Lecture on Python OP concepts of Polymorpysim and Inheritance.pdf
- 2. What is Inheritance? • Definition: Inheritance is a fundamental concept in Object- Oriented Programming (OOP) that allows one class (the child class) to inherit the properties and behaviors (methods) of another class (the parent class). • Purpose: The primary goal of inheritance is to promote code reusability, reduce redundancy, and establish a hierarchical relationship between classes. It allows for a more organized and maintainable code structure. • Analogy: Consider inheritance as a family tree, where traits and behaviors are passed down from parents to children.
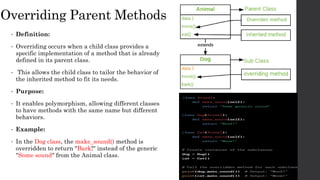
- 3. Parent Class • Definition: The parent class, also known as the base class or super class, serves as a blueprint for other classes. It contains attributes and methods that are common to all derived classes. • Characteristics: Attributes: Variables that hold data related to the class. Methods: Functions that define behaviors and actions related to the class. • Example: • Class Name: Animal Attributes: species, age Methods: make_sound() • class Animal: def __init__(self, species, age): self.species = species self.age = age • def make_sound(self): return "Some sound"
- 4. Child Class • Definition: • The child class, also known as the derived class or sub class, inherits properties and methods from the parent class. • It can also have additional attributes and methods or override existing ones. • Characteristics: • Inheritance: Inherits attributes and methods from the parent class. • Overriding: Can redefine methods to provide specific implementations. • Example: • Class Name: Dog (inherits from Animal) • Additional Attribute: breed • Overridden Method: make_sound() to return "Bark!“ • class Dog(Animal): def __init__(self, species, age, breed): super().__init__(species, age) self.breed = breed • def make_sound(self): return "Bark!"
- 5. Overriding Parent Methods • Definition: • Overriding occurs when a child class provides a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its parent class. • This allows the child class to tailor the behavior of the inherited method to fit its needs. • Purpose: • It enables polymorphism, allowing different classes to have methods with the same name but different behaviors. • Example: • In the Dog class, the make_sound() method is overridden to return "Bark!" instead of the generic "Some sound" from the Animal class.
- 6. The super() Function • Definition: • The super() function is used in a child class to call methods from its parent class. This is particularly useful for invoking the parent class’s constructor or methods. • Benefits: • Simplifies the process of calling parent class methods. • Helps avoid explicitly naming the parent class, making the code more maintainable. • Usage in the Example: • In the Dog class constructor, super().__init__(species, age) initializes the attributes defined in the parent class Animal.
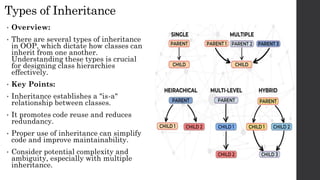
- 7. Types of Inheritance • Overview: • There are several types of inheritance in OOP, which dictate how classes can inherit from one another. Understanding these types is crucial for designing class hierarchies effectively. • Key Points: • Inheritance establishes a "is-a" relationship between classes. • It promotes code reuse and reduces redundancy. • Proper use of inheritance can simplify code and improve maintainability. • Consider potential complexity and ambiguity, especially with multiple inheritance.
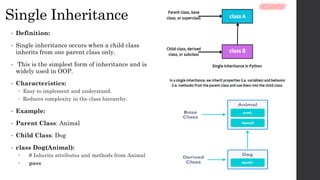
- 8. Single Inheritance • Definition: • Single inheritance occurs when a child class inherits from one parent class only. • This is the simplest form of inheritance and is widely used in OOP. • Characteristics: Easy to implement and understand. Reduces complexity in the class hierarchy. • Example: • Parent Class: Animal • Child Class: Dog • class Dog(Animal): # Inherits attributes and methods from Animal pass
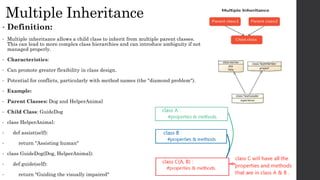
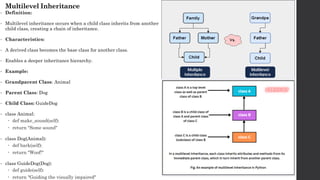
- 9. Multiple Inheritance • Definition: • Multiple inheritance allows a child class to inherit from multiple parent classes. This can lead to more complex class hierarchies and can introduce ambiguity if not managed properly. • Characteristics: • Can promote greater flexibility in class design. • Potential for conflicts, particularly with method names (the "diamond problem"). • Example: • Parent Classes: Dog and HelperAnimal • Child Class: GuideDog • class HelperAnimal: • def assist(self): • return "Assisting human" • class GuideDog(Dog, HelperAnimal): • def guide(self): • return "Guiding the visually impaired"
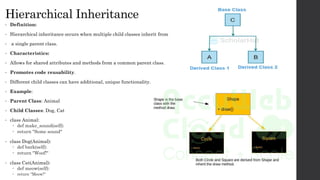
- 10. Hierarchical Inheritance • Definition: • Hierarchical inheritance occurs when multiple child classes inherit from • a single parent class. • Characteristics: • Allows for shared attributes and methods from a common parent class. • Promotes code reusability. • Different child classes can have additional, unique functionality. • Example: • Parent Class: Animal • Child Classes: Dog, Cat • class Animal: def make_sound(self): return "Some sound" • class Dog(Animal): def bark(self): return "Woof!" • class Cat(Animal): def meow(self): return "Meow!"
- 11. Multilevel Inheritance • Definition: • Multilevel inheritance occurs when a child class inherits from another child class, creating a chain of inheritance. • Characteristics: • A derived class becomes the base class for another class. • Enables a deeper inheritance hierarchy. • Example: • Grandparent Class: Animal • Parent Class: Dog • Child Class: GuideDog • class Animal: def make_sound(self): return "Some sound" • class Dog(Animal): def bark(self): return "Woof!" • class GuideDog(Dog): def guide(self): return "Guiding the visually impaired"
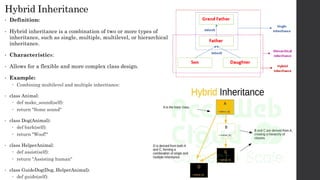
- 12. Hybrid Inheritance • Definition: • Hybrid inheritance is a combination of two or more types of inheritance, such as single, multiple, multilevel, or hierarchical inheritance. • Characteristics: • Allows for a flexible and more complex class design. • Example: Combining multilevel and multiple inheritance: • class Animal: def make_sound(self): return "Some sound" • class Dog(Animal): def bark(self): return "Woof!" • class HelperAnimal: def assist(self): return "Assisting human" • class GuideDog(Dog, HelperAnimal): def guide(self):