Lecture 13 insect nervous system
- 1. INSECT NERVOUS SYSTEM Prepared by Dr. S. Sumaiya
- 2. NERVOUS SYSTEM Basic components Cell body: Soma / Perikaryon Contains nucleus Protoplasmic extension - Axon Dendrites: Branching structure of neuron Receives stimuli from environment pass to axon Shorter than axon An insect nervous system is a network of specialized cells – Neurons
- 3. NERVOUS SYSTEM Axon (Neurite) The long extension of neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the body of the cell. Hair like ends of the axon at the end – Terminal arborisation Provided with schwanns or glial cells Glial cells produce myelin, located in myelin sheath
- 4. TYPES OF NEURONS A. Structural basis i. Monopolar : neuron with a single axon ii. Bipolar : neuron with a proximal axon and a long distal dendrite. iii. Multipolar : neuron with a proximal axon and many distal dendrites.
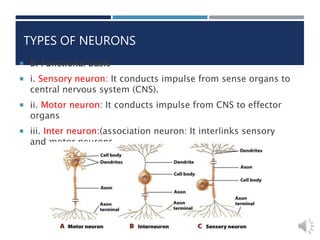
- 5. B. Functional basis i. Sensory neuron: It conducts impulse from sense organs to central nervous system (CNS). ii. Motor neuron: It conducts impulse from CNS to effector organs iii. Inter neuron:(association neuron: It interlinks sensory and motor neurons. TYPES OF NEURONS
- 6. MECHANISM OF IMPULSE CONDUCTION Impulses are conducted by the neurons by two means. A. Axonic conduction: Ionic composition varies between inside and outside of axon resulting in excitable conditions, which leads to impulse conduction as electrical response. B. Synaptic conduction: Neuro chemical transmitters are involved in the impulse conduction through the synaptic gap. Neuro transmitters and the type of reactions helping in the impulse conduction is as follows. Acetyl CO-A + Choline (choline acetylase ) Acetyl choline Acetyl choline + Water (Acetyl choline esterase ) Choline + Acetic acid
- 7. NERVOUS SYSTEM i. Central nervous system (CNS) ii. Visceral nervous system (VNS) iii. Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- 8. I. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM It contains double series of nerve centres (ganglia). These nerve centres (ganglia) are connected by longitudinal tracts of nerve fibres called connectives and transverse tracts of nerve fibres called commissures. Central nervous system is made up of the following. (i).Brain: Formed by the fusion of first three cephalic neuromeres. Protocerebrum : Large, innervate compound eyes and ocelli. Deutocerebrum : Found beneath protocerebrum, innervate antennae. Tritocerebrum : Bilobed, innervate labrum. Functions: i. Main sensory centre controls insect behaviour.
- 10. I. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM ii. Ventral nerve cord: Median chain of segmental ganglia beneath oesophagus iii. Sub esophageal ganglia: Formed by the last three cephalic neuromeres. Innervates mandible, maxillae and labium. iv. Thoracic ganglia: Three pairs found in the respective thoracic segments, largest ganglia, innervate legs and muscles. v. Abdominal ganglia: 8 pairs, number varies due to fusion of ganglia, innervate spiracles. vi. Thoracio abdominal ganglia: Thoracic and abdominal ganglia are fused to form single compound ganglia. Innervate genital organs and cerci.
- 11. II. VISCERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM It is also called stomatogastric nervous system This system is connected to brain and supplies nerves to fore-intestine, mid-intestine and heart Corpora allata, corpora cardiaca, reproductive organs and tracheal system are closely associated with this system
- 12. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM It is composed of fine network of sensory cells and axon, which lies just below the integument