Lecture 2 C++ | Variable Scope, Operators in c++
- 1. Lecture 2 : C++ VARIABLE SCOPE, OPERATORS IN C++
- 2. What is the Scope of A variable ? Scope refers to the visibility of variables. In other words, which parts of your program can see or use it. Normally, every variable has a global scope. Once defined, every part of your program can access a variable.
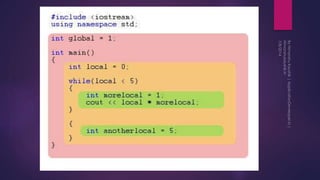
- 3. A scope is a region of the program and broadly speaking there are three places, where variables can be declared: Inside a function or a block which is called local variables, In the definition of function parameters which is called formal parameters. Outside of all functions which is called global variables.
- 4. Local Variables Variables that are declared inside a function or block are local variables. They can be used only by statements that are inside that function or block of code. Local variables are not known to functions outside their own. Following is the example using local variables
- 5. int main() { //local variable declaration int a , b; int c ; // actual initialization a = 10; b = 20; c = a + b; count <<c; return 0; }
- 6. Global Variable Global variables are defined outside of all the functions, usually on top of the program. The global variables will hold their value throughout the life-time of your program. A global variable can be accessed by any function. That is, a global variable is available for use throughout your entire program after its declaration.
- 7. #include <iostream> int g; int main() { //local variable declaration int a ,b; // actual initialization a = 10; b = 20; g = a + b; cout <<g; return 0; }
- 8. #include <iostream> Int g = 20; Int main() { //local variable declaration Int g = 10; Cout <<g; Return 0; }
- 10. Operators in C++ An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical manipulations. C++ is rich in built-in operators and provides the following types of operators: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Assignment Operators Misc Operators
- 11. Arithmetic Operators: Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 Operator Description Result + Adds two operands 30 - Subtracts second operand from first -10 * Multiplies both Operands 200 / Divides numerator by De-numerator 2 % Modulus Operator and reminder of after integer division 0 ++ Increment operator , increases integer value by one 11 -- Decrement Operator, Decreases Integer Value by One 9
- 12. main() { int a = 21; int b = 10; int c ; c = a + b; cout << "Line 1 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; c = a - b; cout << "Line 2 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; c = a * b; cout << "Line 3 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; c = a / b; cout << "Line 4 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; c = a % b; cout << "Line 5 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; c = a++; cout << "Line 6 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; c = a--; cout << "Line 7 - Value of c is :" << c << endl ; return 0; }
- 13. Relational Operators Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 Operator Description Example == Checks if the Value of two Operands are Equal or not , if yes then condition becomes True (A==B) is not true != Checks if the value of two operands are equal or not , if values are not equal then condition becomes true (A!=B) is true > Checks if the value of Left operand is greater than the value of right operand , if yes then condition becomes true, (A>B) is not true
- 14. Relational Operators Contd. Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 Operator Description Example < Checks if the Value of Left Operand is less than the value of right Operand , If yes then condition becomes True. (A<B) is true. >= Checks if the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right Operand, If yes then condition becomes True (A>=B) is not True <= Checks if the value of the left Operand is less than or equal to the value of Right Operand. If yes then condition becomes true. (A<=B) is true
- 15. #include <iostream> using namespace std; main() { int a = 21; int b = 10; int c ; if( a == b ) { cout << "Line 1 - a is equal to b" << endl ; } else { cout << "Line 1 - a is not equal to b" << endl ; } if ( a < b ) { cout << "Line 2 - a is less than b" << endl ; } else { cout << "Line 2 - a is not less than b" << endl ; } if ( a > b ) { cout << "Line 3 - a is greater than b" << endl ; } else { cout << "Line 3 - a is not greater than b" << endl ; } /* Let's change the values of a and b */ a = 5; b = 20; if ( a <= b ) { cout << "Line 4 - a is either less than or euqal to b" << endl ; } if ( b >= a ) { cout << "Line 5 - b is either greater than or equal to b" << endl ; } return 0; }
- 16. Logical Operators Operator Descripton Example && Called Logical And Operator. If Both the operands are non Zero , then Condition becomes true. (A && B) is false || Called Logical OR Operator. If any of the two Operands is non Zero, Then Condition becomes True. A||B is true ! Called Logical NOT Operator. Use to Reverse the logical State of its Operand. If condition is true, Then Logical NOT Operator will make False. !(A && B) is true
- 17. main() { int a = 5; int b = 20; int c ; if ( a && b ) { cout << "Line 1 - Condition is true"<< endl ; } if ( a || b ) { cout << "Line 2 - Condition is true"<< endl ; } /* Let's change the values of a and b */ a = 0; b = 10; if ( a && b ) { cout << "Line 3 - Condition is true"<< endl ; } else { cout << "Line 4 - Condition is not true"<< endl ; } if ( !(a && b) ) { cout << "Line 5 - Condition is true"<< endl ; } return 0; }
- 18. Bitwise Operators Bitwise operator works on bits and perform bit-by-bit operation. P Q P & Q P|Q P^Q 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1
- 19. if A = 60; and B = 13 Assume if A = 60; and B = 13; now in binary format they will be as follows: A = 0011 1100 B = 0000 1101 A&B = 0000 1100 A|B = 0011 1101 A^B = 0011 0001 ~A = 1100 0011
- 20. Operator Description Result & Binary AND Operator copies a bit to the result if it exists in both operands. (A & B) will give 12 which is 0000 1100 | Binary OR Operator copies a bit if it exists in either operand. (A | B) will give 61 which is 0011 1101 ^ Binary XOR Operator copies the bit if it is set in one operand but not both. (A ^ B) will give 49 which is 0011 0001
- 21. Operator Description Result ~ Binary Ones Complement Operator is unary and has the effect of 'flipping' bits. (~A ) will give -61 which is 1100 0011 in 2's complement form due to a signed binary number. << Binary Left Shift Operator. The left operands value is moved left by the number of bits specified by the right operand. A << 2 will give 240 which is 1111 0000 >> Binary Right Shift Operator. The left operands value is moved right by the number of bits specified by the right operand. A >> 2 will give 15 which is 0000 1111
- 22. main() { unsigned int a = 60; // 60 = 0011 1100 unsigned int b = 13; // 13 = 0000 1101 int c = 0; c = a & b; // 12 = 0000 1100 cout << "Line 1 - Value of c is : " << c << endl ; c = a | b; // 61 = 0011 1101 cout << "Line 2 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ; c = a ^ b; // 49 = 0011 0001 cout << "Line 3 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ; c = ~a; // -61 = 1100 0011 cout << "Line 4 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ; c = a << 2; // 240 = 1111 0000 cout << "Line 5 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ; c = a >> 2; // 15 = 0000 1111 cout << "Line 6 - Value of c is: " << c << endl ; return 0; }
- 23. Assignment Operators Operator Description Example = Simple assignment operator, Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand C = A + B will assign value of A + B into C += Add AND assignment operator, It adds right operand to the left operand and assign the result to left operand C += A is equivalent to C = C + A -= Subtract AND assignment operator, It subtracts right operand from the left operand and assign the result to left operand C -= A is equivalent to C = C - A
- 24. Assignment Operators Operator Description Example *= Multiply AND assignment operator, It multiplies right operand with the left operand and assign the result to left operand C *= A is equivalent to C = C * A /= Divide AND assignment operator, It divides left operand with the right operand and assign the result to left operand C /= A is equivalent to C = C / A %= Modulus AND assignment operator, It takes modulus using two operands and assign the result to left operand C %= A is equivalent to C = C % A
- 25. Assignment Operators Operator Description Example <<= Left shift AND assignment operator C<<= 2 is same as C = C << 2 >>= Right shift AND assignment operator C >>= 2 is same as C = C >> 2 &= Bitwise AND assignment operator C &= 2 is same as C = C & 2 ^= bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator C ^= 2 is same as C = C ^ 2 |= bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator C |= 2 is same as C = C | 2
- 26. main() { int a = 21; int c ; c = a; cout << "Line 1 - = Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c += a; cout << "Line 2 - += Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c -= a; cout << "Line 3 - -= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c *= a; cout << "Line 4 - *= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c /= a; cout << "Line 5 - /= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c = 200; c %= a; cout << "Line 6 - %= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c <<= 2; cout << "Line 7 - <<= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c >>= 2; cout << "Line 8 - >>= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c &= 2; cout << "Line 9 - &= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c ^= 2; cout << "Line 10 - ^= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; c |= 2; cout << "Line 11 - |= Operator, Value of c = : " <<c<< endl ; return 0; }
- 27. Any Queries ?
- 28. Thank you ;)