Lecture9 multi kernel_svm
- 1. Lecture 9: Multi Kernel SVM Stéphane Canu stephane.canu@litislab.eu Sao Paulo 2014 April 16, 2014
- 2. Roadmap 1 Tuning the kernel: MKL The multiple kernel problem Sparse kernel machines for regression: SVR SimpleMKL: the multiple kernel solution
- 3. Standard Learning with Kernels User Learning Machine kernel k data f http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~mohri/icml2011-tutorial/tutorial-icml2011-2.pdf Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 3 / 21
- 4. Learning Kernel framework User Learning Machine kernel family km data f , k(., .) http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~mohri/icml2011-tutorial/tutorial-icml2011-2.pdf Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 3 / 21
- 5. from SVM SVM: single kernel k f (x) = n i=1 αi k (x, xi ) + b = http://www.nowozin.net/sebastian/talks/ICCV-2009-LPbeta.pdf Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 4 / 21
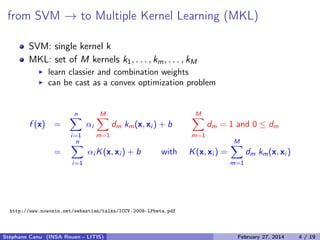
- 6. from SVM → to Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL) SVM: single kernel k MKL: set of M kernels k1, . . . , km, . . . , kM learn classier and combination weights can be cast as a convex optimization problem f (x) = n i=1 αi M m=1 dm km(x, xi ) + b M m=1 dm = 1 and 0 ≤ dm = http://www.nowozin.net/sebastian/talks/ICCV-2009-LPbeta.pdf Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 4 / 21
- 7. from SVM → to Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL) SVM: single kernel k MKL: set of M kernels k1, . . . , km, . . . , kM learn classier and combination weights can be cast as a convex optimization problem f (x) = n i=1 αi M m=1 dm km(x, xi ) + b M m=1 dm = 1 and 0 ≤ dm = n i=1 αi K(x, xi ) + b with K(x, xi ) = M m=1 dm km(x, xi ) http://www.nowozin.net/sebastian/talks/ICCV-2009-LPbeta.pdf Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 4 / 21
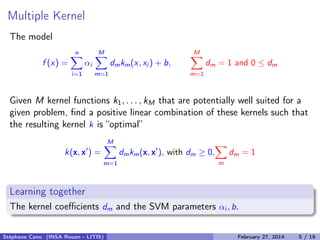
- 8. Multiple Kernel The model f (x) = n i=1 αi M m=1 dmkm(x, xi ) + b, M m=1 dm = 1 and 0 ≤ dm Given M kernel functions k1, . . . , kM that are potentially well suited for a given problem, find a positive linear combination of these kernels such that the resulting kernel k is “optimal” k(x, x ) = M m=1 dmkm(x, x ), with dm ≥ 0, m dm = 1 Learning together The kernel coefficients dm and the SVM parameters αi , b. Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 5 / 21
- 9. Multiple Kernel: illustration Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 6 / 21
- 10. Multiple Kernel Strategies Wrapper method (Weston et al., 2000; Chapelle et al., 2002) solve SVM gradient descent on dm on criterion: margin criterion span criterion Kernel Learning & Feature Selection use Kernels as dictionary Embedded Multi Kernel Learning (MKL) Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 7 / 21
- 11. Multiple Kernel functional Learning The problem (for given C) min f ∈H,b,ξ,d 1 2 f 2 H + C i ξi with yi f (xi ) + b ≥ 1 + ξi ; ξi ≥ 0 ∀i M m=1 dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , f = m fm and k(x, x ) = M m=1 dmkm(x, x ), with dm ≥ 0 The functional framework H = M m=1 Hm f , g Hm = 1 dm f , g Hm Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 8 / 21
- 12. Multiple Kernel functional Learning The problem (for given C) min {fm},b,ξ,d 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi with yi m fm(xi ) + b ≥ 1 + ξi ; ξi ≥ 0 ∀i m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , Treated as a bi-level optimization task min d∈IRM min {fm},b,ξ 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi with yi m fm(xi ) + b ≥ 1 + ξi ; ξi ≥ 0 ∀i s.t. m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 9 / 21
- 13. Multiple Kernel representer theorem and dual The Lagrangian: L = 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi − i αi yi m fm(xi ) + b − 1 − ξi − i βi ξi Associated KKT stationarity conditions: mL = 0 ⇔ 1 dm fm(•) = n i=1 αi yi km(•, xi ) m = 1, M Representer theorem f (•) = m fm(•) = n i=1 αi yi m dmkm(•, xi ) K(•,xi ) We have a standard SVM problem with respect to function f and kernel K. Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 10 / 21
- 14. Multiple Kernel Algorithm Use a Reduced Gradient Algorithm1 min d∈IRM J(d) s.t. m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , SimpleMKL algorithm set dm = 1 M for m = 1, . . . , M while stopping criterion not met do compute J(d) using an QP solver with K = m dmKm compute ∂J ∂dm , and projected gradient as a descent direction D γ ← compute optimal stepsize d ← d + γD end while −→ Improvement reported using the Hessian 1 Rakotomamonjy et al. JMLR 08 Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 11 / 21
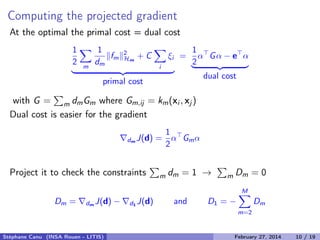
- 15. Computing the reduced gradient At the optimal the primal cost = dual cost 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi primal cost = 1 2 α Gα − e α dual cost with G = m dmGm where Gm,ij = km(xi , xj ) Dual cost is easier for the gradient dm J(d) = 1 2 α Gmα Reduce (or project) to check the constraints m dm = 1 → m Dm = 0 Dm = dm J(d) − d1 J(d) and D1 = − M m=2 Dm Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 12 / 21
- 16. Complexity For each iteration: SVM training: O(nnsv + n3 sv). Inverting Ksv,sv is O(n3 sv), but might already be available as a by-product of the SVM training. Computing H: O(Mn2 sv) Finding d: O(M3). The number of iterations is usually less than 10. −→ When M < nsv, computing d is not more expensive than QP. Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 13 / 21
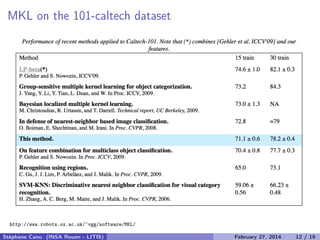
- 17. MKL on the 101-caltech dataset http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/software/MKL/ Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 14 / 21
- 18. Support vector regression (SVR) the t-insensitive loss min f ∈H 1 2 f 2 H with |f (xi ) − yi | ≤ t, i = 1, n The support vector regression introduce slack variables (SVR) min f ∈H 1 2 f 2 H + C |ξi | with |f (xi ) − yi | ≤ t + ξi 0 ≤ ξi i = 1, n a typical multi parametric quadratic program (mpQP) piecewise linear regularization path α(C, t) = α(C0, t0) + ( 1 C − 1 C0 )u + 1 C0 (t − t0)v 2d Pareto’s front (the tube width and the regularity)
- 19. Support vector regression illustration 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 −1 −0.8 −0.6 −0.4 −0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Support Vector Machine Regression x y 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 −1.5 −1 −0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 Support Vector Machine Regression x y C large C small there exists other formulations such as LP SVR...
- 20. Multiple Kernel Learning for regression The problem (for given C and t) min {fm},b,ξ,d 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi s.t. m fm(xi ) + b − yi ≤ t + ξi ∀iξi ≥ 0 ∀i m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , regularization formulation min {fm},b,d 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i max( m fm(xi ) + b − yi − t, 0) m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , Equivalently min m},b,ξ,d i max m fm(xi ) + b − yi − t, 0 + 1 2C m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + µ m |dm| Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 17 / 21
- 21. Multiple Kernel functional Learning The problem (for given C and t) min {fm},b,ξ,d 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi s.t. m fm(xi ) + b − yi ≤ t + ξi ∀iξi ≥ 0 ∀i m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , Treated as a bi-level optimization task min d∈IRM min {fm},b,ξ 1 2 m 1 dm fm 2 Hm + C i ξi s.t. m fm(xi ) + b − yi ≥ t + ξi ∀i ξi ≥ 0 ∀i s.t. m dm = 1 , dm ≥ 0 ∀m , Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 18 / 21
- 22. Multiple Kernel experiments 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 −1 −0.5 0 0.5 1 LinChirp 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 −2 −1 0 1 2 x 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Wave 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.5 1 x 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Blocks 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 x 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Spikes 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.5 1 x Single Kernel Kernel Dil Kernel Dil-Trans Data Set Norm. MSE (%) #Kernel Norm. MSE #Kernel Norm. MSE LinChirp 1.46 ± 0.28 7.0 1.00 ± 0.15 21.5 0.92 ± 0.20 Wave 0.98 ± 0.06 5.5 0.73 ± 0.10 20.6 0.79 ± 0.07 Blocks 1.96 ± 0.14 6.0 2.11 ± 0.12 19.4 1.94 ± 0.13 Spike 6.85 ± 0.68 6.1 6.97 ± 0.84 12.8 5.58 ± 0.84 Table: Normalized Mean Square error averaged over 20 runs. Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 19 / 21
- 23. Conclusion on multiple kernel (MKL) MKL: Kernel tuning, variable selection. . . extention to classification and one class SVM SVM KM: an efficient Matlab toolbox (available at MLOSS)2 Multiple Kernels for Image Classification: Software and Experiments on Caltech-1013 new trend: Multi kernel, Multi task and ∞ number of kernels 2 http://mloss.org/software/view/33/ 3 http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/software/MKL/
- 24. Bibliography A. Rakotomamonjy, F. Bach, S. Canu & Y. Grandvalet. SimpleMKL. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9:2491–2521. M. Gönen & E. Alpaydin Multiple kernel learning algorithms. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008;12:2211-2268. http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~mohri/icml2011-tutorial/tutorial-icml2011-2.pdf http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/software/MKL/ http://www.nowozin.net/sebastian/talks/ICCV-2009-LPbeta.pdf Stéphane Canu (INSA Rouen - LITIS) April 16, 2014 21 / 21