memory management.ppt
- 1. Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Chapter 8: Main Memory
- 2. 8.2 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example: ARM Architecture
- 3. 8.3 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Objectives To provide a detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware To discuss various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide a detailed description of the Intel Pentium, which supports both pure segmentation and segmentation with paging
- 4. 8.4 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Background Program must be brought (from disk) into memory and placed within a process for it to be run Main memory and registers are only storage CPU can access directly Memory unit only sees a stream of addresses + read requests, or address + data and write requests Register access in one CPU clock (or less) Main memory can take many cycles, causing a stall Cache sits between main memory and CPU registers Protection of memory required to ensure correct operation
- 5. 8.5 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Base and Limit Registers A pair of base and limit registers define the logical address space CPU must check every memory access generated in user mode to be sure it is between base and limit for that user
- 6. 8.6 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Hardware Address Protection
- 7. 8.7 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Address Binding Programs on disk, ready to be brought into memory to execute form an input queue Without support, must be loaded into address 0000 Inconvenient to have first user process physical address always at 0000 How can it not be? Further, addresses represented in different ways at different stages of a program’s life Source code addresses usually symbolic Compiled code addresses bind to relocatable addresses i.e. “14 bytes from beginning of this module” Linker or loader will bind relocatable addresses to absolute addresses i.e. 74014 Each binding maps one address space to another
- 8. 8.8 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Binding of Instructions and Data to Memory Address binding of instructions and data to memory addresses can happen at three different stages Compile time: If memory location known a priori, absolute code can be generated; must recompile code if starting location changes Load time: Must generate relocatable code if memory location is not known at compile time Execution time: Binding delayed until run time if the process can be moved during its execution from one memory segment to another Need hardware support for address maps (e.g., base and limit registers)
- 9. 8.9 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Multistep Processing of a User Program
- 10. 8.10 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Logical vs. Physical Address Space The concept of a logical address space that is bound to a separate physical address space is central to proper memory management Logical address – generated by the CPU; also referred to as virtual address Physical address – address seen by the memory unit Logical and physical addresses are the same in compile-time and load-time address-binding schemes; logical (virtual) and physical addresses differ in execution-time address-binding scheme Logical address space is the set of all logical addresses generated by a program Physical address space is the set of all physical addresses generated by a program
- 11. 8.11 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Memory-Management Unit (MMU) Hardware device that at run time maps virtual to physical address Many methods possible, covered in the rest of this chapter To start, consider simple scheme where the value in the relocation register is added to every address generated by a user process at the time it is sent to memory Base register now called relocation register MS-DOS on Intel 80x86 used 4 relocation registers The user program deals with logical addresses; it never sees the real physical addresses Execution-time binding occurs when reference is made to location in memory Logical address bound to physical addresses
- 12. 8.12 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Dynamic relocation using a relocation register Routine is not loaded until it is called Better memory-space utilization; unused routine is never loaded All routines kept on disk in relocatable load format Useful when large amounts of code are needed to handle infrequently occurring cases No special support from the operating system is required Implemented through program design OS can help by providing libraries to implement dynamic loading
- 13. 8.13 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Dynamic Linking Static linking – system libraries and program code combined by the loader into the binary program image Dynamic linking –linking postponed until execution time Small piece of code, stub, used to locate the appropriate memory-resident library routine Stub replaces itself with the address of the routine, and executes the routine Operating system checks if routine is in processes’ memory address If not in address space, add to address space Dynamic linking is particularly useful for libraries System also known as shared libraries Consider applicability to patching system libraries Versioning may be needed
- 14. 8.14 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Swapping A process can be swapped temporarily out of memory to a backing store, and then brought back into memory for continued execution Total physical memory space of processes can exceed physical memory Backing store – fast disk large enough to accommodate copies of all memory images for all users; must provide direct access to these memory images Roll out, roll in – swapping variant used for priority-based scheduling algorithms; lower-priority process is swapped out so higher-priority process can be loaded and executed Major part of swap time is transfer time; total transfer time is directly proportional to the amount of memory swapped System maintains a ready queue of ready-to-run processes which have memory images on disk
- 15. 8.15 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Swapping (Cont.) Does the swapped out process need to swap back in to same physical addresses? Depends on address binding method Plus consider pending I/O to / from process memory space Modified versions of swapping are found on many systems (i.e., UNIX, Linux, and Windows) Swapping normally disabled Started if more than threshold amount of memory allocated Disabled again once memory demand reduced below threshold
- 16. 8.16 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Schematic View of Swapping
- 17. 8.17 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Context Switch Time including Swapping If next processes to be put on CPU is not in memory, need to swap out a process and swap in target process Context switch time can then be very high 100MB process swapping to hard disk with transfer rate of 50MB/sec Swap out time of 2000 ms Plus swap in of same sized process Total context switch swapping component time of 4000ms (4 seconds) Can reduce if reduce size of memory swapped – by knowing how much memory really being used System calls to inform OS of memory use via request_memory() and release_memory()
- 18. 8.18 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Context Switch Time and Swapping (Cont.) Other constraints as well on swapping Pending I/O – can’t swap out as I/O would occur to wrong process Or always transfer I/O to kernel space, then to I/O device Known as double buffering, adds overhead Standard swapping not used in modern operating systems But modified version common Swap only when free memory extremely low
- 19. 8.19 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Swapping on Mobile Systems Not typically supported Flash memory based Small amount of space Limited number of write cycles Poor throughput between flash memory and CPU on mobile platform Instead use other methods to free memory if low iOS asks apps to voluntarily relinquish allocated memory Read-only data thrown out and reloaded from flash if needed Failure to free can result in termination Android terminates apps if low free memory, but first writes application state to flash for fast restart Both OSes support paging as discussed below
- 20. 8.20 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Contiguous Allocation Main memory must support both OS and user processes Limited resource, must allocate efficiently Contiguous allocation is one early method Main memory usually into two partitions: Resident operating system, usually held in low memory with interrupt vector User processes then held in high memory Each process contained in single contiguous section of memory
- 21. 8.21 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Contiguous Allocation (Cont.) Relocation registers used to protect user processes from each other, and from changing operating-system code and data Base register contains value of smallest physical address Limit register contains range of logical addresses – each logical address must be less than the limit register MMU maps logical address dynamically Can then allow actions such as kernel code being transient and kernel changing size
- 22. 8.22 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Hardware Support for Relocation and Limit Registers
- 23. 8.23 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Multiple-partition allocation Multiple-partition allocation Degree of multiprogramming limited by number of partitions Variable-partition sizes for efficiency (sized to a given process’ needs) Hole – block of available memory; holes of various size are scattered throughout memory When a process arrives, it is allocated memory from a hole large enough to accommodate it Process exiting frees its partition, adjacent free partitions combined Operating system maintains information about: a) allocated partitions b) free partitions (hole)
- 24. 8.24 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Dynamic Storage-Allocation Problem First-fit: Allocate the first hole that is big enough Best-fit: Allocate the smallest hole that is big enough; must search entire list, unless ordered by size Produces the smallest leftover hole Worst-fit: Allocate the largest hole; must also search entire list Produces the largest leftover hole How to satisfy a request of size n from a list of free holes? First-fit and best-fit better than worst-fit in terms of speed and storage utilization
- 25. 8.25 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Fragmentation External Fragmentation – total memory space exists to satisfy a request, but it is not contiguous Internal Fragmentation – allocated memory may be slightly larger than requested memory; this size difference is memory internal to a partition, but not being used First fit analysis reveals that given N blocks allocated, 0.5 N blocks lost to fragmentation 1/3 may be unusable -> 50-percent rule
- 26. 8.26 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Fragmentation (Cont.) Reduce external fragmentation by compaction Shuffle memory contents to place all free memory together in one large block Compaction is possible only if relocation is dynamic, and is done at execution time I/O problem Latch job in memory while it is involved in I/O Do I/O only into OS buffers Now consider that backing store has same fragmentation problems
- 27. 8.27 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Segmentation Memory-management scheme that supports user view of memory A program is a collection of segments A segment is a logical unit such as: main program procedure function method object local variables, global variables common block stack symbol table arrays
- 28. 8.28 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition User’s View of a Program
- 29. 8.29 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Logical View of Segmentation 1 3 2 4 1 4 2 3 user space physical memory space
- 30. 8.30 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Segmentation Architecture Logical address consists of a two tuple: <segment-number, offset>, Segment table – maps two-dimensional physical addresses; each table entry has: base – contains the starting physical address where the segments reside in memory limit – specifies the length of the segment Segment-table base register (STBR) points to the segment table’s location in memory Segment-table length register (STLR) indicates number of segments used by a program; segment number s is legal if s < STLR
- 31. 8.31 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Segmentation Architecture (Cont.) Protection With each entry in segment table associate: validation bit = 0 illegal segment read/write/execute privileges Protection bits associated with segments; code sharing occurs at segment level Since segments vary in length, memory allocation is a dynamic storage-allocation problem A segmentation example is shown in the following diagram
- 32. 8.32 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Segmentation Hardware
- 33. 8.33 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Paging Physical address space of a process can be noncontiguous; process is allocated physical memory whenever the latter is available Avoids external fragmentation Avoids problem of varying sized memory chunks Divide physical memory into fixed-sized blocks called frames Size is power of 2, between 512 bytes and 16 Mbytes Divide logical memory into blocks of same size called pages Keep track of all free frames To run a program of size N pages, need to find N free frames and load program Set up a page table to translate logical to physical addresses Backing store likewise split into pages Still have Internal fragmentation
- 34. 8.34 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Address Translation Scheme Address generated by CPU is divided into: Page number (p) – used as an index into a page table which contains base address of each page in physical memory Page offset (d) – combined with base address to define the physical memory address that is sent to the memory unit For given logical address space 2m and page size 2n page number page offset p d m -n n
- 35. 8.35 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Paging Hardware
- 36. 8.36 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Paging Model of Logical and Physical Memory
- 37. 8.37 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Paging Example n=2 and m=4 32-byte memory and 4-byte pages
- 38. 8.38 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Paging (Cont.) Calculating internal fragmentation Page size = 2,048 bytes Process size = 72,766 bytes 35 pages + 1,086 bytes Internal fragmentation of 2,048 - 1,086 = 962 bytes Worst case fragmentation = 1 frame – 1 byte On average fragmentation = 1 / 2 frame size So small frame sizes desirable? But each page table entry takes memory to track Page sizes growing over time Solaris supports two page sizes – 8 KB and 4 MB Process view and physical memory now very different By implementation process can only access its own memory
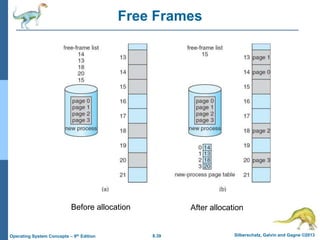
- 39. 8.39 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Free Frames Before allocation After allocation
- 40. 8.40 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Implementation of Page Table Page table is kept in main memory Page-table base register (PTBR) points to the page table Page-table length register (PTLR) indicates size of the page table In this scheme every data/instruction access requires two memory accesses One for the page table and one for the data / instruction The two memory access problem can be solved by the use of a special fast-lookup hardware cache called associative memory or translation look-aside buffers (TLBs)
- 41. 8.41 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Implementation of Page Table (Cont.) Some TLBs store address-space identifiers (ASIDs) in each TLB entry – uniquely identifies each process to provide address-space protection for that process Otherwise need to flush at every context switch TLBs typically small (64 to 1,024 entries) On a TLB miss, value is loaded into the TLB for faster access next time Replacement policies must be considered Some entries can be wired down for permanent fast access
- 42. 8.42 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Associative Memory Associative memory – parallel search Address translation (p, d) If p is in associative register, get frame # out Otherwise get frame # from page table in memory Page # Frame #
- 43. 8.43 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Paging Hardware With TLB
- 44. 8.44 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Effective Access Time Associative Lookup = time unit Can be < 10% of memory access time Hit ratio = Hit ratio – percentage of times that a page number is found in the associative registers; ratio related to number of associative registers Consider = 80%, = 20ns for TLB search, 100ns for memory access Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1 + ) + (2 + )(1 – ) = 2 + – Consider = 80%, = 20ns for TLB search, 100ns for memory access EAT = 0.80 x 100 + 0.20 x 200 = 120ns Consider more realistic hit ratio -> = 99%, = 20ns for TLB search, 100ns for memory access EAT = 0.99 x 100 + 0.01 x 200 = 101ns
- 45. 8.45 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Memory Protection Memory protection implemented by associating protection bit with each frame to indicate if read-only or read-write access is allowed Can also add more bits to indicate page execute-only, and so on Valid-invalid bit attached to each entry in the page table: “valid” indicates that the associated page is in the process’ logical address space, and is thus a legal page “invalid” indicates that the page is not in the process’ logical address space Or use page-table length register (PTLR) Any violations result in a trap to the kernel
- 46. 8.46 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Valid (v) or Invalid (i) Bit In A Page Table
- 47. 8.47 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Shared Pages Shared code One copy of read-only (reentrant) code shared among processes (i.e., text editors, compilers, window systems) Similar to multiple threads sharing the same process space Also useful for interprocess communication if sharing of read-write pages is allowed Private code and data Each process keeps a separate copy of the code and data The pages for the private code and data can appear anywhere in the logical address space
- 48. 8.48 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Shared Pages Example
- 49. 8.49 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Structure of the Page Table Memory structures for paging can get huge using straight- forward methods Consider a 32-bit logical address space as on modern computers Page size of 4 KB (212) Page table would have 1 million entries (232 / 212) If each entry is 4 bytes -> 4 MB of physical address space / memory for page table alone That amount of memory used to cost a lot Don’t want to allocate that contiguously in main memory Hierarchical Paging Hashed Page Tables Inverted Page Tables
- 50. 8.50 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Hierarchical Page Tables Break up the logical address space into multiple page tables A simple technique is a two-level page table We then page the page table
- 51. 8.51 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Two-Level Page-Table Scheme
- 52. 8.52 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Two-Level Paging Example A logical address (on 32-bit machine with 1K page size) is divided into: a page number consisting of 22 bits a page offset consisting of 10 bits Since the page table is paged, the page number is further divided into: a 12-bit page number a 10-bit page offset Thus, a logical address is as follows: where p1 is an index into the outer page table, and p2 is the displacement within the page of the inner page table Known as forward-mapped page table
- 53. 8.53 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Address-Translation Scheme
- 54. 8.54 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition 64-bit Logical Address Space Even two-level paging scheme not sufficient If page size is 4 KB (212) Then page table has 252 entries If two level scheme, inner page tables could be 210 4-byte entries Address would look like Outer page table has 242 entries or 244 bytes One solution is to add a 2nd outer page table But in the following example the 2nd outer page table is still 234 bytes in size And possibly 4 memory access to get to one physical memory location
- 55. 8.55 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Three-level Paging Scheme
- 56. 8.56 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Hashed Page Tables Common in address spaces > 32 bits The virtual page number is hashed into a page table This page table contains a chain of elements hashing to the same location Each element contains (1) the virtual page number (2) the value of the mapped page frame (3) a pointer to the next element Virtual page numbers are compared in this chain searching for a match If a match is found, the corresponding physical frame is extracted Variation for 64-bit addresses is clustered page tables Similar to hashed but each entry refers to several pages (such as 16) rather than 1 Especially useful for sparse address spaces (where memory references are non-contiguous and scattered)
- 57. 8.57 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Hashed Page Table
- 58. 8.58 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Inverted Page Table Rather than each process having a page table and keeping track of all possible logical pages, track all physical pages One entry for each real page of memory Entry consists of the virtual address of the page stored in that real memory location, with information about the process that owns that page Decreases memory needed to store each page table, but increases time needed to search the table when a page reference occurs Use hash table to limit the search to one — or at most a few — page-table entries TLB can accelerate access But how to implement shared memory? One mapping of a virtual address to the shared physical address
- 59. 8.59 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Inverted Page Table Architecture
- 60. 8.60 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Oracle SPARC Solaris Consider modern, 64-bit operating system example with tightly integrated HW Goals are efficiency, low overhead Based on hashing, but more complex Two hash tables One kernel and one for all user processes Each maps memory addresses from virtual to physical memory Each entry represents a contiguous area of mapped virtual memory, More efficient than having a separate hash-table entry for each page Each entry has base address and span (indicating the number of pages the entry represents)
- 61. 8.61 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Oracle SPARC Solaris (Cont.) TLB holds translation table entries (TTEs) for fast hardware lookups A cache of TTEs reside in a translation storage buffer (TSB) Includes an entry per recently accessed page Virtual address reference causes TLB search If miss, hardware walks the in-memory TSB looking for the TTE corresponding to the address If match found, the CPU copies the TSB entry into the TLB and translation completes If no match found, kernel interrupted to search the hash table – The kernel then creates a TTE from the appropriate hash table and stores it in the TSB, Interrupt handler returns control to the MMU, which completes the address translation.
- 62. 8.62 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Dominant industry chips Pentium CPUs are 32-bit and called IA-32 architecture Current Intel CPUs are 64-bit and called IA-64 architecture Many variations in the chips, cover the main ideas here
- 63. 8.63 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Example: The Intel IA-32 Architecture Supports both segmentation and segmentation with paging Each segment can be 4 GB Up to 16 K segments per process Divided into two partitions First partition of up to 8 K segments are private to process (kept in local descriptor table (LDT)) Second partition of up to 8K segments shared among all processes (kept in global descriptor table (GDT))
- 64. 8.64 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Example: The Intel IA-32 Architecture (Cont.) CPU generates logical address Selector given to segmentation unit Which produces linear addresses Linear address given to paging unit Which generates physical address in main memory Paging units form equivalent of MMU Pages sizes can be 4 KB or 4 MB
- 65. 8.65 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Logical to Physical Address Translation in IA-32
- 66. 8.66 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Intel IA-32 Segmentation
- 67. 8.67 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Intel IA-32 Paging Architecture
- 68. 8.68 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Intel IA-32 Page Address Extensions 32-bit address limits led Intel to create page address extension (PAE), allowing 32-bit apps access to more than 4GB of memory space Paging went to a 3-level scheme Top two bits refer to a page directory pointer table Page-directory and page-table entries moved to 64-bits in size Net effect is increasing address space to 36 bits – 64GB of physical memory
- 69. 8.69 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Intel x86-64 Current generation Intel x86 architecture 64 bits is ginormous (> 16 exabytes) In practice only implement 48 bit addressing Page sizes of 4 KB, 2 MB, 1 GB Four levels of paging hierarchy Can also use PAE so virtual addresses are 48 bits and physical addresses are 52 bits
- 70. 8.70 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition Example: ARM Architecture Dominant mobile platform chip (Apple iOS and Google Android devices for example) Modern, energy efficient, 32-bit CPU 4 KB and 16 KB pages 1 MB and 16 MB pages (termed sections) One-level paging for sections, two- level for smaller pages Two levels of TLBs Outer level has two micro TLBs (one data, one instruction) Inner is single main TLB First inner is checked, on miss outers are checked, and on miss page table walk performed by CPU outer page inner page offset 4-KB or 16-KB page 1-MB or 16-MB section 32 bits
- 71. Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts – 9th Edition End of Chapter 8