Hazardous organics and inorganics – Ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite – Suspended solids – Color and odor – Pathogens
- 5. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 5 Leachate Leachate is the liquid (or wastewater) that forms when water (rainfall, groundwater) travels through solid waste Leachate can migrate into underlying groundwater, resulting in contamination Leachate can contain many different chemicals, depending on what is in the solid waste
- 6. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 6 Leachate
- 7. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 7 Leachate How is Leachate Produced? Waste Decomposition • Phase I – Aerobic • Phase II – Anaerobic – Facultative • Phase III – Methanogenic
- 8. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 8 Leachate Leaching Mechanisms Leaching of inherently soluble materials Leaching of soluble biodegradation products Leaching of soluble products of chemical reactions Washout of fines and colloids Leachate generation continues for typically 30-40 years following site closure
- 9. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 9 Leachate Importance of Leachate Quality and Quantity Determination Design leachate collection systems Design leachate treatment facilities Determine acceptability of offsite treatment Estimate offsite migration potential
- 10. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 10 Leachate Leachate Management Principles Chemical composition of leachate varies considerably depending on:- – Waste composition – Site characteristics – Climatic conditions – Age of landfill Leachate management strategies must be:- – Practical – Cost effective – Flexible – Developed for long term environmental management
- 11. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 11 Leachate Leachate Management Technologies There is a wide range of leachate management technologies adopted by Landfill Managers. Technology selection often depends on a number of critical factors including: – Composition of leachate – Type of collection method – Volume of leachate generated – Available space on site – Access to sewer – Availability of technologies
- 12. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 12 Leachate Planning Treatment and Disposal Estimate leachate flow, Q – WBM/HELP – Variations with site age Estimate leachate contaminant conc., C – Type – Variations with age Identify treatment and disposal options with discharge standards and cost Select treatment and disposal system – Introduce uncertainty – Maintain flexibility
- 13. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 13 Leachate Leachate Production Characteristics
- 14. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 14 Leachate What Characterizes Leachate? Phase I – Brief – CO2 – H2 Phase II – Years – High BOD • >10,000mg/L – High BOD:COD • >0.7 – Low pH • 5-6 Phase II – Smells – High Ammonia • 500-1000 mg/L – High Levels • Fe, Mg, Zn, Ca, Mn Phase III Decades (never) High fatty acids No O2 CH4 CO2 Stabilized Low BOD Low BOD:COD Phase III High Ammonia/Nitrogen High Levels Fe, Na, K, Cl2, SO4
- 15. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 15 Leachate Factors Affecting Leachate Quality and Quantity Particle size Compaction Waste composition Site Hydrology Cover Design Conditions within Landfill • Chemical & Biological Activities • MC %, Temperature, pH, Degree of Stabilization Waste Age Landfill design/operation Sampling procedures Interaction of leachate with environment
- 16. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 16 Leachate What are Trends in Leachate Contamination?
- 17. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 17 Leachate Landfill Leachate
- 18. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 18 Leachate pH Influence chemical and biological processes of precipitation, redox, sorption, methanogenesis Controlled by volatile acids during acid phase After methanogenesis begins, controlled by carbonates and ammonia Major factor in controlling metal solubility
- 19. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 19 Leachate Heavy Metals May act as inhibitors of biological stabilization process Water quality concerns No discernable chronological pattern Leachate concentration controlled by sulfide, carbonate, chloride, and phosphate
- 20. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 20 Leachate Nitrogen/Phosphorus Indication of nutrient availability Phosphorus may be limiting nutrient Ammonia important buffer Nitrogen present for long periods of time
- 21. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 21 Leachate How do you Remove Leachate from the Landfill? Drain as much as you can by gravity (liner system and pipes) Pump from low points – Penetration through the liner – Pumps inside landfill
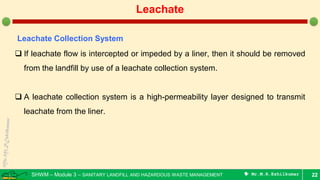
- 22. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 22 Leachate Leachate Collection System If leachate flow is intercepted or impeded by a liner, then it should be removed from the landfill by use of a leachate collection system. A leachate collection system is a high-permeability layer designed to transmit leachate from the liner.
- 23. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 23 Leachate Leachate Collection System with Graded Terraces
- 24. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 24 Leachate How is Leachate Removed
- 25. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 25 Leachate Leachate is then sent to Treatment and/or Storage Facility
- 26. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 26 Leachate Leachate Storage Underground storage tanks Lagoons Above ground tanks Three day’s storage at peak annual flow
- 27. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 27 Leachate How do you Predict Leachate Generation? You must estimate how much leachate is generated to design your landfill. HELP -- Hydrologic Evaluation of Landfill Performance A Water Balance Model
- 28. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 28 Leachate Notes about HELP Model Must assume an area and a depth (therefore not good for an open, operating landfill) Many ways to manipulate Hydraulic conductivity of waste to high
- 29. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 29 Leachate Porous cup suction Lysimeter for the collection of liquid samples from the landfill
- 30. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 30 Leachate Leachate Treatment Systems? Options Full On-Site Treatment Partial On-Site Treatment Transport Off-Site Considerations o Recirculation o Proximity of Sewer o Haul Distance o Pump System Costs o WWTP Capacity o Leachate Strength Considerations o Local Sewer Use Laws o Sewer Surcharges o Surface Water Discharge Standards (On-Site)
- 31. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 31 Leachate What are Common Leachate Treatment Types? Anaerobic or Aerobic Biological Treatment Physical & Chemical Treatment Leachate Recirculation & Land Application
- 32. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 32 Leachate Anaerobic or Aerobic Biological Treatment Biological Treatment Changes the form of Organic Constituents Removes BOD5, SS,NH3-N, Organic-N & Metals Generates large quantities of biomass (sludge) Anaerobic Treatment Two-Stage Reactor Fixed Film Filters Aerobic Treatment Lagoons Activated Sludge RBC’s Trickling Filters
- 33. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 33 Leachate Anaerobic or Aerobic Biological Treatment Biological Treatment Essential if BOD > 50 mg/L Expect • BOD removal • SS removal with sedimentation • NH3-N and Org-N removal by biouptake and nitrification • Metal removal by biosorption and precipitation at oxides and carbonates • Priority organics removal
- 34. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 34 Leachate Leachate Management Technologies
- 35. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 35 Leachate Physical & Chemical Treatment More appropriate treatment as a landfill stabilizes Polishes biologically treated leachate Types of Treatment Granular Filtration Carbon Adsorption Chemical Precipitation Ultrafiltration Reverse Osmosis Breakpoint Chlorination Air Stripping Ion Exchange
- 36. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 36 Leachate Reed Bed Removal of heavy metals, BOD, TSS, Nitrogen, & Phosphorus
- 37. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 37 Leachate Constructed Wetland Uses Polishing treatment Complete treatment Advantages Relatively inexpensive to build/operate Associated with ‘green’ technologies Wetlands credits Disadvantages Large land requirement Cold weather Mediocre results especially for complete treatment systems
- 38. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 38 Leachate Proposed Leachate Treatment
- 39. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 39 Leachate Suitability Of Evaporation Cost Of Operation Extremely Cost Effective Relatively High Initial Capital Costs Minimal Operating Costs Effect Of Evaporation Leachate Volume Reduction Extremely Concentrated Solution Minimal Contamination Level Reduction Risks Pond Overflow Leaks - Monitoring Bores Drowning - Perimeter Fencing
- 40. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 40 Leachate Suitability Of Evaporation Local Weather Conditions Evaporation Substantially Higher Than Precipitation Local Weather Data Theoretical Evaporation Greater Than Actual Evaporation Leachate Composition Leachate Composition Affects Evaporation Rate Salinity and Concentration Reduce Evaporation Rate Dark Colour Increases Evaporation Rate
- 41. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 41 Leachate Suitability Of Evaporation Site Constraints Large Surface Area Required Possible Odour Issues Hence Buffer Zones Required Wind Direction And Intensity Regulatory Approval Possible Regulatory Approval Required Location and Design Constraints Operational and Management Constraints
- 42. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 42 Leachate Leachate treatment-issues High strength and magnitude of pollution potential Variation from landfill to landfill Seasonal and temporal variations in quantity and quality Processes designed to treat the leachates from an young landfill should be modified in the future to treat old leachate/ to achieve changes in effluent standards
- 43. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 43 Leachate Leachate Recirculation & Land Application Leachate is collected & returned to the top of landfill Accelerates the stabilization of organic materials present in the MSW Spray Irrigation or Well Injection Evapotranspiration
- 44. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 44 Leachate Landfill as a Bioreactor Measure of Success Faster landfill stabilization Increased air space Reduced leachate management costs Reduced gases and odors Reduced long-term care costs Possibly, mining to regenerate cover material - a perpetual landfill?
- 45. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 45 Leachate Leachate Recirculation Demerits:- Ponding/localized accumulation of leachate Severe localized subsidence/side slope stability problems Other management requirement due to excess leachate production Selective attenuation of contaminants recirculation, thus further treatment required Mass/fluid transfer limitation
- 46. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 46 Leachate Leachate Recirculation Methods of Recirculation Spray irrigation Working face application Gravity well/trench Injection well/trench Infiltration ponds
- 47. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 47 Leachate It is important to consider Leachate characteristics Its hazardous nature Discharge alternatives Regulatory limits Operational needs Costs Conduct of treatability studies
- 48. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 48 Assessment Time Review Question Recommend a suitable landfill method for Coimbatore region based on the composition of waste generated in the city.
- 49. SHWM – Module 3 – SANITARY LANDFILL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT Mr.M.R.Ezhilkumar 49