Microscopy
- 1. My work, which I've done for a long time, was not pursued in order to gain the praise I now enjoy, but chiefly from a craving after knowledge, which I notice resides in me more than in most other men. And therewithal, whenever I found out anything remarkable, I have thought it my duty to put down my discovery on paper, so that all ingenious people might be informed thereof. Antony van Leeuwenhoek. Letter of June 12, 1716
- 2. MICROSCOPY A Brief Overview Dr SANTOSH KARADE
- 3. INTRODUCTION DEFINITION HISTORICAL BACKGROUND VARIBLES USED IN MICROSCOPY COMPOUND MICROSCOPE - Structure and Function USE OF MICROSCOPE VARIOUS TYPES OF MICROSCOPES CARE OF MICROSCOPE
- 4. INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Understanding the optical principles and construction of microscopes Role of microscopy Microscopic techniques and application
- 5. DEFINITION A microscope ( Greek : micron = small and scopos = aim) MICROSCOPE - An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen by the naked or unaided eye MICROSCOPY - The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy
- 6. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND 1590 - Hans Janssen and his son Zacharias Janssen, developed first microscope. 1609 - Galileo Galilei - occhiolino or compound microscope. 1620 - Christian Huygens, another Dutchman, developed a simple 2-lens ocular system that was chromatically corrected.
- 7. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) Anton van Leeuwenhoek is generally credited with bringing the microscope to the attention of biologists. A tradesman of Delft, Holland. 1661 - He discovered bacteria, free-living and parasitic microscopic protists, sperm cells, blood cells, microscopic nematodes etc.
- 8. Microscope used by Anton von Leeuwenhoek An old pocket Microscope
- 9. VARIABLES USED IN MICROSCOPY
- 10. MAGNIFICATION Degree of enlargement No of times the length, breadth or diameter, of an object is multiplied. MAGNIFICATION VS SHARPNESS USEFUL MAGNIFICATION AND EMPTY MAGNIFICATION
- 11. RESOLUTION – Ability to reveal closely adjacent structural details as separate and distinct LIMIT OF RESOLUTION (LR) – The min distance between two visible bodies at which they can be seen as separate and not in contact with each other
- 12. LR = 0.61 x W W = Wavelength NA = Num aperture NA Types of microscope Resolving power Compound Microscope 200 nanometers Scanning Electron Microscope 10 nanometers Transmission Electron Microscope 0.2 nanometers
- 13. NUMERICAL APERTURE(NA) Ratio of diameter of lens to its focal length NA = n Sin θ /2 n = refractive index, θ = angle of aperture (CAD) θ /2 A B D C n of air = 1 n of oil = 1.5
- 14. DEFINITION Capacity of an objective to render outline of the image of an object clear and distinct Depends of elimination of Spherical and Chromatic aberration
- 15. ABERRATION Chromatic aberration Correction of aberration – Achromatic objective and Apochromatic objectives. Blue focus Red focus Incident light
- 16. Spherical aberration Focus of marginal rays Focus of axial rays
- 17. TYPES OF MICROSCOPE Simple microscope Compound microscope Phase Contrast Microscope Dark Ground Microscope Fluorescent Microscope Electron Microscope Others
- 18. COMPOUND MICROSCOPE Compound microscope made by John Cuff 1750
- 19. PARTS OF COMPOUND MICROSCOPE Ocular (Eye piece) Body or Tube Coarse focusing knob Fine focusing knob Objective Lens Movable stage Condenser Lenses Field (Iris) Diaphragm Mirror and light source
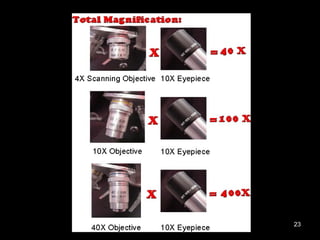
- 20. OBJECTIVE LENS It forms magnified real image. Mounted on Nose piece Magnification of objective = Optical Tube length Focal Length Scan - 4X Low Power - 10X High Power - 40X Oil immersion - 100X TYPES
- 21. OIL IMMERSION OBJECTIVE Highest magnification Oil prevents refraction of light outwards and allows it to pass straight in to objective GLASS OIL A B C D E G F FBEG - OIL ABCD - AIR
- 22. EYE PIECE Forms magnified virtual & erect image TYPES (a) Monocular (b) Binocular (c) Trinocular or (a) Huygenian (b) Ramsden (c) Compensating
- 24. PARTS OF MICROSCOPE (Cont) Iris Diaphragm Condenser Field Diaphragm Diaphragm control ring Focusing knob illumination source
- 25. I LLUMINATION - Lamp, sunlight, battery operated lamp, 60 W bulb, Quartz halogen light. FILTERS - Blue, Green, Heat absorbing filters, Barrier filters.
- 26. Multiple step operation employed to attain optimal illumination: 1. Remove any diffusing filter. 2. Put a slide on the stage and focus. 3. Completely close the field diaphragm . 4. Move the condenser until the border or the iris hexagon is neat and clear. 5. Center if necessary. 6. Open the field diaphragm until the tip of the hexagon touches the field limit KOHLER’S ILLUMINATION
- 27. HOW A MICROSCOPE WORKS ?
- 28. OPTICAL PATH IN COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
- 29. METHOD OF USING COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
- 30. Grasp the microscopes arm with one hand and place your other hand under the base . 2. Place the microscope on a bench. Adjust seat 3. Clean Lenses. 4. Turn the coarse adjustment knob to raise the body tube arm arm
- 31. 5. Revolve the nose piece to set low-power objective lens. 6. Adjust the Condenser lenses and diaphragm . 7. Place a slide on the stage and secure with stage clips. 8. Switch on the light at low intensity and then increase intensity.
- 32. 9. Turn the coarse adjustment knob to lower the body tube until the low power objective reaches its lowest point. 10. Looking through the eyepiece, very slowly move the coarse adjustment knob until the specimen comes into focus. 11. Adjust distance between eye piece.
- 33. 12. Switch to the high power objective lens only after adjusting condenser and iris diaphragm. 13. Place a drop of oil over specimen before using oil immersion objective. 14. Lower the objective until oil makes contact with objective. 15. Looking through the eyepiece, very slowly focus the objective away from the slide i.e by raising the objective lens.
- 34. HOW TO OBSERVE A SLIDE ?
- 35. CAUSES OF ERROR IN FOCUSING Revolving Nose Piece is off centre Preparation is upside down Thick cover slip Dirt or Dried oil over Lens Air bubble in immersion oil Poor illumination – Condenser not fully racked up
- 37. PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPE First described in 1934 by Dutch physicist Frits Zernike Produces high-contrast images of transparent specimens Advantage - Living cells can be examined in their natural state
- 38. PRINCIPLE OF PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY Unstained bacteria have constituents of different refractive index . Diffraction of light Phase contrast microscope employs an optical mechanism to translate minute variations in phase into corresponding changes in intensity of image.
- 40. REQUISITE FOR PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY ANNULAR DIAPHRAGM PHASE PLATE
- 41. CONDENSER ANNULUS The condenser annulus or annular diaphragm is opaque flat-black (light absorbing) plate with a transparent annular ring. Produces hollow cone of light.
- 43. PHASE PLATE Placed in back focal plane of objective. FUNCTION :- 1. Enhances phase difference by retarding diffracted wave front by one quarter of wavelength . 2. Reduces intensity of direct rays and equalizes it with diffracted rays intensity.
- 44. Phase plate
- 45. IMAGES OF PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCPY Clostridium botulinum Spirilium volutans
- 46. COMPARISION OF IMAGES OF BRIGHT FIELD AND PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY
- 47. USES OF PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY Phase contrast enables visualization of internal cellular components. Diagnosis of tumor cells . Examination of growth, dynamics, and behavior of a wide variety of living cells in cell culture
- 48. DARK GROUND MICROSCOPE Optical system to enhance the contrast of unstained bodies . Specimen appears gleaming bright against dark background PRINCIPLE OF DGI
- 49. OPTICAL PATH IN DARK GROUND MICROSCOPY
- 50. REQUISITES FOR DARK GROUND MICROSCOPY Dark ground condenser High intensity lamp Funnel stop
- 51. USES OF DARK GROUND MICROSCOPY Treponema pallidum Useful in demonstrating - Treponema pallidum - Leptospira - Campylobacter jejuni - Endospore
- 52. FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY PRINCIPLE UV light Fluorochrome Visible radiation FITC EX - 495 nm EM - 520nm TRITC EX – 540 nm EM – 590 nm Texas Red Ex – 600 nm EM – 615 nm
- 53. UV rays passes through exciter filter Dark ground condenser Micro organisms stained with fluorescent dye, when examined under microscope with ultraviolet light are seen as bright object against dark background
- 54. USE OF FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Auramine Rhodamine – Yellow Fl - Tubercle bacilli Acridine Orange R - gives orange red Fl with RNA and yellow green Fl with DNA QBC IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE
- 56. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE Electron Microscopes uses a beam of highly energetic electrons to examine objects on a very fine scale. This examination can yield the info about Topography Morphology Composition Crystallographic structure
- 57. TYPES OF EM Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- 58. TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM) Stream of electrons is formed Accelerated using a positive electrical potential Focused by metallic aperture and Electro magnets Interactions occur inside the irradiated sample which are detected and transformed into an image .
- 59. TEM (Cont) Projector Lens forms image on Fluorescent viewing screen 2D Image Magnification 10,000 X to 100,000 X
- 60. Scan a gold-plated specimen to give a 3-D view of the surface of an object which is black and white. Used to study surface features of cells and viruses. Scanning Electron microscope has resolution 1000 times better than Light microscope . SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
- 61. WORKING OF SEM
- 62. SEM IMAGES Vibrio cholerae with polar flagella Treponema pallidum
- 63. INVERTED MICROSCOPE Used in metallurgy Examination of cultures in flat bottom dishes Micro dissection Examination of parasites Observation of agglutination in serology OTHER MICROSCOPES
- 64. STEREO MICROSCOPE Double Microscope Produces 3D images POLARIZING MICROSCOPE Uses two Polariser Gives info about Birefringence of a body Used in Crystallography, Urine examination Apple Green Birefringerence in AMYLODOSIS
- 65. Uses a laser beam to illuminate a specimen whose image is then digitally enhanced for viewing on a computer monitor. Laser beam scans single plane of 1 µm thickness. CONFOCAL SCANNING LASER MICROSCOPE
- 66. Comparison of Depth of Light Collection and Image clarity Light Microscope Confocal Scanning Laser Microscope
- 67. PRINCIPLE OF CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY
- 68. USES OF CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE Observing cellular morphology in multilayered specimen Eg. used in diagnosing Ca cervix Evaluation and diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma of skin
- 69. What is the advantage of using a confocal microscope? By having a confocal pinhole, the microscope is really efficient at rejecting out of focus fluorescent light so that very thin section of a sample can be analyzed. By scanning many thin sections through a sample, one can build up a very clean three-dimensional image .
- 70. NEWER MICROSCOPE SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPE -Class of Microscope that measures surface features by moving a sharp probe over object surface. Used to visualize atoms and molecules Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
- 71. CARE OF THE MICROSCOPE Handling Proper storage Care of Lenses Care of oil emersion objective Care of lamp
- 72. THANK YOU