Learn C# Programming - Variables & Constants
- 1. Learn C# Programming Variables and Constants Eng Teong Cheah Microsoft MVP in Visual Studio & Development Technologies
- 4. C# - Variables A variable is nothing but a name given to a storage area that our programs can manipulate. Each variable in C# has a specific type, which determines the size and layout of the variable’s memory the range of values that can be stored within that memory and the set of operations that can be applied to the variable.
- 5. C# - Variables The basic value types provided in C# can be categorized as:
- 6. C# - Variables C# also allows defining other value types of variable such as enum and reference types of variables such as class, which we will cover in subsequent chapters.
- 7. C# - Variables Defining Variables Syntax for variable definition in C# is: Here, data_type must be a valid C# data type including char, int, float, double, or any user-defined data type, and variable_list may consist of one or more identifier names separated by commas. <data_type> <variable_list>;
- 8. C# - Variables Defining Variables Some valid variable definitions are shown here: int i, j, k; char c, ch; float f, salary; double d; You can initialize a variable at the time of definition as: int i = 100;
- 9. C# - Variables Initializing Variables Variables are initialized (assigned a value) with an equal sign followed by a constant expression. The general form of initialization is: Variables can be initialized in their declaration. The initializer consists of an equal sign followed by a constant expression as: variable_name = value; <data_type> <variable_name> = value;
- 10. C# - Variables Initializing Variables Some examples are: int d = 3, f = 5; /* initializing d and f. */ byte z = 22; /* initializes z. */ double pi = 3.14159; /*declares an approximation of pi. */ char x = ‘x’;
- 11. C# - Variables Initializing Variables It is a good programming practice to initialize variables properly, otherwise sometimes program may produce unexpected result.
- 12. Demo
- 13. C# - Variables Accepting Values from User The Console class in the System namespace provides function ReadLine() for accepting input from the user and store it into a variable. For example, int num; num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
- 14. C# - Variables Accepting Values from User The function Convert.ToInt32() converts the data entered by the user to int data type, because Console.ReadLine() accepts the data in string format.
- 15. C# - Variables Lvalue and Rvalue Expression in C#: The are two kinds of expressions in C#: - lvalue: An expression that is an lvalue may appear as either the left-hand or right-hand side of an assignment. - rvalue: AN expression that is an rvalue may appear on the right-hand but not left-hand side of an assignment.
- 16. C# - Variables Lvalue and Rvalue Expression in C#: Variables are lvalues and hence they may appear on the left- hand side of an assignment. Numeric literals are rvalues and hence they may not be assigned and cannot appear on the left-hand side. Following is a valid C# statement: int g =20;
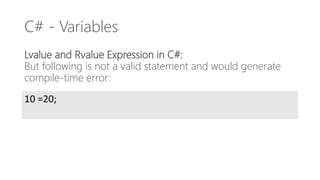
- 17. C# - Variables Lvalue and Rvalue Expression in C#: But following is not a valid statement and would generate compile-time error: 10 =20;
- 18. C# - Constants and Literals
- 19. C# - Constants and Literals The constants refer to fixed values that the program may not alter during its execution. These fixed values also called literals. Constants can be of any of the basic data types like an integer constant, a floating constant, a character constant, or a string literal. There are also enumeration constant as well.
- 20. C# - Constants and Literals The constants are treated just like regular variables except that their values cannot be modified after their definition.
- 21. C# - Constants and Literals Integer Literals An integer literal can be a decimal, or hexadecimal constant. A prefix specifies the base or radix: 0x or 0X for hexadecimal, and there is no prefix id for decimal. An integer literal can also have a suffix that is a combination of U and L, for unsigned and long, respectively. The suffix can be uppercase or lowercase and can be in any order.
- 22. C# - Constants and Literals Integer Literals Here are some examples of integer literals: 212 /*Legal*/ 215u /*Legal*/ 0xFeeL /*Legal*/
- 23. C# - Constants and Literals Integer Literals Following are other examples of various types of Integer literals: 85 /*decimal*/ 0x4b /*hexadecimal*/ 30 /*int*/ 30u /*unsigned int*/ 301 /*long*/ 30u1 /*unsigned long*/
- 24. C# - Constants and Literals Integer Literals Following are other examples of various types of Integer literals: 85 /*decimal*/ 0x4b /*hexadecimal*/ 30 /*int*/ 30u /*unsigned int*/ 301 /*long*/ 30u1 /*unsigned long*/
- 25. C# - Constants and Literals Floating-point Literals A floating-point literal has an integer part, a decimal point, a fractional part, and an exponent part. You can represent floating point literals either in decimal form or exponential form.
- 26. C# - Constants and Literals Floating-point Literals Here are some examples of floating-point literals: 3.14159 /* Legal */ 314159E-5F /* Legal */ 510E /* Illegal: incomplete exponent */ 210f /* Illegal: no decimal or exponent */ .e55 /* Illegal: missing integer or fraction */
- 27. C# - Constants and Literals Floating-point Literals While representing in decimal form, you must include the decimal point, the exponent, or both; and representing using exponential form you must include the integer part, the fractional part, or both. The signed exponent is introduced by e or E.
- 28. C# - Constants and Literals Character Constants Character literals are enclosed in single quotes. For example, 'x' and can be stored in a simple variable of char type. A character literal can be a plain character (such as 'x'), an escape sequence (such as 't'), or a universal character (such as 'u02C0').
- 29. C# - Constants and Literals Character Constants There are certain characters in C# when they are preceded by a backslash. They have special meaning and they are used to represent like newline (n) or tab (t). Here, is a list of some of such escape sequence codes:
- 30. C# - Constants and Literals Character Constants
- 31. Demo
- 32. C# - Constants and Literals String Literals String literals or constants are enclosed in double quotes "" or with @"". A string contains characters that are similar to character literals: plain characters, escape sequences, and universal characters. You can break a long line into multiple lines using string literals and separating the parts using whitespaces.
- 33. C# - Constants and Literals String Literals Here are some examples of string literals. All the three forms are identical strings. "hello, dear" "hello, dear" "hello, " "d" "ear" @"hello dear"
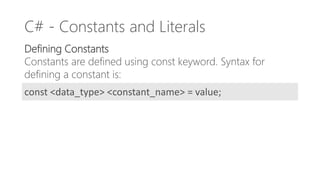
- 34. C# - Constants and Literals Defining Constants Constants are defined using const keyword. Syntax for defining a constant is: const <data_type> <constant_name> = value;
- 35. Demo
- 37. Thank You