Lecture 09 uninformed problem solving
- 1. Problem Solving (Uninformed Search) Lecture-09 Hema Kashyap 18 August 2015 1
- 2. Water Jug Problem Definition: • Some jugs are given which should have non-calibrated properties. At least any one of the jugs should have filled with water. Then the process through which we can divide the whole water into different jugs according to the question can be called as water jug problem. Procedure: • Suppose that you are given 3 jugs A,B,C with capacities 8,5 and 3 liters respectively but are not calibrated (i.e. no measuring mark will be there). Jug A is filled with 8 liters of water. By a series of pouring back and forth among the 3 jugs, divide the 8 liters into 2 equal parts i.e. 4 liters in jug A and 4 liters in jug B. 18 August 2015 2
- 3. Production rules for Water Jug Problem The production rules are formulated as follows: Step 1: In this step, the initial state will be (8, 0, 0) as the jug B and jug C will be empty. So the water of jug A can be poured like: (5, 0, 3) means 3 liters to jug C and 5 liters will remain in jug A. (3, 5, 0) means 5 liters to jug B and 3 liters will be in jug A. (0, 5, 3) means 5 liters to jug B and 3 liters to jug C and jug C and jug A will be empty. Step2: In this step, start with the first current state of step-1 i.e. (5, 0, 3). This state can only be implemented by pouring the 3 liters water of jug C into jug B. so the state will be (5, 3, 0). Next, come to the second current state of step-1 i.e. (3, 5, 0). This state can be implemented by only pouring the 5 liters water of jug B into jug C. So the remaining water in jug B will be 2 liters. So the state will be (3, 2, 3). Finally come to the third current state of step-1 i.e. (0, 5, 3). But from this state no more state can be implemented because after implementing we may get (5, 0, 3) or (3, 5, 0) or (8, 0, 0) which are repeated state. Hence these states are not considerably again for going towards goal. So the state will be like: 5, 0, 3 5, 3, 0 3, 5, 0 3, 2, 3 0, 5, 3 X 18 August 2015 3
- 4. Step 3: In this step, start with the first current state of step-2 i.e. (5, 3, 0) and proceed likewise the above steps. 5, 3, 0 2, 3, 3 3, 2, 3 6, 2, 0 Step 4: In this step, start with the first current state of step-3 i.e. (2, 3, 3) and proceed. 2, 3, 3 2, 5, 1 6, 2, 0 7, 0, 1 Step 5: 2, 5, 1 7, 0, 1 6, 0, 2 1, 5, 2 Step6: 7, 0, 1 7, 1, 0 1, 4, 3 1, 4, 3 Step7: 7, 1, 0 4, 1, 3 1, 4, 3 4, 4, 0 Goal So finally the state will be (4, 4, 0) that means jug A and jug B contains 4 liters of water each which is our goal state. One thing you have to very careful about the pouring of water from one jug to another that the capacity of jug must satisfy the condition to contain that much of water. 18 August 2015 4
- 5. Missionaries and Carnivals Problem Definition: In Missionaries and Carnivals Problem, initially there are some missionaries and some carnivals will be at a side of a river. They want to cross the river. But there is only one boat available to cross the river. The capacity of the boat is 2 and no one missionary or no Carnivals can cross the river together. So for solving the problem and to find out the solution on different states is called the Missionaries and Carnival Problem. Procedure: Let us take an example. Initially a boatman, Grass, Tiger and Goat is present at the left bank of the river and want to cross it. The only boat available is one capable of carrying 2 objects of portions at a time. The condition of safe crossing is that at no time the tiger present with goat, the goat present with the grass at the either side of the river. How they will cross the river? 18 August 2015 5
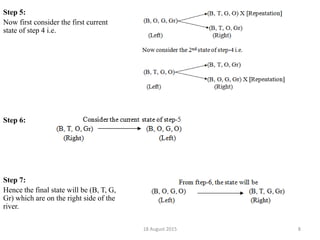
- 6. Production Rules Step 1: According to the question, this step will be (B, T, G, Gr) as all the Missionaries and the Carnivals are at one side of the bank of the river. Different states from this state can be implemented as `The states (B, T, O, O) and (B, O, O, Gr) will not be countable because at a time the Boatman and the Tiger or the Boatman and grass cannot go. (According to the question). 18 August 2015 6
- 7. Step 2: Now consider the current state of step-1 i.e. the state (B, O, G, O). The state is the right side of the river. So on the left side the state may be (B, T, O, Gr) i.e. B,O,G,O ------------ B, T, O, Gr (Right) ------------------(Left) Step 3: Now proceed according to the left and right sides of the river such that the condition of the problem must be satisfied. Step 4: First, consider the first current state on the right side of step 3 i.e. Now consider the second current state on the right side of step-3 i.e. 18 August 2015 7
- 8. Step 5: Now first consider the first current state of step 4 i.e. Step 6: Step 7: Hence the final state will be (B, T, G, Gr) which are on the right side of the river. 18 August 2015 8
- 9. 8 Queens Problem Definition: “We have 8 queens and an 8x8 Chess board having alternate black and white squares. The queens are placed on the chessboard. Any queen can attack any other queen placed on same row, or column or diagonal. We have to find the proper placement of queens on the Chess board in such a way that no queen attacks other queen”. Figure A possible board configuration of 8 queen problem Procedure: In figure , the possible board configuration for 8-queen problem has been shown. The board has alternative black and white positions on it. The different positions on the board hold the queens. The production rule for this game is you cannot put the same queens in a same row or same column or in same diagonal. After shifting a single queen from its position on the board, the user have to shift other queens according to the production rule. Starting from the first row on the board the queen of their corresponding row and column are to be moved from their original positions to another position. Finally the player has to be ensured that no rows or columns or diagonals of on the table is same. 18 August 2015 9