Microsoft project server 2010 administrators guide
- 1. 1 Microsoft Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide
- 2. Copyright This document is provided “as-is”. Information and views expressed in this document, including URL and other Internet Web site references, may change without notice. This document does not provide you with any legal rights to any intellectual property in any Microsoft product. You may copy and use this document for your internal, reference purposes. © 2011 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Active Directory, Excel, Internet Explorer, Outlook, SharePoint, SQL Server, and Windows are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
- 3. Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction 1 What Will You Learn from this Book? ..................................... 1 Who Should Read this Book? ................................................. 1 How is this Book Structured? ................................................. 2 1 Security 5 Manage Permissions .............................................................. 6 Manage Users ......................................................................... 8 Add or Edit a User ...................................................................................................... 8 Deactivate a user account ...................................................................................... 19 Reactivate a user account ....................................................................................... 20 Manage Groups..................................................................... 20 Create or modify a security group ........................................................................... 21 Delete a security group ............................................................................................ 26 Active Directory Group Synchronization ................................................................. 26 Manage Categories ................................................................31 Create or modify a category .................................................................................... 32 Delete a category ..................................................................................................... 39 Manage Security Templates ................................................. 40 Create or modify a security template ...................................................................... 40 Delete a security template ...................................................................................... 43 Manage Project Web App Permissions ................................. 44 Manage Delegates ................................................................ 45 Turn Delegation on or off ......................................................................................... 46 Set up who can act as delegate .............................................................................. 46 Set up who can have delegates assigned to them ................................................ 48 Create a new delegation .......................................................................................... 49 2 Enterprise Data 50 Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables .......................51 Understanding Enterprise Custom Fields ............................................................... 52 Creating Enterprise Custom Fields ......................................................................... 52 Creating Enterprise Custom Lookup Tables ........................................................... 64
- 4. Departments ......................................................................... 68 Configuring departments ......................................................................................... 72 The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) ............................74 Enterprise Global................................................................... 77 Enterprise Calendars ............................................................ 79 Create a New Calendar ............................................................................................ 80 Copy an Existing Calendar ....................................................................................... 81 Edit an Existing Calendar ......................................................................................... 82 Delete a Calendar .................................................................................................... 83 Modify Working and Nonworking Times ................................................................. 84 Resource Center.................................................................... 95 Create a New Resource ........................................................................................... 95 3 Database Administration 103 Delete Enterprise Objects ................................................... 103 Delete projects .......................................................................................................103 Delete resources and users ..................................................................................105 Delete status report responses.............................................................................106 Delete timesheets ..................................................................................................106 Delete user delegates............................................................................................107 Force Check-in Enterprise Objects ...................................... 108 Check-in Enterprise Projects .................................................................................109 Check in Enterprise Resources .............................................................................110 Check in Enterprise Custom Fields .......................................................................110 Check in Enterprise Calendars ..............................................................................111 Check in Lookup Tables for Enterprise Custom Fields ........................................111 Check in Resource Plans .......................................................................................112 Daily Schedule Backup ....................................................... 113 Project Retention Policy Versions .........................................................................113 Items .......................................................................................................................113 Administrative Backup and Restore ................................... 115 Administrative Backup ...........................................................................................115 Administrative Restore ..........................................................................................115 OLAP Database Management.............................................. 117 Create an OLAP Cube ............................................................................................117 Configure an OLAP cube ........................................................................................121 Copy an OLAP cube ................................................................................................125 Delete an OLAP cube .............................................................................................126 Build an OLAP cube ...............................................................................................126
- 5. Table of Contents 4 Look and Feel 128 Manage Views ..................................................................... 129 Create a New View .................................................................................................134 Modify a View .........................................................................................................137 Copy a View ............................................................................................................138 Delete a View .........................................................................................................139 Grouping Formats ............................................................... 139 Gantt Chart Formats ............................................................ 141 Quick Launch .......................................................................142 Change Quick Launch Behavior ............................................................................143 Add a New Link ......................................................................................................144 Modify an Existing Link ..........................................................................................145 Reorder Quick Launch Items .................................................................................145 Delete a Link ..........................................................................................................146 5 Time and Task Management 147 Fiscal Periods .......................................................................148 Define Fiscal Periods .............................................................................................148 Delete Fiscal Periods .............................................................................................151 Time Reporting Periods ....................................................... 151 Create Bulk Time Reporting Periods .....................................................................152 Insert or Delete Time Reporting Periods...............................................................153 Timesheet Adjustment .........................................................155 Line Classifications ..............................................................156 Timesheet Settings and Defaults ........................................158 Administrative Time .............................................................160 Task Settings and Display ....................................................162 Close Tasks to Update..........................................................163 6 Queue Management 165 Queue System Overview ......................................................165 Queuing process ..................................................................167 Queuing architecture ...........................................................168 Queuing modules ...................................................................................................168 How it all works together .......................................................................................172 The Project and Timesheet queues ..................................... 174 How the Project and Timesheet queues are used ...............................................175
- 6. Queue groupings ..................................................................177 Parent/Child Relationships between submitted Jobs .........178 Queuing states .....................................................................179 Changes in queue state.........................................................................................180 Queue Administration Settings ........................................... 181 Manage Queue Jobs ..............................................................................................182 Queue Settings .......................................................................................................186 7 Operational Policies Management 197 Alerts and Reminders ......................................................... 197 Notification E-mail Settings ...................................................................................198 Schedule E-Mail Reminder Service .......................................................................199 Additional Server Settings................................................... 199 Project 2007 Compatibility Mode .........................................................................200 Project Professional Versions ................................................................................202 Enterprise Settings ................................................................................................203 Currency Settings ...................................................................................................204 Resource Capacity Settings...................................................................................206 Resource Plan Work Day .......................................................................................208 Exchange Server Details ........................................................................................208 Task Mode Settings ...............................................................................................209 Server Side Event Handlers .................................................210 Active Directory Resource Pool Synchronization ................ 212 To configure Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization .....................................213 Project Sites .........................................................................216 Create Site ..............................................................................................................217 Edit Site Address ....................................................................................................218 Synchronize ............................................................................................................219 Delete Site ..............................................................................................................220 Go to Project Site Settings .....................................................................................220 Project Site Provisioning Settings ....................................... 221 Site URL ..................................................................................................................222 Default Site Properties ..........................................................................................222 Automatic Provisioning ..........................................................................................223 Project Site Permissions ........................................................................................224 Bulk Update Project Sites ................................................... 225 Update Site Paths ..................................................................................................226 Update Content Types ...........................................................................................227 Project Site Permissions ........................................................................................227
- 7. Table of Contents 8 Workflow and Project Detail Pages 228 Enterprise Project Types ..................................................... 229 Create New Enterprise Project Type .....................................................................229 Workflow Phases .................................................................. 231 New Workflow Phase .............................................................................................231 Workflow Stages ................................................................. 233 New Workflow Stages ............................................................................................233 Change or Restart Workflows ............................................. 236 Change or Restart a Workflow ..............................................................................236 Project Detail Pages .............................................................237 Create or Edit Project Detail Pages .......................................................................237 Project Workflow Settings ....................................................240 A Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 243 B Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 255 C Project Server 2010 Default Security Groups 280 Default global permissions ..................................................281 Default category permissions ............................................. 285 D Project Server 2010 Default Categories 289 Categories ........................................................................... 289 Category permissions ......................................................... 290
- 9. 1 Introduction The Microsoft Project Server 2010 Administrator’s Guide helps your organization understand the tasks involved with administering Microsoft Project Server 2010. Send us your feedback (projdocs@microsoft.com). Please let us know what you think about the quality of this content. If this text does not meet your needs, let us know how we can improve it. If this text was helpful to you, let us know how it helped. What Will You Learn from this Book? There are several important tasks that an administrator must manage in Microsoft Project Server 2010 for Project Web App users to access and interact effectively with project data, including: Managing users, groups, and categories. Customizing Project Web App to fit the specific needs of your organization. Managing workflows. Managing enterprise data (custom fields, calendars, views, etc.). Managing queue settings for your specific environment. Managing time and task tracking. Configuring Active Directory synchronization to security groups and resources. Who Should Read this Book? This book is designed to produce maximum benefits for the following professionals: Project Server administrators Those individuals who will have administrative privileges for Project Server and will perform the duties required to configure and maintain Project Server. SharePoint Server farm administrators Those individuals responsible for administering the SharePoint Server Central Administration web site and ensuring that Project Server and Microsoft SharePoint
- 10. 2 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Server are always properly synchronized and that SharePoint Server features and functionality are available. Project Management Office (PMO) Those individuals who help to define and maintain project management standards and practices throughout the organization. Project site administrators Those individuals who will have administrative privileges for Project Server and will perform the duties required to configure Project Server to meet organizational portfolio and project management needs. Active Directory administrators Those individuals responsible for setting up individual e-mail accounts and security groups in the Active Directory directory service that will be mapped to the Project Server Enterprise Resource Pool and Project Server security groups. Any member of your organization’s Project Server deployment planning team Those individuals within your organization who will plan the deployment of Project Server 2010 and who may need a better understanding of the day-to-day Project Server administrative tasks that are available in Project Web App. How is this Book Structured? This book has eight chapters and four appendices. You can review these chapters in any order you need to; they are organized in the same manner in this book as they are organized in Project Web App. Appendix data is primarily reference data and lists:
- 11. Introduction Introduction Chapter 1, “Security” Chapter 2, “Enterprise Data” Chapter 3, “Database Administration” Chapter 4, “Look and Feel” Chapter 5, “Time and Task Management” Chapter 6, “Queue Management” Chapter 7, “Operational Policies Management” Chapter 8, “Workflow and Project Detail Pages” Appendix A, “Project Server 2010 Category Permissions” Appendix B “ Project Server 2010 Global Permissions” Appendix C “ Project Server 2010 Default Security Groups” Appendix D “ Project Server 2010 Default Categories”
- 13. 5 1 Security This chapter about Project Server 2010 Security contains the following sections: Manage Permissions Manage Users Manage Groups Manage Categories Manage Security Templates Manage Project Web App Permissions Manage Delegates
- 14. 6 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Manage Permissions A permission is the authority to perform a specific action within the context of Project Server. You can Allow, Deny, or not configure (select neither Allow nor Deny) each permission in Project Server. For example, the Log On permission can be allowed or denied for any given user or group. There are two types of permissions in Project Server: Global Permissions grant users and groups the ability to perform actions throughout an instance of Microsoft Project Web App (PWA). Global Permissions are assigned on a user or group level. Category Permissions grant users and groups the ability to perform actions on specific projects and resources. Category Permissions also grant permissions to Views in PWA. Category Permissions are assigned on a category level. Permissions can be set in a number of different places within the Project Server 2010 administration menu. You can allow or deny permissions by selecting the check boxes in the Allow and Deny columns. If neither the Allow nor the Deny check boxes are selected, the default state is Not Allow. The Not Allow state does not prevent users from accessing the feature associated with the permission if they are granted permission in some other way. For example, a user might belong to one group for which permission is not configured (Not Allowed), but might be granted permission by means of membership in a group for which the permission is allowed. However, if the permission is explicitly denied anywhere, permission is denied everywhere for a particular user or group.
- 15. Security 7 Project Server permissions You can configure all Project Server 2010 permissions from the Project Web App Server Settings page. Permissions can be configured in the following ways: Allow Enables users or group members to perform the actions associated with the permission. Deny Prevents a user or group from performing the actions associated with the permission. Use caution when denying permissions. Note that if a user is denied a specific permission, the deny setting supersedes any Allow settings that might apply to other groups to which the user belongs. No permissions are set to Deny by default. Not Allow If you select neither Allow nor Deny for a permission, the default state is Not Allow. If a user belongs to more than one group, and a permission is set to Not Allow for one group and is set to Allow (but not Deny) for another group, then the user is allowed to perform the actions associated with the permission. It is important to consider when you are configuring a permission to Deny that the Deny setting supersedes any Allow settings that apply to the user for that permission by means of other group memberships. Limiting your use of the Deny setting can simplify permissions management for large groups of users. Important The Deny setting enables you to deny access to functionality, because this setting overrides the Allow setting. Therefore, use caution when selecting the Deny check box. Select the Deny check box to prevent a user from outside the organization from accessing Project Server security objects or to deny functionality to a user or group). For organizations that include a large number of users, assigning and administering permissions on an individual basis can be an overwhelming task. You can use groups to assign permissions to multiple users with a single action. Create the groups and define the set of permissions to associate with the groups as part of your initial Project Server 2010 deployment planning process, before you assign users to groups and groups to categories.
- 16. 8 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide After you define groups, the permissions associated with the groups, and group memberships, the day-to-day administration of users, groups, and categories involves adding users to or removing users from security groups. This helps to reduce the volume of required day-to-day administrative tasks, and can simplify troubleshooting permissions issues. Manage Users When you make the initial connection to Microsoft Project Server 2010 through the Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site, you must be logged on by using the account used to provision the PWA site. You can use this initial account to create other user accounts that can access Project Server. For example, this initial account can be used to create the user accounts for Project Server administrators, who can create other user accounts and do additional post-installation configuration. You can use the Manage Users page that is available from the Server Settings page to add new individual users, modify existing users, deactivate user accounts, and reactivate inactive user accounts. You can also assign permissions to users by adding them to one of the built- in groups or by creating a custom group and assigning specific permissions to the custom group. Note If you have more than 2,000 users in PWA, the Manage Users page will not display users until you select one of the Show options at the top of the page. Add or Edit a User To add a new user account, perform the following procedure. To add a user account 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Users. 2. On the Manage Users page, click New User. 3. On the New User page, fill out the required information for the user. See the following sections for details on each option. 4. Click Save. To edit an existing user account, perform the following procedure. To edit a user account 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Users. 2. On the Manage Users page, click the user that you want to edit. 3. On the Edit User page, fill out the required information for the user. See the following sections for details on each option.
- 17. Security 9 4. Click Save. Identification Information Use the Identification Information section to specify user information such as name, email address, and account status. Project Server user identification information The following table describes the user identification options. Attribute Description User can be assigned Select User can be assigned as a resource if you want this as a resource user account to be able to be assigned tasks as a resource. Selecting this entry makes the user an Enterprise Resource. This setting is selected by default. Once a user account becomes an Enterprise Resource it cannot be changed back to a non-Enterprise Resource even if the check box is
- 18. 10 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide deselected. Display Name The name for the user account. This is a required field. E-mail address The email address for the user. This field is required to synchronize tasks with Exchange Server. RBS The user’s position in the Resource Breakdown Structure hierarchy. Initials The user’s initials. Hyperlink Name The name of the user’s web site (for example, a team web site) if applicable. Hyperlink URL The URL of the user’s web site, if applicable. Account Status Can be set to Active or Inactive. If the value is set to Active, the user account functions normally. If the value is set to Inactive, the user will be unable to access the account. User Authentication Use the User Authentication section to specify the user’s logon account and whether the user account should be synchronized with Active Directory. Project Server user account information The following table describes the user account options. Attribute Description User logon account If you are using Integrated Windows authentication, type the user's account name in the form of DomainNameUserAccountName. If you are using forms-based authentication, type the user account name in the form of MembershipProviderName:UserAccount. Prevent Active Directory Selecting the Prevent Active Directory synchronization for synchronization for this user this user check box prevents a user account from being synchronized during Active Directory Resource Pool Synchronization.
- 19. Security 11 Assignment Attributes Use the Assignment Attributes section to define information associated with the user’s assignment to tasks, including calendar, booking type, timesheet manager, assignment owner, and cost and availability information. Note If you have not selected the User can be assigned as a resource check box, these options are not available. Project Server assignment attributes The following table describes the Project Server user assignment attribute options. Attribute Description Resource can be leveled Indicates whether the resource can be leveled. Leveling is the process that is used to resolve resource conflicts or over-allocations by delaying or splitting certain tasks.
- 20. 12 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Attribute Description When Project levels a resource, its selected assignments are distributed and rescheduled. Base Calendar A base calendar is a calendar that can be used as a project and task calendar that specifies default working and non-working time for a set of resources. Default Booking Type Using the Default Booking Type list, you can configure a user's booking type as either Committed or Proposed. A committed resource is formally allocated to any task assignment within a project. A proposed resource has a pending resource allocation to a task assignment that has not yet been authorized. This resource assignment does not detract from the availability of the resource to work on other projects. Timesheet manager If the user has a timesheet manager, specify that user here. Default Assignment Owner An assignment owner is an enterprise resource who is responsible for entering progress information in PWA. This person can differ from the person first assigned to the task. For example, a material resource cannot log on to PWA but the assignment owner field allows an enterprise resource to enter progress for the resource within PWA. Earliest Available The earliest date that the user is available as a resource. This date corresponds to the resource availability dates for a resource that can be seen in Microsoft Project Professional. Latest Available The latest date that the user is available as a resource. This date corresponds to the resource availability dates for a resource that can be seen in Project Professional. Standard Rate The rate for the work on an assignment that is scheduled during the regular working hours of an assigned resource. To establish variable rates, open the enterprise resource in Project Professional and set this information in the Cost Rate tables. Overtime Rate The rate for the work on an assignment that is scheduled beyond the regular working hours of an assigned resource. To establish variable rates, open the enterprise resource in Project Professional and set this information in the Cost Rate tables. Current Max. Units (%) The percentage of time that the resource is available for assignments. The current max units is tied to the early and late availability dates, if set. For example, if today is 1/1/2011 and the earliest available date is 1/2/2011
- 21. Security 13 Attribute Description then the max value is 0% and text next to the field will say “Custom availability detected, edit in Project Professional.” Cost/Use The per-use cost of the resource, if applicable. For work resources, a per-use cost accrues every time that the resource is used. For material resources, a per-use cost is accrued only one time. Exchange Server Details Use the Exchange Server Details section to specify whether the user’s tasks should be synchronized with Exchange Server. Exchange synchronization configuration Select the Synchronize Tasks check box if you want to enable task synchronization using Microsoft Exchange for this user. Exchange integration must be configured for task synchronization to function. For more information about how to configure task synchronization with Exchange Server, see Deploy Project Server 2010 with Exchange Server (http://technet.microsoft.com/en- us/library/ff793353.aspx). Departments Use the Departments section to define whether the user is a member of a particular department. You define departments for your organization by populating the Departments custom lookup table. User department configuration
- 22. 14 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide If the user is a member of a department, click the expand button (...) and select the department from the displayed hierarchy. Security Groups Use the Security Groups section to specify the user’s membership in security groups. Security group configuration To add the user to a security group, select the group in the Available Groups list, and then click Add. The following table describes the security group configuration options for a user. Attribute Description Available Groups The Available Groups list contains the groups that the user is currently not a member of. Groups that contain this The Groups that contain this user list contains the groups user that the user is currently a member of. Security Categories Use the Security Categories section to specify the user’s membership in security categories.
- 23. Security 15 Security category configuration To add the user to a category, select the category in the Available Categories list, and then click Add. To modify the category permissions for this user in a category, select the category in the Selected Categories list, and then select Allow for the permissions that you want to allow. Important We recommend that you do not set category permissions for a single user. Instead, assign the user to a group and set category permission for the group. This allows for easier maintenance. The following table describes the security category configuration options for a user. Attribute Description Available Categories The Available Categories list contains the categories that the user is not a member of. Selected Categories The Selected Categories list contains the categories that the user is a member of. Permissions for <category> The Permissions for <category> area lets you configure category permissions for this user for the selected category. Set permissions with The Set permission with Template option can be used to Template prepopulate a set of category permissions based on a predefined template for the user’s role (such as Executive or Project Manager).
- 24. 16 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Global Permissions Use the Global Permissions section to configure global permissions for the user. Global permissions configuration To allow or deny a global permission for the user, select the Allow or Deny check box for the permission. We recommend that you do not configure global permission for a single user. Instead, configure permissions at the group level and add users to the appropriate group. Doing this allows for much easier administration and helps in troubleshooting permissions issues. For a complete list of global permissions, see Appendix B, “Project Server 2010 Global Permissions.” Group Fields Use the Group Fields section to define group and cost information for the user. Group fields are not tied to Project Server security, but are a way of specifying that a user belongs to a particular group in your organization. These fields appear in the Project Server reporting database and can be used for reporting. Cost Type can be added to the resource and assignment OLAP cubes.
- 25. Security 17 Group fields configuration If your organization uses group names, codes, or cost center information for individuals, type the information in the Group Fields area. The values available for Cost Type are those that are defined in the Cost Type custom lookup table. By default, the Group field is synchronized with Active Directory if you use Active Directory synchronization. Team Details Use the Team Details section to define a team association for the user. To use teams, you must first do the following: 1. Create a custom lookup table and populate it with the team names that you want to use. 2. Edit the Team Name custom field to use the new lookup table. Team details configuration You can use teams to pool assignments under a single resource where they can be later reassigned to other resources. For example, you could create a team resource named “Development” to which you assign software development tasks. By assigning this resource to the Development team and selecting the Team Assignment Pool check box, you enable other users on the Development team to see any tasks assigned to the Development resource and to accept the assignments in PWA. You could also select Team Assignment Pool for a team lead and have all assignments go through that person for distribution to team members.
- 26. 18 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide System Identification Data The System Identification Data section displays user meta data, such as when the account was created, updated, or checked out. System identification data In the System Identification Data section, type additional identifying information for the user in the External ID box. This information can be used to link the person to corresponding information elsewhere in the organization, or to facilitate the consolidation of reporting of resource use beyond what Project Server provides. The following table describes the system identification data fields. Attribute Description GUID The unique ID associated with this user. External ID Can be used to link this user to external data. Active Directory GUID The unique ID for this user’s Active Directory account. Date Created The date this user account was created. Date last updated The date this user account was last updated. Checked out by The user who currently has this user account checked out. Checkout date The date this user account was checked out.
- 27. Security 19 Deactivate a user account At times, you may need to make Project Server user accounts unavailable. When you deactivate a user account, that user’s information and data remains in the database, but the user is unavailable for new assignments. The user account is inactive until it is reactivated. Deactivating a user account means that it can no longer be used to log on to Project Server 2010. Users cannot use this account to send assignment updates, request status reports, or delegate tasks. Once a user is deactivated, the Project Manager is prompted to reassign the user’s remaining work. This prompt occurs when the Project Manager opens the project in Microsoft Project Professional 2010. User accounts, when deactivated, are not actually deleted from the Project Server database. This ensures that any relationships that resource might have with project data can be preserved in case the account is reactivated later. The option to delete a user is available in the Database Administration section in Server Settings. However, deactivating a user to preserve data is recommended. After deactivating an account, the account cannot access Project Server 2010 until it has been reactivated. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. When using Active Directory synchronization, Project Server users not found in the Active Directory group being synchronized will be deactivated. If a user is to be removed from Active Directory but you do not want the account deactivated, select the Prevent Active Directory synchronization for this user check box under User Authentication on the Edit User page. Deactivate users Use this procedure to deactivate an active Project Server 2010 user account. To deactivate a user account 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings.
- 28. 20 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Users. 3. On the Manage Users page, in the Users list, find the user account you want to deactivate. (You can use the Search box to search for a specific user.) Click the check box next to the user name of the account you want to deactivate. Note that you can select multiple user accounts. 4. Click Deactivate Users. 5. A message box will appear asking confirmation. Click OK to deactivate the user account or user accounts. Reactivate a user account After deactivating a user account, you may need to reactivate it at some later time. Because the user information still exists in the Project Server database, you simply need to change the account status from Inactive to Active. Use this procedure to reactivate a deactivated Project Server 2010 user account. After you have performed this procedure, the reactivated account is able to access Project Server 2010. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. To reactivate a user account 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 5. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Users. 6. On the Manage Users page, in the Users list, find the user account you want to reactivate. (You can use the Search box to search for a specific user.) Click the user name of the account. 7. On the Edit User page for the selected user, in the Identification Information section, select Active from the Account Status drop-down list. 8. Click Save. Manage Groups A group is a container for users that can be assigned permissions in Microsoft Project Server 2010. Users automatically inherit the permissions of any group to which they belong. By adding users to groups, you can significantly reduce the amount of time spent managing user
- 29. Security 21 permissions. You can manage groups from the Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) Server Settings page. The following groups are created by default when Project Server 2010 is installed: Team Members Users have general permissions for using PWA, but limited project-level permissions. This group is intended to give everyone basic access to PWA. All new users are automatically added to the Team Members group. This group is associated with the My Tasks category. Project Managers Users have most global and category-level project permissions and limited resource permissions. This group is intended for users who maintain project schedules on a daily basis. This group is associated with the My Organization and My Projects categories. Resource Managers Users have most global and category-level resource permissions. This group is intended for users who manage and assign resources and edit resource data. This group is associated with the My Direct Reports, My Organization, My Projects, and My Resources categories. Executives Users have permissions to view project and Project Server data, but cannot make changes. This group is intended for high-level users who need visibility into projects but are not themselves assigned project tasks. This group is associated with the My Organization category. Team Leads Users have limited permissions around task creation and status reports. This group is intended for people in a lead capacity who do not have regular assignments on a project. This group is associated with the My Projects category. Portfolio Managers Users can create and edit data, but cannot perform Project Server administrative tasks such as adding users or creating groups. Portfolio Managers are able to view and edit all projects and resources in the organization. This group is associated with the My Organization category. Administrators This group is granted all available Project Server permissions. It is associated with the My Organization category. These default groups are designed to be used together with the five default categories. Create or modify a security group Seven default security groups are installed with Microsoft Project Server 2010. To better meet the security requirements of your own organization, you can also create custom groups by using the Manage Groups page on the Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site Server Settings page. Perform the following procedure to create a custom group in Project Server 2010. To add a security group 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Groups.
- 30. 22 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 2. On the Manage Groups page, click New Group. 3. Complete the required fields on the Add or Edit Group page. See the sections below for information about each area. 4. Click Save. Avoid creating unnecessary groups. Having a large number of groups and categories within an organization can lead to additional management complexity. Additionally, large numbers of groups and categories can stress the authorization system, which can affect performance. You can modify the information associated with any security group in Microsoft Project Server 2010. For example, you may need to modify the group for changes to users or categories, or for changes to the Active Directory group to which it is currently being synchronized. We recommend not modifying the default Project Server groups, but rather creating a new group with the same permissions and modifying the new group. Perform the following procedure to modify an existing group in Project Server 2010. To modify a security group 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Groups. 3. On the Manage Groups page, in the Group Name list, click the name of the group you want to modify. 4. On the Add or Edit Group page for the selected group, make your changes to the group information. See the sections below for information about each area. 5. Click Save. Group Information Use the Group Information section to specify a name and description for the group. Group information If you want to synchronize the membership of this group with an Active Directory group, click Find Group and search for the group that you want to synchronize. To stop synchronizing an existing group, click Clear Group.
- 31. Security 23 The following table describes the group information options. Attribute Description Group Name The name of the group. Description A description of the group. Active Directory Group to The name of the Active Directory group from which this Synchronize group gets its membership. If you configure this group to synchronize with an Active Directory group, the membership of this group will be synchronized with the Active Directory group specified on the schedule that you configure. Users Use the users section to specify which Project Server users are a member of this group. Available users and users in the group To add users to the group, select the users in the Available Users list, and then click Add. To remove users from the group, select the users in the Selected Users list, and then click Remove. If you have configured Active Directory synchronization for this group, the group membership is maintained by that mechanism. Any changes you make manually may be overwritten the next time the group is synchronized with Active Directory. The following table describes the options for users in the group. Attribute Description Available Users The users in Project Server that are not members of this group. Selected Users The users in Project Server that are members of this group. Categories Use the Categories section to define which security categories area associated with this group.
- 32. 24 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Categories options To associate a category with this group, select the category in the Available Categories list, and then click Add. To set the category-level permissions for a particular category, select the category in the Selected Categories list, and then click Allow for the permissions that you want to allow for this category/group combination. The following table describes the categories options for a group. Attribute Description Available Categories The categories that are not associated with this group. Selected Categories The categories that are associated with this group. Permissions for <category> The permissions that members of this group have within
- 33. Security 25 Attribute Description the selected category. This option appears when you select a category in the Available Categories list. Set permissions with To set the category permissions for the selected category Template from a template – such as Project Manager or Team Member – select the desired template from the dropdown list, and then click Apply. Global Permissions Use the Global Permissions section to configure global permissions for this group. Global permissions To allow a permission for the group, select the Allow check box for that permission. To deny a permission for the group, select the Deny check box for that permission. For a complete list of global permissions, see Appendix B, “Project Server 2010 Global Permissions.” Note If neither check box is selected for a permission, the user is not allowed the permission unless it is allowed in another group that the user is a member of, or it is allowed at the user level. If the Deny check box is selected for a permission, that permission is denied for all users in the group and cannot be allowed through other group or user settings.
- 34. 26 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Delete a security group If you no longer need a security group in Microsoft Project Server 2010, you can delete it. Before you delete a group, ensure that no other users or groups depend on it for required permissions. Security groups are permanently deleted, unlike deactivated user accounts (which can be reactivated). If you delete a security group and then find that you want to have it again, you must recreate it. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. Important We highly recommend not deleting the default Project Server groups. The Team Members group cannot be deleted. Delete a custom security group Perform the following procedure to delete a group in Project Server 2010. To delete a custom group 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Groups. 2. On the Manage Groups page, in the Group Name list, find the group you want to delete. Select the check box next to the group that you want to delete. Note that you can select multiple groups. 3. Click Delete Group. 4. A message box appears, asking for confirmation and noting that the group will be permanently removed. Click OK to delete the group. Active Directory Group Synchronization Project Server 2010 security group synchronization controls Project Server security group membership by automatically adding and removing users from specified Project Server security groups based on group membership in the Active Directory directory service. Each Project Server
- 35. Security 27 security group can be mapped to a single Active Directory group. This Active Directory group can, however, contain nested groups whose members will also be synchronized. The following actions can occur during a Project Server security group synchronization process: A new Project Server user account can be created based on an Active Directory account. An existing Project Server user can be removed from a Project Server security group. An existing Project Server user can be added to a Project Server security group. An existing Project Server user account's metadata (name, e-mail address, and so on) can be updated if it has changed in Active Directory. A previously inactive Project Server user account can be reactivated. Before you perform this procedure, confirm that: You have access to Project Server through Project Web Access with an account with the Manage Active Directory Settings and the Manage users and groups global settings. The Service Application service account for the Project Server instance has Read access to all Active Directory groups and user accounts involved in the synchronization. You can verify this account in the on the Service Application page on the Central Administration site. To configure security group synchronization Use this procedure to configure security group synchronization with Active Directory in Project Server 2010. The following table describes possible scenarios and corresponding actions that occur when security group synchronization takes place: Scenario Action The user exists in Active Directory and is a A new corresponding user account is created in member of the Active Directory group Project Server and is granted membership to the mapped to the current Project Server current Project Server security group. security group. The user does not exist in Project Server. The user is not a member of the Active The existing Project Server user is removed as a Directory group mapped to the current member of the current Project Server security Project Server security group. The user group. also exists in Project Server and is a
- 36. 28 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Scenario Action member of the current Project Server security group. The user exists in Active Directory and is a The existing Project Server user is given member of the Active Directory group membership to the current Project Server security mapped to the current Project Server group. security group. The user also exists in Project Server, but is not a member of the current Project Server security group. The user exists in Active Directory and is a The corresponding Project Server user member of the Active Directory group information is updated (if applicable). mapped to the current Project Server security group. The user also exists in Project Server and is a member of the current Project Server security group. User information has been updated in Active Directory. The user exists in Active Directory and is a If the Automatically reactivate currently member of the Active Directory group inactive users if found in Active Directory mapped to the current Project Server during synchronization option is selected in security group. The user also exists in Project Server, the account is reactivated and is Project Server, but as an inactive account. added to the current Project Server security group. If the option is not selected, the account remains inactive in Project Server. To configure security group synchronization 1. On the Project Web App Home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Groups. 3. On the Manage Groups page, in the Group Name column, click the name of the security group that you want to synchronize. 4. On the Add or Edit page for the group you selected, in the Group Information section, for Active Directory Group to Synchronize, click Find Group.
- 37. Security 29 5. On the Find Group in Active Directory page, in the Group Name field, enter all or part of the name of the Active Directory group which you want to synchronize with your security group. Click the button next to the Group Name field to search the Active Directory forest based on your search criteria. To select a group from a remote forest, type the fully qualified domain name of the group (for example, group@corp.contoso.com). You can synchronize to a security or distribution group of any scope (Local, Global, or Universal). Note The Active Directory forest that is search is displayed at the top of the Find Group in the Active Directory page. The forest is defined by the fully qualified domain name of the account for the Service Application on which the Project Server instance is running. 6. From the Group Name list, select the group with which you want to synchronize your Project Server security group. Click OK. 7. On the Add or Edit Group page, you should see the Active Directory group you selected in the Group Information section next to Active Directory Group to Synchronize. Click Save. 8. On the Manage Groups page, in the Group Name column, select the check box next to the security group that you just configured for synchronization. Then click Active Directory Sync Options.
- 38. 30 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Synchronize Project Server Groups with Active Directory 9. If you want to schedule synchronization to occur on a scheduled basis, on the Synchronize Project Server Groups with Active Directory page, in the Scheduling section, select Schedule Synchronization. Alternatively, you can choose to manually run the security group synchronization. If you prefer the manual option, skip the following step and continue to step 11. 10. In the Frequency fields, define the frequency at which you want synchronization to occur between the Project Server security group and the Active Directory group. This can be scheduled over a defined period of days, weeks, or months. Select a start date and time. 11. You can enable inactive user accounts to be reactivated if they are found in the Active Directory group during synchronization. To do so, in the Options section, select Automatically reactivate currently inactive users if found in Active Directory during synchronization. (For example, enabling this option would ensure that if an employee were rehired, the employee's user account would be reactivated). 12. Click Save to save the settings. Click Save and Synchronize Now if you want to synchronize your Project Server security group immediately. If you choose not to schedule the synchronization, you can rerun it manually when needed by returning to this page and clicking Save and Synchronize Now. 13. You can check the status of the security group synchronization by returning to the Synchronize Project Server Groups with Active Directory page for the specific security
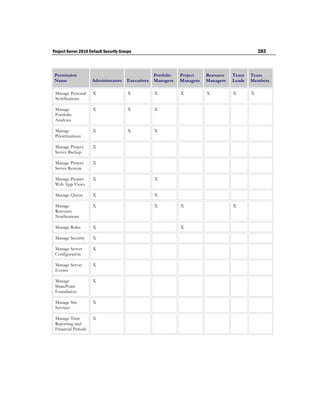
- 39. Security 31 group and reviewing the information in the Status section. It will contain information such as when the last successful synchronization occurred. Manage Categories Categories are the collections of projects, resources, and views to which users and groups in Project Server are granted access. Categories define which collections of specific data (projects, resources, and views) that these users and groups have access to. Categories also allow the administrator to filter data using security rules, like Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS), that can help organize and display data in specific ways. You can manually add projects and resources to categories by choosing them from lists, or you can use dynamic filters to automatically add them to categories. Any user associated with a category can be granted permission to the projects and resources in that category. You must have the Manage users and groups global permission to add, modify, or delete a group. Avoid creating unnecessary categories. Having a large number of groups and categories within an organization can stress the authorization system, which can affect performance. Microsoft Project Server 2010 creates five default categories during installation. These default categories enable Project Server to provide the most common layer of security for a hierarchical organization or matrix organization. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required in order to create, modify, or delete a category. Default category Default groups in the Description category My Tasks Team Members Primarily used by project resources who have assigned tasks. My Projects Project Managers Provides access to all projects that a user Resource Managers owns. Team Leads My Resources Resource Managers Intended for resource managers and is useful only after the Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is defined. My Direct Reports Resource Managers Intended for users who need to approve timesheets. My Organization Executives Used to grant access to all information in Portfolio Managers the organization. This category is intended Project Managers for members of a Project Management Office (PMO), executives in an organization, Resource Managers
- 40. 32 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Default category Default groups in the Description category Administrators and other key users who require the ability to view projects and resources across the entire organization. Create or modify a category In Microsoft Project Server 2010, you can add custom security categories as necessary to create a Project Server security model that meets the specific needs of users and groups in your organization. Avoid creating unnecessary categories. Having a large number of groups and categories within an organization can lead to greater administrative complexity. Additionally, large numbers of groups and categories can stress the authorization system, which can affect performance. If there are many users at the highest level of the RBS, consider adding them to a custom category that gives them visibility of all projects (avoiding dynamic rules). Top-level RBS users probably have access to all projects, so assigning them to this category avoids unneeded work by the authorization system. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete these procedures. To create a new category, perform the following procedure. To create a category 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Categories. 3. On the Manage Categories page, click New Category. 4. Complete the Add or Edit Category page. See the following sections for information about each setting. 5. Click Save. To modify an existing category, perform the following procedure. To modify a category 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Categories. 3. On the Manage Categories page, click the category that you want to modify. 4. Complete the Add or Edit Category page. See the following sections for information about each setting. 5. Click Save.
- 41. Security 33 Name and Description Use the Name and Description section to specify a name and description for the category. Category name and description The following table describes the name and description options for a category. Attribute Description Category Name The name of the category. This name must different be than that of other categories. Description Description of the category. Users and Groups Use the Users and Groups section to specify which users and groups are associated with this category. Category users and groups To associate a user or group with this category, select the user or group in the Available Users and Groups list, and then click Add. To remove the association between a user or group and this category, select the user or group in the Users and Groups with Permissions list and then click Remove. For easiest administration, only associate groups with categories. Attribute Description Available Users and Groups Users and groups that are not associated with this category. Users and Groups with Users and groups that are associated with this category. Permissions
- 42. 34 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide To select the category permissions for each user or group, select the user or group in the Users and Groups with Permissions list. This will display the category permissions for the selected group in this category. Category permissions for the Project Managers group Each user or group can be assigned distinct permission within a category. For a complete list of category permissions, see Appendix A, “Project Server 2010 Category Permissions.” Projects Use the Projects section to specify the projects that users associated with this category can view.
- 43. Security 35 Category / project association You can explicitly select projects that users with permissions in this category can view, or you can use one of the dynamic security options to have projects made available to users based on their relationship to the project or their RBS value. Attribute Description All current and future When this option is selected, users in this category can projects in Project Server see all projects in this instance of Project Web App. database Only the projects indicated When this option is selected, users in this category can view the projects in the Selected Projects list and any projects from the Available Projects list that the user has permissions to see using the dynamic permissions options. The dynamic permissions features only work when this option is selected. Available projects Projects that are not explicitly part of this category. Users may still be able to view these projects if any of the dynamic permissions options are configured to allow it. Selected projects Projects that users in this category can view. The User is the Project Gives users permissions on any project they own. Also Owner or the User is the gives Status Managers permissions on projects that Status Manager on contain assignments that they manage.
- 44. 36 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Attribute Description assignments within that Project. The User is on that Gives users permissions on any project where they are on project's Project Team the project team. Users do not need to have assignments on the project. The Project Owner is a Gives users permissions on any project that is managed descendant of the User via by resources subordinate to them in the Resource RBS Breakdown Structure (RBS) hierarchy. A resource on the project's Allows a user to view any project where a resource Project Team is a subordinate to the user in the RBS is on the project team. descendant of the User via Avoid using this rule for users who have many resources RBS under them in the RBS. If the resources under them are on many projects involving many categories, this stress on the authorization system can affect performance (for example, delay the loading of the Project Center page). The Project Owner has the Allows a user to view projects managed by persons that same RBS value as the have the same RBS value that the user has. User Resources Use the Resources section to specify which resources the users associated with this category can view.
- 45. Security 37 Category / resource association You can explicitly select resources that users with permissions in this category can view, or you can use one of the dynamic security options to have resources made available to users based on their relationship to the resource or their RBS value. Attribute Description All current and future When this option is selected, users in this category can resources in Project Server see all resources in this instance of Project Web App. database Only the resources When this option is selected, users in this category can indicated view the resources in the Selected Resources list and any resources from the Available Resources list that the user has permissions to see using the dynamic permissions options. Available Resources Resources that are not explicitly part of this category. Users may still be able to view these resources if any of the dynamic permissions options are configured to allow it. Selected Resources Resources that users in this category can view. The User is the resource Gives users permissions to view information about themselves (such as assignments). They are members of a Gives users permissions to view information for all
- 46. 38 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Attribute Description Project Team on a project resources in projects they own. owned by the User They are descendants of Gives users permissions to view information for all the User via RBS resources under them in the RBS. They are direct Gives users permissions to view information about descendants of the User resources that are directly under them in the RBS. via RBS They have the same RBS Gives user permissions to view information about value as the User resources that have the same RBS value. Views – Add to Category Use the Views – Add to Category section to specify views that users associated with this category can see. Global permissions To add a view to the category, select the Add check box for that view. To remove a view, clear the Add check box for that view.
- 47. Security 39 Delete a category In Project Server 2010, you can delete any existing custom category from the Manage Categories page in Microsoft Project Web App. Note Default Project Server categories cannot be deleted. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. Delete a custom category Perform the following procedure to delete an existing category in Project Server 2010. Caution Verify that the category you are deleting is the one you intend to delete. If you accidentally delete the wrong category, it is permanently deleted and will need to be recreated. To delete a category 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Categories. 3. On the Manage Categories page, in the Category Name list, find the category that you want to delete. Select the check box next to the category that you want to delete. Note that you can select multiple categories. 4. Click Delete Categories. 5. A warning message appears, noting that the category will be permanently removed. Click OK.
- 48. 40 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Manage Security Templates Security templates provide a method for you to quickly apply or reset predefined permission profiles to new or existing users, groups, and categories. By applying security templates, you can easily standardize the permissions that you assign according to user's role in the organization. A number of predefined security templates are created by default when Microsoft Project Server 2010 is installed. These align with the predefined groups. You can customize these security templates or create new security templates according to your needs. Creating custom templates requires planning. You must first identify the common Project Server usage patterns in your organization that are not reflected in the default Project Server security templates. This helps you to identify your requirements for custom security templates. Then, determine the permissions that the users who share the common Project Server usage patterns require. This defines the security template. Next, determine the set of projects, resources, views, and so on, that the users and groups require access to; this defines the security category. Create the custom security template and apply it to the group of users that share the common usage pattern. The permissions that you define in the custom security template enables users to access the Project Server security objects that they require. Project Server 2010 creates eight default security templates during installation: Administrators Executives Portfolio Managers Project Managers Proposal Reviewers Resource Managers Team Leads Team Members Each security template is given a set of default category and global permissions, based on the functions that each group typically does in an organization. As mentioned previously, when creating new security templates, you are allowed to copy the permissions for a default security template and then customize it to suit your needs. We recommend not modifying the default templates. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to create, modify, or delete a security template. Create or modify a security template In Microsoft Project Server 2010, you can group commonly used permissions into a security template and then use it to assign permissions to users, groups, and categories.
- 49. Security 41 The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. Perform the following procedure to create a template in Project Server 2010. To create a template 1. On the PWA home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Templates. 3. On the Manage Templates page, click New Template. 4. Complete the Add or Edit Template page. See the following sections for information about each setting. 5. Click Save. In Microsoft Project Server 2010, you can modify the permissions for any existing template in the Manage Templates page in Microsoft Project Web App Server Settings. As a best practice, do not make any changes to the default Project Server templates. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. Note Modifying a template does not make any changes to users, groups, or categories to which the template was applied in the past. Perform the following procedure to modify an existing template in Project Server 2010. To modify a template 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Templates. 3. On the Manage Templates page, in the Template Name list, click the template that you want to edit. 4. On the Add or Edit Template page, make your changes to the template. See the following sections for information about each setting. 5. Click Save. Name Use the Name section to specify a name and description of the template and, optionally, to select an existing template to copy the settings from an existing template into the new template.
- 50. 42 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Template name and Copy Template options If you choose a template from the Copy Template dropdown list, the values from that template are copied to this template. Important The values from the copied template will overwrite any existing values in this template. After you copy the template, you can modify the values as needed to meet your needs. If you do not copy a template, this template will be blank and you can modify the values as needed. Category Permissions Use the Category Permissions section to set the category permissions for this template. Category Permissions To allow a category permission for this template, select the Allow check box for that permission. If you do not select the Allow check box for a permission, that permission will not be allowed in the categories where you use this template, but could be allowed in other categories.
- 51. Security 43 To deny a category permission for this template, select the Deny check box for that permission. Global Permissions Use the Global Permissions section to set the global permissions for this template. Global Permissions To allow a global permission for this template, select the Allow check box for that permission. If you do not select the Allow check box for a permission, that permission will not be allowed in the groups where you use this template, but could be allowed in other groups. To deny a global permission for this template, select the Deny check box for that permission. Delete a security template In Microsoft Project Server 2010, you can delete any existing security templates from the Manage Templates page on the Microsoft Project Web App site. As a best practice, do not delete any of the default Project Server templates. The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure.
- 52. 44 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Delete a template Perform the following procedure to delete a template. To delete a template 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Manage Templates. 3. On the Manage Templates page, in the Template Name list, select the check box next to the templates that you want to delete. 4. Click Delete Template. A warning message appears, noting that the template will be permanently removed. 5. Click OK. Manage Project Web App Permissions You can use the Manage Project Web App Permissions page to control which global and category permissions are enabled on a given Microsoft Project Server 2010 instance. An administrator can use the Project Web App Permissions page to deny access to all Project Server 2010 users for a particular feature in Microsoft Project Professional or a Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) instance. If a Project Web App permission is disabled on this page, the equivalent global or category permission is disabled for users throughout PWA. All permissions on this page are enabled by default. For example, if you deny the Delete project permission, users throughout PWA cannot delete projects, regardless of whether they have the Delete project category permission. Important Before disabling a Project Web App permission, thoroughly consider the effects on your organization of doing so. If you want to turn off a permission for only some Project Web App users, verify whether you can do it by creating a custom group and denying the permissions you want to restrict.
- 53. Security 45 Disable Project Web App Permission The Manage users and groups global permission in Project Server 2010 is required to complete this procedure. Perform the following procedure to disable a Project Web App organizational permission in Project Server 2010. To disable a Project Web App permission 1. On the Project Web App home page, in the Quick Launch, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Security section, click Project Web App Permissions. 3. On the Project Web App Permissions page, in the Available Project Web App Permissions list, clear the Enable check box next to the permission that you no longer want to make available to Project Web App users. (All Project Web App permissions are enabled by default.) 4. Click Save. Enabling a previously disabled permission is simply done by selecting the Enable check box next to the permission that has been disabled. Manage Delegates Microsoft Project Server 2010 enables user delegation throughout all of Project Web App. This means that one user can act as another user in every part of Project Web App, regardless of the permission level difference of one user compared to the other.
- 54. 46 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Turn Delegation on or off The user delegation feature in Project Web App can be enabled or disabled globally, for all users and groups. When user delegation is turned on, you can set permissions to control the specific behavior of the feature in Project Web App. To turn delegation on or off 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Security, click Project Web App Permissions 3. In the Resource section, select the check box for the Manage Resource Delegates permission to turn on the user delegation feature within Project Web App. 4. Choose any additional delegation permissions that meet your organization's needs: Manage My Resource Delegations Select this check box to enable users to set up delegations for other users. Manage My Delegations Select this check box to enable users to create delegations for themselves. Can be Delegate Select this check box to enable users to actively become a delegate for another user, after a delegation has been created. 5. Click Save to save the permissions on the server. Set up who can act as delegate In Project Web App, there are user or group level permissions that enable you to determine which users or groups can act as delegates for other people. By default, the only group with these permissions turned on is the administrators group, so if you want users in your organization to be able to act as delegates, you'll need to set the appropriate permissions.
- 55. Security 47 To set permissions for a specific user 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. Under Security, click Manage Users. 3. Click the name of the user for which you are setting permissions. 4. On the Edit User page, expand the Global Permissions section. 5. In the Global Permissions section, under Resource, choose the appropriate permissions for this user. Can be Delegate Select the Allow check box for this permission to enable this user to actively become a delegate for another user. Manage My Delegations Select the Allow check box for this permission to enable this user to create his or her own delegations. Manage My Resource Delegations Select the Allow check box for this permission to enable this user to set up delegations for other users. 6. Click Save to save the permissions on the server. To set permissions for a group 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. Under Security, click Manage Groups. 3. Click the name of the group for which you are setting permissions. 4. On the Add or Edit Group page, expand the Global Permissions section. 5. In the Global Permissions section, under Resource, choose the appropriate permissions for this group.
- 56. 48 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Can be Delegate Select the Allow check box for this permission to enable members of this group to actively become delegates for other users. Manage My Delegations Select the Allow check box for this permission to enable members of this group to create their own delegations. Manage My Resource Delegations Select the Allow check box for this permission to enable members of this group to set up delegations for other users. 6. Click Save to save the permissions on the server. Set up who can have delegates assigned to them Categories are used to determine which users or groups can have delegates do work on their behalf. For a delegation to work properly, the user requesting the delegation must have the correct category permissions, and the user who will act as the delegate must have the correct individual user or group permissions. To set up who can have delegates assigned to them 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. Under Security, click Manage Categories. 3. Click the name of the category that contains the user or group for which you want to enable user delegation. 4. In the Users and Groups section, click the name of group or a specific user in the Users and Groups with Permissions box.
- 57. Security 49 5. In the permissions box that appears, scroll down to the Resource section, and select the check box for the Manage Resource Delegates permission to turn on the user delegation feature for that user or group. 6. Click Save to save the permissions on the server. Create a new delegation Creating a new delegation allows one user to work on behalf of another user, such as submitting a second user’s timesheet. To create a delegation 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. Under Security, click Manage Delegates. 3. On the interface ribbon click New 4. In the Set Delegation Period section, select the date range for the period during which the delegate will be able to manage work. 5. In the Set Delegation section, select the delegate that you want to manage work during the specified period. 6. In the Working on Behalf of section, select the user who requires a substitute. 7. Click Save to save the permissions on the server.
- 58. 50 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 2 Enterprise Data This chapter about Project Server 2010 Enterprise Data Administration contains the following sections: Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables Departments The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) Enterprise Global Enterprise Calendars Resource Center
- 59. Enterprise Data 51 Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables You can use Enterprise Custom Fields to help to establish consistency across all of your organization’s projects. That way you can ensure that fields and associated lookup tables are used in the same way for all projects, tasks, resources, and assignments. Enterprise Custom Fields can include custom formulas and can allow the use of lookup tables and graphical indicators. By using Enterprise Custom Fields effectively, you can help to customize Project Server 2010 to fit the unique needs of your organization. When you use Enterprise Custom Fields, all users in your organization have access to a standard set of fields, which enables operations to be applied the in same way across entire sets of projects. For example: You can customize project management to reflect your organization’s structure and processes. All users in your organization can have access to a standard set of fields, enabling the same operations to be completed across entire sets of projects. You can set Enterprise Custom Fields as required fields so that users are prompted to enter information in that field before saving. You can use Enterprise Custom Fields on a per-department basis. Because creating Enterprise Custom Fields can range from being simple to being very complex and time-consuming, it is important to correctly design your Enterprise Custom Fields. To determine the scope of Enterprise Custom Fields that your organization requires, consider the following questions:
- 60. 52 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide What words or phrases are used by stakeholders in your organization, such as return on investment (ROI), Key Performance Indicator (KPI), and so on? You might want to quantify and codify these concepts by means of Enterprise Custom Fields. Also consider the concepts behind the common words and phrases used by stakeholders in your organization. What are the user requirements in your organization? User requirements are frequently based on reporting requirements. How will you sort and select data? How will you use graphical indicators to help users identify the correct data? Understanding Enterprise Custom Fields You can use Enterprise Custom Fields to create a set of project management standards that can be applied across your organization and to enhance the capabilities of Project Server 2010. You can create Enterprise Custom Fields at the task, project, and resource level. It is important to determine which specific Enterprise Custom Fields your organization needs when you review your business requirements while planning your Project Server 2010 deployment. It is best to do this after you have performed a gap analysis by comparing the capabilities of Project Server 2010 against the business needs of your organization. For example, a group of executives in an organization wants to be able to view project data by department. In order to achieve this business requirement, they need to define a consistent method for identifying departments within the organization. In addition, if each department has a different accounting method or funding process, the executives might need to identify a method for defining this, as well. You can use the Project Departments or Resource Departments custom fields in conjunction with the Department custom lookup table, or any enterprise custom filed with the Department property set to accomplish this. The most important use for Enterprise Custom Fields is to enable organizations to enforce consistency across all projects. For example, if two project managers use different fields to identify a resource’s location, then users will be unable to identify when the same resource is assigned to projects managed by each project manager. Creating Enterprise Custom Fields Project Server Enterprise Custom Fields are created and maintained through the Server Settings page in Microsoft Project Web App (PWA).
- 61. Enterprise Data 53 New Custom Field page The New Custom Field page allows you to specify the options for a custom field. Use the following procedure to create a new enterprise custom field. To create Enterprise Custom Fields 1. On the PWA Server Settings page, click Enterprise Custom fields and Lookup Tables. 2. Under Enterprise Custom Fields, click New Field.
- 62. 54 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 3. Fill out the New Custom Field page with the custom field options that you want to use. See the descriptions for each field in the following sections. 4. Click Save. Name and Description Use the Name and Description areas to specify a name and description for the custom field. Custom Field Name and Description The following table describes the name and description fields. Attribute Description Name The name of the custom field. Description A description of the custom field. Entity and Type Use the Entity and Type areas to specify whether you want a Project, Resource, or Task custom field, and what data type the field should be. Custom Field Entities The following table describes each of the available entities. Attribute Description Project Select to create Enterprise Custom Fields that are applied at the project level. Resource Select to create Enterprise Custom Fields
- 63. Enterprise Data 55 Attribute Description that are applied at the resource level. Task Select to create Enterprise Custom Fields that are applied at the task level. The Type selection defines the data type of the custom field. The value you choose here will affect which options are available in the Custom Attributes, Calculation for Summary Rows, and Behavior section. Custom Field Types The following table describes the available custom field types. Attribute Description Cost Use custom cost fields to define currency data. For example, you can use a custom cost field to define a project’s Approved Budget. Date Use custom date fields to specify date-driven data. For example, you can create an Enterprise Custom Field called Project Approval Date, and use it to record the date on which a project is approved. Duration Use custom duration fields to define a duration. These are frequently defined as calculations that use custom formulas. For example, a custom duration field can enable your organization to define a way for a project manager to show and store the difference between a project’s original schedule and the actual schedule. Flag Use custom flag fields to define anything that can have only two choices for defining the data. For example, you might use a flag field to determine whether to display a field or to enable a macro that controls whether a particular set of data will be available in the project. Number Use custom number fields to define any numeric set of data or to perform a custom calculation by using a custom formula. For example, you might use a task-level field to record the estimated lines of code in a software development project or to compare a project’s actual cost to its proposed cost. Text Use custom text fields to define simple, non-hierarchical, alphanumeric
- 64. 56 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Attribute Description data. For example, you can create a custom text field called Project Status that includes options such as Initiated, Approved, In-Progress, Suspended, Cancelled, and Closed. Custom Attributes When you select a Project Text custom field, you have the option of specifying one or multiple lines of text for the custom field. Custom Attributes - text The following table describes the custom text options. Attribute Description Single line of text Select if you want the custom field to be a single line of text. This option is available only for Project Text fields. Multiple lines of text Select if you want the custom field to be multiple lines of text. This option is available only for Project Text fields. The project field created with this option is not visible in project information tab in Project Professional. This field however can be exposed via web based PDP page. You can choose to have a custom lookup table supply the values for a custom field. This allows you to control the values chosen for the custom field. You can: Choose whether to have a default value if no other is chosen Choose whether to allow multiple values to be selected from the lookup table Choose to restrict available values to those values in the table that have no subordinates The lookup table option is available when you have selected Text as the filed type. Custom Attributes – lookup table
- 65. Enterprise Data 57 The following table describes the lookup table options for custom fields. Attribute Description Lookup Table The name of the Enterprise Custom Lookup Table that you want to associate with this custom field. Once you have associated a lookup table with a field and have saved it, you will not be able to remove the lookup table relationship. Therefore, make sure you need the lookup table before making this association. Choose a values to use as If you want to have a default value included in this custom field a default when adding in cases where the user does not specify one, select this check new items box, and then select the default value. Default value The default value to be used in this field when users do not specify a value. To set the value, click the browse button and select the desired value. Only allow codes with no Select this option if you want to allow only values in the lookup subordinate values table that have no subordinate values (that is, values at the lowest level of each branch). Allow multiple values to Select this option if you want to allow users to select more than be selected from lookup one value from the lookup table. Once this selection has been table made and saved, it cannot be removed. Note If you plan to create a custom field that will refer to a lookup table, create the lookup table before creating the custom field. You can use formulas to define your own parameters for how your Enterprise Custom Fields will measure data or present information when they are used in a project. Formulas cannot be used with all types of Enterprise Custom Fields. The formula option is available with all field types.
- 66. 58 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Custom Attributes - formula Note Once a formula is associated with a custom field, it can be edited but it cannot be removed. To use a known formula, type the formula in the Edit formula box. To add a field to the formula, click Pick field, point to a field type, and then click the name of the field that you want to reference. For example, Baseline Finish and Finish in this example. To reference an existing Enterprise Custom Field, point to a field type, point again to a custom field type (such as Custom Date or Custom Finish), and then click the Enterprise Custom Field that you want. To use a function in the formula, click Pick function, click a function type, and then click the function that you want. Each function includes placeholder arguments that you can replace with the fields and values that you want to use.
- 67. Enterprise Data 59 To build a formula by using a standard set of operators, click Pick operator and choose the operator that you need. The formula can operate by using referenced fields, functions, or literal data. The following table describes the formula options. Attribute Description Enter formula Type the formula you want to use in the Enter formula text box. Insert field Use Insert field to insert a field (cost, date, duration, flag, number, or text) into the formula. Insert function Use Insert function to insert a function (conversion, date/time, general, math, Microsoft Project, or text) into the formula. Insert operator Use Insert operator to insert an operator (mathematical or Boolean) into the formula. Department You can select a department to be associated with a custom field. Selecting a department allows you to limit a user’s ability to see the custom field if they are not a member of that department. If you do not specify a department, then all users will be able to see the custom field.
- 68. 60 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Custom fields department selector The values available for Department are specified in the Department custom lookup table. Calculation for Summary Rows For entity types of Resource and Task, you can select options for the calculation of summary rows. Summary row calculation options Note that summary row calculation is not available with a field type of Text. The following table describes the options for summary task calculation. Attribute Description None Choose None if you do not want the custom field to be applied to summary and group summary rows. Rollup Choose Rollup to roll up the individual rows for the summary row. Use formula Choose Use formula to use a specific formula to calculate the summary row. You must specify the formula to use under Custom Attributes. Calculation for Assignment Rows For resource types of Resource and Task, you choose to use a roll down calculation for assignment rows. The following table describes the options for calculating assignment rows.
- 69. Enterprise Data 61 Attribute Description None Choose None if you do not want to roll down assignment rows. Roll down, unless Choose Roll down if you want data entered at task or resource level to manually specified be rolled down and copied to each assignment with the same value. Values to Display You can choose to display raw data or to have the data represented graphically. Values to display - data If you choose Graphical indicators, you can choose different criteria for Non-summary rows, Summary rows, and, if you are using an entity type of Project, Project summary. Graphical indicators options When you choose an option, further configurable parameters specific to that option will be displayed. The following table describes the options for graphical indicators. Attribute Description Non-summary rows Choose Non-summary rows to specify criteria for graphical representation of data rows that are not summary rows. Summary rows Choose Summary rows to specify criteria for graphical representation of summary rows. Project summary Choose Project summary to specify criteria for graphical representation of the project summary. When you configure graphical indicators, you can specify the exact value and comparison parameters that determine when a particular graphic will be used. The available comparison (test) parameters are: Equals
- 70. 62 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Does not equal Is greater than Is greater than or equal to Is less than Is less than or equal to Is within Is not within Contains Does not contain Contains exactly Is any value These are used to compare the data value with a threshold value that you specify to determine which graphic to display. For example, you can configure values greater than or equal to 50 to display a green indicator and values less than 50 to display a red indicator. Graphical indicators You can specify as many different images for different values as required. Add a new row to the table for each test/value comparison. Rows in the table will be evaluated from top to bottom and the image associated with the first row where the test/value combination is true will be displayed. The following table describes the graphical indicator options for non-summary rows. Attribute Description
- 71. Enterprise Data 63 Attribute Description Test Choose the operator (equals, less than, etc.) to apply to the field value to determine the image to use. Values Type the field value or a field reference (e.g., [cost]) that, combined with the operator in the test column, determines when to use the image in the Image column. Image Choose the image to display when the test/value combination is true. Move Use the move buttons to move a row up or down in the table. Show data values in Select the Show data values in ToolTips to show the field value in ToolTips the tool tip associated with the image. When using graphical indicators for summary rows, you can choose to inherit the graphical indicator settings that you have defined for non-summary rows. Graphical indicators – summary rows If you select the Inherit criteria from non-summary rows check box when configuring graphical indicators for summary rows, the graphical indicator parameters you configured for the non-summary rows will be used. Graphical indicators – project summary If you select the Inherit criteria from summary rows check box when configuring graphical indicators for project summary, the graphical indicator parameters you configured for the summary rows will be used. Behavior You can configure a custom field to be controlled by workflow or to require a value.
- 72. 64 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Behavior options If you choose to have the custom field controlled by a workflow, the required field option will not be available since that behavior will be controlled by workflow. The following table describes the options for configuring custom field behavior. Attribute Description Behavior controlled by Select this check box if you want the custom field behavior to workflow be controlled by workflow. Require that this field has Choose whether you want this to be a required field (that is, the information field cannot be left blank). This option is not available if the Behavior controlled by workflow option is selected. Creating Enterprise Custom Lookup Tables Consider using custom lookup tables for any Enterprise Custom Field for which standardization of data is the most important factor. For example, it might not be a good practice to allow users to enter any integer value in a custom Status field. One project manager might enter Started, and another might enter In-Progress, both indicating that the project has begun and is underway. Without using lookup tables, it is difficult to standardize terminology in your organization. For example, you might create a custom text field that is associated with Resources. To do this, you click the Resource option, select Text from the list, and rename it Manager. If you do not specify a lookup table for this custom text field, a user can enter any text value in the Manager field.
- 73. Enterprise Data 65 New custom lookup table page The New Lookup table page allows you to specify the options for a custom lookup table. Use the following procedure to create a new enterprise custom lookup table. To create Enterprise Custom Fields 1. On the PWA Server Settings page, click Enterprise Custom fields and Lookup Tables. 2. Under Lookup Tables for Custom Fields, click New Field. 3. Type a name for the lookup table in the Name box. 4. Fill out the New Custom Field page with the custom field options that you want to use. See the descriptions for each field in the following sections. 5. Click Save.
- 74. 66 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Type You must specify a data type for each lookup table. It is not possible to mix field types within a table. Lookup table types The table below describes the options for data types within a custom lookup table. Attribute Description Cost Each field in the table will be a cost value. Date Each field in the table will be a date value. Duration Each value in the table will be treated as a duration. Number Each value in the table will be a number. Text Each value in the table will be text. Choosing Text also allows a hierarchy of values to be specified if desired. Code Mask The code mask option only appears when a field type of Text has been selected. Code mask options The code mask allows you to specify what type of text characters will appear in the lookup table, the length of the string, and what characters to use to separate levels in a hierarchy. If you
- 75. Enterprise Data 67 are creating a hierarchical lookup table, you must specify a code mask for each level of the hierarchy. The following table describes the options available for configuring code masks. Attribute Description Code preview Displays a preview of the code mask for the table. Sequence Specify the type of text characters to allow. Choose Numbers, Uppercase characters, Lowercase characters, or Characters. Length Specify the maximum length of the string. Choose a number from 1 to 255 or Any. Separator Specify from one to three characters to use as a separator between levels of the table hierarchy. Lookup Table Use the Lookup Table section of the New Lookup table page to specify the values in the lookup table. Lookup table options Type each that you want in the lookup table in the Value column. Create as many rows as needed to accommodate the values that you want to include. Optionally, include a description for the value in the Description column. The following table describes the options for creating lookup table values. Attribute Description
- 76. 68 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Attribute Description Level Denotes the level in the hierarchy. This is a read-only field. Select the row and use the Indent and Outdent buttons to change levels. Value The value of the field. Description An optional description of what the field represents. Move Use the Move buttons to change the position of rows in the table. Select the row and click the Up or Down Move button to move a row. Display Use the display order options do specify how to sort the lookup table. If you order for choose By row number, the table will remain sorted as you specify it. If you lookup table choose to sort ascending or descending, the table will be sorted based on the values in the Value column. Departments The Department field is a new feature for Project Server 2010. Both projects and resources can have departments. The main purpose of departments is to act as a filter for what custom fields are displayed to users within given areas of Microsoft Project Professional 2010 and PWA. Departments allow for different business units to define and make visible their own set of custom fields. Departments are also used to filter OLAP databases so that only the data for that department is loaded. When configuring a cube, you can specify both the project and resource departments so that the database data is filtered based on these criteria. These values are specified in the OLAP Database Build Settings page. Also, within the OLAP database configuration, you can add the Project department field as a dimension to the Project and Tasks cubes. And you can add the Resource department field as a dimension to the Resource cube as long as the department field has not been converted to a multi-value field. With Project Server 2010, departmental custom fields help relieve the problem of too much information and too many choices. Departments help you manage the custom field list, and help you define, at a resource, task, or project level, which fields are required or not required. In Microsoft Office Project Server 2007 all custom fields are globally scoped, which means the fields are available to all users. In Project Server 2010, fields can be globally scoped or they can be scoped to a specific department. Departmental fields enable two primary functions: Filtering custom fields so that a user sees, by default, only those fields that are either global to the system or in the department that the user belongs to. Controlling which fields require input.
- 77. Enterprise Data 69 Example of departments in use Field Scope Department Required? ProjectCustomText1 Global - No ProjectCustomText2 Global - Yes ProjectCustomText3 Department Marketing No ProjectCustomText4 Department Marketing Yes ProjectCustomText5 Department Development Yes ProjectCustomText6 Department Development No If John Woods belongs to the Development department, then when he views areas of the product that have departmental custom fields enabled, he will see: ProjectCustomText1 ProjectCustomText2 ProjectCustomText5 ProjectCustomText6 John will be required to enter data into ProjectCustomText2 and ProjectCustomText5. Cindy White belongs to the Marketing department; when she views areas of the product that have departmental custom fields enabled, she will see: ProjectCustomText1 ProjectCustomText2 ProjectCustomText3 ProjectCustomText4 Cindy will be required to enter data into ProjectCustomText2 and ProjectCustomText4. By default, departments filter the list of custom fields that John Woods and Cindy White see. But the filter does not prevent them from viewing custom fields assigned to the other departments. Important Departmental fields are not tied into security. You cannot use them with security categories and groups to enable or disable fields and their functions. Instead, their main purpose is to filter out fields which are not useful for the target user. Department considerations for cubes Which cubes are No project department Project department specified filtered by which value specified No resource department All data is loaded for all Project non-timephased cube specified cubes Task non-timephased cube Issues cube Risks cube
- 78. 70 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Which cubes are No project department Project department specified filtered by which value specified Deliverables cube MSP_Project_WSS virtual cube MSP_Project_Timesheet virtual cube MSP_Portfolio_Analyzer virtual cube Assignment non-timephased cube Assignment timephased cube EPM timesheet cube Resource department Assignment non- Filtered by Project Department: specified timephased cube Project non-timephased cube Task non-timephased cube Assignment timephased Issues cube cube Risks cube Resource non- Deliverables cube timephased cube MSP_Project_WSS virtual cube Resource timephased cube Filtered by Resource & Project Department: Timesheet cube Assignment non-timephased cube MSP_Project_Timesheet Assignment timephased cube virtual cube EPM timesheet cube MSP_Project_Timesheet MSP_Portfolio_Analyzer virtual cube virtual cube MSP_Portfolio_Analyzer virtual cube Filtered by Resource Department: Resource no- timephased cube Resource timephased cube Timesheet cube
- 79. Enterprise Data 71 Cubes include assignments for resources in projects that belong to other departments or to no department. This ensures that all data is present when examining data such as a department's resources full calendar capacity. The subset of projects and resources will be used to filter at the project and timesheet level as follows: Project non-timephased: The data in this cube will be filtered by the departmental project list. Projects with assignments to the department’s resources will be included. Task non-timephased: Non-departmental tasks with assignments to the department's resources will be included. The full non-departmental project will not be included. All tasks for departmental projects will be included. Assignment non-timephased: Non-departmental project assignments for the department’s resources will be included. All assignments for departmental projects will be included. Assignment timephased: Non-departmental project assignments for the department's resources will be included. All assignments for departmental projects will be included. Deliverables: All deliverables owned by the filtered list of projects will be included. All deliverables to which the filtered list subscribes and the projects/tasks that subscribe to the filtered list's deliverables will be included. All deliverables offered by non-departmental projects that are subscribed to by departmental projects will be included. Issues: Issues connected to the filtered list of projects and tasks will be included. Risks: Risks connected to the filtered list of projects and tasks will be included. Resource non-timephased: Resources in the departmental list will be included. Resource timephased: Resources in the departmental list will be included. Timesheet: Timesheets for departmental list resources will be included.
- 80. 72 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide EPM Timesheet: Timesheets for departmental list resources will be included. Task assignments from projects outside the department will be included. Resources are described in three ways in the OLAP databases: Fact focus (timesheets, capacity) Associated with Facts (project task assignments) Owning Facts (project owner, issue owner, assignment owner) The departmental resource list is used to filter facts with focus (Timesheets). Consequently, a non-departmental resource will never have any timesheets or capacity in the OLAP database if the database has a resource filter. However the non-departmental resource will be in the Resource List dimension if it has association with a departmental project, and will only have the relevant assignment facts. Resources who own things that have separate dimensions (that is, Assignment Owner) do not have to be in the resource list. The Resource List dimension for a specific OLAP database contains: The departmental resources All resources with assignments to departmental projects Configuring departments Departments are configured using a built in Enterprise Custom Lookup Table called Departments. By configuring values in this table, you can define a hierarchy of departments for your organization.
- 81. Enterprise Data 73 Department custom lookup table Use the following procedure to add initial values to the Department custom lookup table or to modify it. To modify the Department lookup table 1. On the PWA Server Settings page, click Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables. 2. On the Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables page, under Lookup Tables for Custom Fields, click Department. 3. In the Code Mask section, create a code mask for each level of the hierarchy that you plan to have for the Department lookup table: a. In the Sequence column, choose Characters from the dropdown list. b. Keep the defaults for the Length and Separator columns.
- 82. 74 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. In the Lookup Table section, type a Value and optionally a Description for each Department. 5. If you are creating a hierarchy with more than one level, use the Indent and Outdent buttons to change the level values for each department as required for you hierarchy. 6. Click Save. The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a hierarchical structure typically based on the management reporting structure of your organization, although it can also be structured in other ways. The RBS can be an important element in your Project Server security model when it is used to define the reporting relationships among users and projects in your organization. When you specify an RBS value for each Project Server user, you can take advantage of the dynamic security options that can be defined for each security category.
- 83. Enterprise Data 75 RBS custom lookup table The RBS structure is defined by adding values to the RBS custom lookup table that is built in to Project Server 2010. Once you define the structure, you can assign RBS values to individual users by setting the RBS property in the user's account settings page. Once the RBS is configured, Categories can use RBS codes to dynamically determine which projects and resources particular users can view or access. Dynamic filtering based on RBS code can be applied to projects in the following ways: Users can see projects owned by their descendants in the RBS Users can see projects on which their descendants in the RBS are a resource Users can see projects owned by other users with the same RBS value Dynamic filtering based on RBS can applied to resources in the following ways: Users can see their descendants in the RBS Users can see their direct descendants in the RBS Users can see other users with the same RBS value Use the following procedure to create a new Resource Breakdown Structure or to modify an existing one. To modify the Resource Breakdown Structure 1. On the PWA Server Settings page, click Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables. 2. On the Enterprise Custom Fields and Lookup Tables page, under Lookup Tables for Custom Fields, click RBS. 3. In the Code Mask section, create a code mask for each level of the hierarchy that you plan to have for the Department lookup table:
- 84. 76 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide a. In the Sequence column, choose Characters from the dropdown list. b. Keep the defaults for the Length and Separator columns. 4. In the Lookup Table section, type a Value and optionally a Description for each Department. 5. If you are creating a hierarchy with more than one level, use the Indent and Outdent buttons to change the level values for each department as required for you hierarchy.
- 85. Enterprise Data 77 6. Click Save. Enterprise Global The Enterprise Global setting allows you to make changes to the Enterprise Global file in Project Professional 2010. The Enterprise Global file contains all custom enterprise objects that are available to your users (for example, views, tables, groups, filters, and reports). When a Project Professional user connects to Project Server 2010, the latest version of the Enterprise Global file is loaded and cached on the client computer. This allows the user to access all enterprise custom objects available on the server. Through the Enterprise Global file, you are able to enforce standards in your organization that can be applied to all project and resources that work with Project Server data. By using views, tables, filters, and other related elements contains in the Enterprise Global file, you can help to ensure effective standardization in your organization.
- 86. 78 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Decisions regarding what to include in the Enterprise Global file should be made at an organizational level. You should check with your Project Management Office (PMO) before making any significant changes to the Enterprise Global file. Note To be able to modify the Enterprise Global file, you must have the Save Enterprise Global permission Project Server 2010. To open the Enterprise Global file through the Enterprise Global setting: 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Configure Project Professional. 3. Project Professional will open the Enterprise Global file. The name of the project in the title bar will be “Checked-out Enterprise Global”. 4. Make changes to your custom objects through your Enterprise Global file. 5. After you have completed your changes, click File, and then click Save. 6. After Save has completed successfully, click File, and then click Close. 7. A dialog box will display asking if you would like to check-in the Enterprise Global file. Click Yes.
- 87. Enterprise Data 79 Note If users have Project Professional open when an updated Enterprise Global file is checked in to the server, the changes in the updated Enterprise Global file will not be available until Project Professional is closed and reopened. Important Make sure not to add into the Enterprise Global file any view, table, filter, grouping, reports, etc. that has the same name as an element that exists natively in Project. Verify that you give any new enterprise-wide elements a unique name that does not conflict. Enterprise Calendars Enterprise calendars capture the predefined working hours, holidays, and other schedule details within an organization. They are used to standardize the working time for all of an organization’s projects. In Project Web App, you can view a list of existing calendars, select a calendar to edit, or begin the process of creating a new calendar. However, to create or modify a calendar, you must have Project Professional 2010 installed on the computer that you are using to access Project Web App.
- 88. 80 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Create a New Calendar Project Server uses a standard enterprise calendar for scheduling, by default. Some organizations may use multiple calendars. For example, if some of your organization’s employees work in another country, those workers will likely observe different holidays, and so will need a different enterprise calendar for scheduling project work. You can create a new, blank enterprise calendar using Project Web App and Project Professional 2010. To create a new, blank enterprise calendar 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Enterprise Calendars. 3. On the Enterprise Calendars page, click New Calendar. 4. On the Windows Security dialog box, type your user name and password to connect to Project Server through Project Professional 2010, and then click OK. Note If you are using integrated Windows authentication and your Internet Explorer settings are set to automatically log you on, or if Project is already connected to the server using the correct profile, then you will not be prompted for credentials. Project Professional 2010 opens and displays the Change Working Time dialog box. 5. Type a name for the new calendar in the For calendar box.
- 89. Enterprise Data 81 6. Use the calendar with the Exceptions and Work Weeks tabs to modify the working and nonworking times for your organization. For more information, see the “Modify Working and Nonworking Times” section of this guide. 7. Click OK on the Change Working Time dialog box to save the new calendar to Project Server. 8. Close Project Professional 2010. Copy an Existing Calendar If an existing calendar has many of the same holidays and other calendar items that you want to use in a new calendar, you can base a new calendar on an existing calendar. Copy the existing calendar in Project Web App, and then modify the copy in Project Professional 2010. For example, if the standard calendar in your organization captures all of your organization’s unique holidays and events, but you need a separate calendar to reflect a 24/7 working schedule, you can copy the standard calendar and then modify it for the 24/7 schedule. To create a new calendar as a copy of an existing calendar 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Enterprise Calendars. 3. Click the row containing the calendar you want to copy, and then click Copy Calendar. 4. On the Copy Calendar dialog box, type a name for the new calendar in the Name box, and then click OK. The calendar is added to the list on the Enterprise Calendars page.
- 90. 82 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 5. Click the row containing the new, copied calendar, and then click Edit Calendar. If the Windows Security dialog box appears, log on to Project Server. Project Professional 2010 opens and displays the Change Working Time dialog box. 6. Use the calendar with the Exceptions and Work Weeks tabs to modify the working and nonworking times for your organization. For more information, see the “Modify Working and Nonworking Times” section of this guide. 7. Click OK on the Change Working Time dialog box to save the new calendar to Project Server. 8. Close Project Professional 2010. Edit an Existing Calendar As you are initially configuring Project Server, you can modify the default standard enterprise calendar to account for the working and nonworking times observed by your organization. You can modify any enterprise calendar at any time by selecting the calendar in Project Web App, and making changes in Project Professional 2010. To modify an existing enterprise calendar 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Enterprise Calendars. 3. Click the row containing the calendar you want to change, and then click Edit Calendar.
- 91. Enterprise Data 83 If the Windows Security dialog box appears, log on to Project Server. Project Professional 2010 opens and displays the Change Working Time dialog box. 4. Use the calendar with the Exceptions and Work Weeks tabs to modify the working and nonworking times for your organization. For more information, see the “Modify Working and Nonworking Times” section of this guide. 5. Click OK on the Change Working Time dialog box to save the new calendar to Project Server. 6. Close Project Professional 2010. Delete a Calendar If you find your organization is not using a specific enterprise calendar, you can easily delete it in Project Web App. To delete an enterprise calendar 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Enterprise Calendars. 3. Click the row containing the calendar you want to delete, and then click Delete Calendar. 4. When prompted, click OK to delete the selected calendar. Note If the calendar is currently in use, a notification will appear.
- 92. 84 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Modify Working and Nonworking Times When working with calendars in Project Professional 2010, there are a few different things you can do to accurately account for working and nonworking time in your organization. The following sections provide examples for each type of change, and walk you through the steps involved with making each change. Change a working day into a nonworking day Occasionally, you may need to turn a working day into a nonworking day. For example, if your organization observes specific days as holidays, you can turn those holidays into nonworking days. Project Server will not schedule work on nonworking days. To change a working day into a nonworking day 1. Click the date on the calendar that you want to turn into a nonworking day. 2. On the Exceptions tab, type a name for the nonworking day in the Name column. The Start and Finish columns are automatically populated with the date you clicked in Step 1.
- 93. Enterprise Data 85 Note While you can create multiple exceptions that contain a specific day, only the lowest-level exception will apply on that day. For example, you might have one exception that changes the standard working times for a month, and another exception that calls out a specific day within that month as a nonworking day. Because the single-day exception is at a lower level than the month-long exception, the single nonworking day exception will be applied on that day. You cannot create multiple single-day exceptions on the same day. Change a nonworking day into a working day There may be times when your organization has to work on what would otherwise be a nonworking day. For example, say your organization participates in a convention each year that takes place over a weekend. You can turn the weekend days of the convention into working days, so that Project Server knows to schedule work on those days. To change a nonworking day into a working day 1. Click the date on the calendar that you want to turn into a nonworking day.
- 94. 86 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 2. On the Exceptions tab, type a name for the working day in the Name column, and then press Enter. Note While you can create multiple exceptions that contain a specific day, only the lowest-level exception will apply on that day. For example, you might have one exception that changes the standard working times for a month, and another exception that calls out a specific day within that month as a nonworking day. Because the single-day exception is at a lower level than the month-long exception, the single nonworking day exception will be applied on that day. You cannot create multiple single-day exceptions on the same day.
- 95. Enterprise Data 87 3. Click the row you added for the working day, and then click Details. 4. Under Set working times for these exceptions, click Working times, and then set the working times for that day by adjusting the times in the From and To columns. 5. If your organization observes these working times on a regular basis (for example, once a month or once a year), under Recurrence pattern, choose whether these times should recur Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Yearly, and then set the following options: Daily Set the frequency for these working times. For example, every 10 days. Tip If you find that the working day exception is happening very frequently, you may find it easier to change the default calendar options under Schedule on the Project Options dialog box in Project Professional 2010. All calendars begin with these default days and times. It may be easier to change the default calendar options than to set up exceptions that recur frequently. Weekly Specify how often you want the working times to recur, and on what day of the week you want them to recur. For example, every two weeks on Saturday.
- 96. 88 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Monthly Choose what day of the month and at what monthly frequency you want the working times to recur. For example, day 15 of every 3 months, or the third Saturday of every 6 months. Yearly Choose what day of the year you want the working times to recur. For example, August 21, or the third Saturday of July. 6. Under Range of recurrence, choose the period when you want the recurrence to take place, if appropriate. Start Choose the date when you want the recurrence pattern to begin. End after If you want the recurrence to happen only a set number of times, choose End after, and then type the number of instances when the working times should occur. End by If you want the recurrence to happen only during a certain time period, choose End by, and then choose when the recurrence should stop. 7. Click OK.
- 97. Enterprise Data 89 Change the working times for a working day While the specific days on the calendar may be accurately accounted for as working and nonworking, there may be working days that use a different time schedule than the typical 8- hour work day. You can adjust the working times for a specific working day so that work is accurately scheduled on that day. To change the working times for a working day 1. Click the date on the calendar for the working day that you want to adjust. 2. On the Exceptions tab, type a name for the changed working day in the Name column, and then press Enter.
- 98. 90 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Note While you can create multiple exceptions that contain a specific day, only the lowest- level exception will apply on that day. For example, you might have one exception that changes the standard working times for a month, and another exception that calls out a specific day within that month as a nonworking day. Because the single-day exception is at a lower level than the month-long exception, the single nonworking day exception will be applied on that day. You cannot create multiple single-day exceptions on the same day. 3. Click the row you added for the changed working day, and then click Details. 4. Under Set working times for these exceptions, click Working times, and then set the working times for that day by adjusting the times in the From and To columns.
- 99. Enterprise Data 91 5. If your organization observes these working times on a regular basis (for example, once a month or once a year), under Recurrence pattern, choose whether these times should recur Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Yearly, and then set the following options: Daily Set the frequency for these working times. For example, every 10 days. Weekly Specify how often you want the working times to recur, and on what day of the week you want them to recur. For example, every two weeks on Saturday. Monthly Choose what day of the month and at what monthly frequency you want the working times to recur. For example, day 15 of every 3 months, or the third Saturday of every 6 months.
- 100. 92 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Yearly Choose what day of the year you want the working times to recur. For example, August 21, or the third Saturday of July. 6. Under Range of recurrence, choose the period when you want the recurrence to take place, if appropriate. Start Choose the date when you want the recurrence pattern to begin. End after If you want the recurrence to happen only a set number of times, choose End after, and then type the number of instances when the working times should occur. End by If you want the recurrence to happen only during a certain time period, choose End by, and then choose when the recurrence should stop. 7. Click OK. Change the working times for each day of a work week If your organization has a specific work week (or set of work weeks) when the working times are different from the default, you can make those changes to the working times for each day in a work week, during a set period of time. For example, if your organization does not use the default Monday through Friday, 8am to 5pm schedule, you can change the working times for each day in the work week to reflect your organization’s accurate schedule. To change the working times for each day of a work week 1. Click the date on the calendar when you want the changed working times to begin.
- 101. Enterprise Data 93 2. On the Work Weeks tab, type a name for the changed work week(s) in the Name column, and then press Enter. 3. Change the date in the Finish column for the row you just added, to reflect the last day that you want to include in the changed work week(s).
- 102. 94 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. Click Details. 5. Under Select day(s), click the day of the week that you want to use adjusted working times. Press Ctrl and click, or press Shift and click to select multiple days. 6. If you want to turn the selected day(s) into nonworking time, click Set days to nonworking time. 7. If you want to change the working times for the selected day(s), click Set day(s) to these specific working times, and then set the working times by typing in the From and To columns.
- 103. Enterprise Data 95 8. Click OK. Resource Center The Resource Center is a view in Project Web App that can be used to create new resources and modify existing ones. It can be accessed from the Server Settings page. Tip Depending on how your organization has Project Web App configured, you may also be able to access the Resource Center from the Quick Launch. Create a New Resource When you create a new Project Server user, you can choose to also make that user a resource. However, sometimes you may want to create a resource that cannot log on to Project Server. For example, you may want to add a material resource, such as a conference room, that has no need to be able to log on to Project Server. Project managers can still assign the resource to work, but if there is not any work to track, and the project manager can account for when the resource is actually used, there is not a need for that resource to also be a user. To create a new resource 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Resource Center. 3. On the Resources tab, in the Editing group, click New Resource.
- 104. 96 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. In the Type section, complete the following: Type Choose whether you are creating a Work, Material, or Cost resource. Budget If the resource is a budget resource, select the Budget check box. Generic If the resource is generic, meaning that you will use it for planning purposes and replace it with at least one named resource further in the planning process, select the Generic check box. 5. In the Identification Information section, complete the following: Resource can logon to Project Server Select this check box if you want the resource to also be a Project Web App user. Display Name Type the resource’s name in this box. This field is required. E-mail address If this resource has an e-mail address that he or she wants associated with project work, type the address in this box. RBS If your organization uses a resource breakdown structure (RBS), click the button next to this field and choose the appropriate RBS code for this resource from the list. Initials This field is automatically populated with the resource’s initials, based on the name typed in the Display Name box. If you want to use different initials to refer to this resource, type them in the Initials box. Hyperlink Name If this resource has an associated Web site, type the name of that site in this box. Hyperlink URL If this resource has an associated Web site, type the URL to that site in this box.
- 105. Enterprise Data 97 6. In the Assignment Attributes section, complete the following: Resource can be leveled If you want to enable project managers to balance this resource’s workload based on his or her availability and assignments (leveling), select this check box. Base Calendar Choose the calendar that most closely represents this resource’s overall availability. For example, if your organization has a base calendar that accounts for specific holidays or events, you can set that as this resource’s calendar, and work assigned to this resource will be scheduled around the calendar’s nonworking days. Default Booking Type Choose whether you want this resource to be Committed or Proposed when assigning work. Timesheet manager Type the name of the person who approves or rejects this resource’s timesheets, or click Browse to choose the timesheet manager from a list. Resources may not have separate timesheet managers. Default Assignment Owner Type the name of the person who approves or rejects this resource’s task progress, or click Browse to choose the assignment owner from a list. Resources may not have separate assignment owners. For example, if the resource is a conference room, and the project manager tracks the amount of time that the conference room is used, the assignment owner may be the project manager. Tip You can set the assignment owner within the project on an assignment-by-assignment basis. Earliest Available Choose the date when the resource becomes available to assign to tasks, if appropriate. If the resource does not have a set period of availability (that is, if he or she is always available), leave this blank.
- 106. 98 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Note The earliest and latest available dates correspond to the resource availability dates for a resource, as seen in Project Professional. Latest Available Choose the last date that the resource is available to work on tasks, if appropriate. If the resource does not have a set period of availability (that is, if he or she is always available), leave this blank. Standard Rate Type the resource’s standard pay rate in this box. Overtime Rate Type the resource’s overtime pay rate in this box. Current Max. Units (%) Specify the maximum amount of time that a resource is available for work, as a percentage. For example, if the resource is available full-time, type 100%. If the resource is available half-time, type 50%. Cost/Use If the resource has a flat fee associated with each use, type that cost in this box. For example, a van rental may require a flat fee upfront, with an added standard cost per mile. The flat fee is its cost per use.
- 107. Enterprise Data 99 7. In the Departments section, click the button next to the Resource Departments box, and choose which department(s) the resource is associated with. If the resource is not associated with a particular department, leave this blank. Tip Associating a resource with a department narrows down what the resource sees when using Project Web App. It can help the resource find what he or she is looking for more quickly, by removing things from other departments that do not apply to his or her work. 8. If your organization created codes for grouping and costing purposes, in the Group Fields section, complete the following: Group Type the name of the group in this box. Code Type the code for the group in this box. Cost Center Type the cost center code for the group in this box.
- 108. 100 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Cost Type Click the button next to the Cost Type field, and then choose the type of cost associated with this group. 9. In the Team Details section, click the button next to the Team Name box, and choose which team the resource belongs to, if appropriate. If the resource will be managing and delegating tasks that are assigned to the team, select the Team Assignment Pool check box. Tip Some organizations create a generic resource for each team, so that tasks assigned to the team first go to the generic resource. This way, no single resource takes on the task assignment before it is appropriately delegated. If you choose to use a generic resource in this way, set the assignment owner for the resource as the team manager, select the Team Assignment Pool check box, and choose the team from the Team Name list. 10. In the System Identification Data section, type additional identifying information for the user in the External ID box, if appropriate. For example, your organization’s HR department may use employee ID numbers to track data in their HR systems. By providing that ID number in the External ID box, you identify an association between the resource that you are creating and the HR department’s employee data. The External ID box can also be used to facilitate the consolidation of reporting of resource use beyond what Project Server provides. Tip If you are not sure whether you should be capturing any data in the External ID box, check with other departments in your organization to find out if it would be useful to connect resource data with other systems, or simply leave this box blank.
- 109. Enterprise Data 101 11. Click Save to create the new resource. Once a resource is added, you may find that you need to make changes to the resource’s information. Perhaps the resource had a rate change, or needs to use a different base calendar. To edit a resource 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Resource Center. 3. Select the check box in the left column for the row containing the resource you are editing. Tip If your organization has a lot of resources and you cannot easily find the one you want to edit, you can filter the Resource Center. On the Resources tab, in the Data group, click Custom Filter in the Filter list. Identify the parameters for the resource you are editing, and then click OK. 4. On the Resources tab, in the Editing group, click Edit Resource. 5. Make changes to the resource data, as needed, and then click Save. In some cases, several resources may require the same change. For example, if several resources use the same timesheet manager, and that person takes a job elsewhere, you will need to replace
- 110. 102 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide the timesheet manager for those resources with whoever steps in as a replacement. Project Web App supports bulk editing of several resources at once. You can bulk edit the Timesheet manager, Default Assignment Owner, RBS, Team Name, Cost Type, and Resource Departments fields. Tip Another good way to edit many resources simultaneously is by using Project Professional 2010. By making changes through the Project Professional 2010, you can add fields that you will not see if you make bulk changes through Project Server 2010, and you can also copy and paste from Microsoft Excel or another list. To make the same change to several resources simultaneously 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Enterprise Data, click Resource Center. 3. Select the check box in the left column for each row containing a resource you are editing. 4. On the Resources tab, in the Editing group, click Bulk Edit. 5. For each field that you want to edit, select the Apply Changes check box, to the left of the field, and then make your changes. Tip If you are having trouble remembering which resources you are editing, expand the Resources Selected section. This section displays a list of all resources that will be changed when you click Save. 6. Click Save to save your changes to all selected resources.
- 111. Database Administration 103 3 Database Administration This chapter about Project Server 2010 Database Administration contains the following sections: Delete Enterprise Objects Force Check-in Enterprise Objects Daily Schedule Backup Administrative Backup and Restore OLAP Database Management Delete Enterprise Objects You can delete enterprise objects from Project Server when they are no longer needed. You can delete the following types of objects from PWA: Projects Resources and users Status report responses Timesheets User delegates Delete projects When a project is no longer needed, you can delete it from Project Server. Note that this process deletes the project entirely from Project Server and it cannot be retrieved.
- 112. 104 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Delete project Use the following procedure to delete a project from Project Server. Important The project will be permanently deleted from Project Server. To delete a project 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Delete Enterprise Objects. 3. On the Delete Enterprise Objects page, select the Projects option. 4. Select one of the following options: Delete projects from Draft and Published databases to display a list of projects found in both the Draft and Published databases. Delete projects only from the Published database to display a list of projects in the Published database. Delete projects only from the Archived database to display a list of projects in the Archive database.
- 113. Database Administration 105 5. To delete the associated SharePoint site, select the Delete the associated Microsoft SharePoint Foundation sites check box. Note If you do not delete the associate SharePoint site and you save and publish a new project with the same name as the deleted project, the SharePoint site publish process will fail. 6. Select the project that you want to delete. 7. Click Delete. Delete resources and users When a resource or user is no longer needed, you can delete it from Project Server. Important We recommend not deleting resources from Project Server as this can affect the reporting of actuals. Instead, deactivate resources that are no longer needed. Delete resources and users Use the following procedure to delete resources and users from Project Server. Important The resources and users will be permanently deleted from Project Server. To delete resources and users 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Delete Enterprise Objects. 3. On the Delete Enterprise Objects page, select the Resources and Users option.
- 114. 106 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. Select the user or resource that you want to delete. 5. Click Delete. Delete status report responses When a status report response is no longer needed, you can delete it from Project Server. Note that this process deletes the status report response entirely from Project Server and it cannot be retrieved. Delete status report responses Use the following procedure to delete status report responses from Project Server. To delete status report responses 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Delete Enterprise Objects. 3. On the Delete Enterprise Objects page, select the Status Report Responses option. 4. Specify a period end date parameter (number of days, weeks, months, or years ago prior to which you want to delete all status report responses). 5. Click Delete. Delete timesheets When a timesheet is no longer needed, you can delete it from Project Server. Note that this process deletes the timesheet entirely from Project Server and it cannot be retrieved.
- 115. Database Administration 107 Delete timesheets Use the following procedure to delete timesheets from Project Server. To delete timesheets 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Delete Enterprise Objects. 3. On the Delete Enterprise Objects page, select the Timesheets option. 4. Select the range of timesheet end dates that you want to delete. 5. Click Delete. Delete user delegates When a user delegate is no longer needed, you can delete it from Project Server. Note that this process deletes the user delegate entirely from Project Server and it cannot be retrieved.
- 116. 108 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Delete delegates Use the following procedure to delete user delegates from Project Server. To delete 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Delete Enterprise Objects. 3. On the Delete Enterprise Objects page, select the User Delegates option. 4. Specify a period end date parameter (number of days, weeks, months, or years prior to which you want to delete all user delegates). 5. Click Delete. Force Check-in Enterprise Objects If an enterprise object has been checked out and the user who checked it out is unavailable or unable to check it back in, you can force a check-in. Important If you force check-in an enterprise object that a user is modifying, the modifications may be lost. You can force check-in the following types of enterprise objects: Enterprise projects Enterprise resources Enterprise custom fields Enterprise calendars Lookup tables for enterprise custom fields Resource plans
- 117. Database Administration 109 Enterprise object check-in options On the Force Check-in Enterprise Objects page in PWA Server Settings, choose the type of enterprise object that you want to check in to see a list of objects of that type that are checked out. Check-in Enterprise Projects You can force the check-in of an enterprise project that is checked out. Note that forcing a check-in of a project that is being modified by a user may result in the loss of those changes. We highly recommend that users check in projects normally and that you use force check-in only when absolutely necessary. Check in Enterprise Projects Use the following procedure to check in enterprise projects. To check in Enterprise Projects 1. On the Server Settings page, click Force Check-in Enterprise Objects. 2. From the Select the type of object you want to force check-in dropdown list, choose Enterprise Projects. 3. Select the projects that you want to check in. 4. Click Check In.
- 118. 110 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Check in Enterprise Resources You can force the check-in of an enterprise resource that is checked out. Note that forcing a check-in of a resource that is being modified by a user may result in the loss of those changes. Check in Enterprise Resources Use the following procedure to check in enterprise resources. To check in Enterprise Resources 1. On the Server Settings page, click Force Check-in Enterprise Objects. 2. From the Select the type of object you want to force check-in dropdown list, choose Enterprise Resources. 3. Select the resources that you want to check in. 4. Click Check In. Check in Enterprise Custom Fields You can force the check-in of an enterprise custom field that is checked out. Note that forcing a check-in of a custom field that is being modified by a user may result in the loss of those changes. Check in Enterprise Custom Field Use the following procedure to check in enterprise custom fields.
- 119. Database Administration 111 To check in Enterprise Custom Fields 1. On the Server Settings page, click Force Check-in Enterprise Objects. 2. From the Select the type of object you want to force check-in dropdown list, choose Enterprise Custom Fields. 3. Select the custom fields that you want to check in. 4. Click Check In. Check in Enterprise Calendars You can force the check-in of an enterprise calendar that is checked out. Note that forcing a check-in of an enterprise calendar that is being modified by a user may result in the loss of those changes. Check in Enterprise Calendars Use the following procedure to check in enterprise calendars. To check in Enterprise Calendars 1. On the Server Settings page, click Force Check-in Enterprise Objects. 2. From the Select the type of object you want to force check-in dropdown list, choose Enterprise Calendars. 3. Select the calendars that you want to check in. 4. Click Check In. Check in Lookup Tables for Enterprise Custom Fields You can force the check-in of an enterprise lookup table that is checked out. Note that forcing a check-in of a lookup table that is being modified by a user may result in the loss of those changes.
- 120. 112 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Check in Lookup Tables for Enterprise Custom Fields Use the following procedure to check in lookup tables. To check in Lookup Tables for Enterprise Custom Fields 1. On the Server Settings page, click Force Check-in Enterprise Objects. 2. From the Select the type of object you want to force check-in dropdown list, choose Lookup Tables for Enterprise Custom Fields. 3. Select the lookup tables that you want to check in. 4. Click Check In. Check in Resource Plans You can force the check-in of an enterprise resource plan that is checked out. Note that forcing a check-in of a resource plan that is being modified by a user may result in the loss of those changes. Check in Resource Plans Use the following procedure to check in resource plans. To check in Resource Plans 1. On the Server Settings page, click Force Check-in Enterprise Objects. 2. From the Select the type of object you want to force check-in dropdown list, choose Resource Plans.
- 121. Database Administration 113 3. Select the resource plans that you want to check in. 4. Click Check In. Daily Schedule Backup Daily Schedule Backup allows you to define your daily backup schedule to support item-level restore. Item-level backup is designed to work with, not instead of, SQL Server database backups. Project Retention Policy Versions The Project Retention Policy sets the number of versions of daily backups that will be kept for item level restore. Increasing the project retention policy will affect your archive database. The more versions in the Project Retention Policy that you keep, the greater the disk space required. Project Retention Policy Items In this area you can select whether or not you want to schedule item level backups for Projects, Enterprise Resource Pool and Calendars, Enterprise Custom Fields, Enterprise Global, View Definitions, System settings, and Category and Group settings. Delete resources and users Use the following procedure to delete resources and users from Project Server.
- 122. 114 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Important The resources and users will be permanently deleted from Project Server. To schedule an item level backup 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Daily Backup Schedule 3. On the Daily Backup Schedule page, set the Project Retention Policy to your desired number keeping in mind your disk storage capacity and backup needs. 4. Under Item change the Option dropdown from “Never” to “Schedule” for each item you would like to backup daily. 5. Under Time set the dropdown for the time for which you would like to have the system perform he daily backup. 6. Click Save.
- 123. Database Administration 115 Administrative Backup and Restore Administrative Backup allows you to manually backup individual item-level objects to your archive database. As an administrator, you can also restore items that have been accidentally deleted from the database using Administrative Restore. Administrative Backup On this page you can manually select the items that you wish to have backed up. Items that can be backed up are: Projects, Enterprise Resource Pool and Calendars, Enterprise Custom Fields, Enterprise Global, View Definitions, System settings, and Category and Group settings. Items For Backup To Backup data manually 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Administrative Backup. 3. In the Select Items section, select the check box next to each project item that you want to back up. 4. Click Backup. The items that you selected are backed up immediately. Administrative Restore Here you can individually select backed up items that you wish to restore.
- 124. 116 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Delete resources and users Use the following procedure to delete resources and users from Project Server. Important The resources and users will be permanently deleted from Project Server. To restore project items manually 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Database Administration, click Administrative Restore. 3. In the Item list, select the item that you want to restore. 4. If you selected Projects from the Item list, select the version of the project that you want to restore as the current working version of the project. Note The versions that are available for you to restore depend upon the number of backups that have been completed and the total number of backups that you have chosen to retain. Project Version Selection 5. Click Restore.
- 125. Database Administration 117 OLAP Database Management Through Microsoft Project Web App (PWA), multiple OLAP databases can be delivered that contain the specific resources, projects, and custom fields that each group within your organization requires for its particular group reporting needs. In Microsoft Project Server 2010, you can create multiple OLAP databases that have the following characteristics: They only contain data for projects and resources that they administer They only contain facts and dimensions that they select from the new integrated OLAP database management user interface They support departmental filtering to restrict which projects and resources are loaded into the OLAP database They include data for Inactive Tasks and User Scheduled Tasks They have support for Multiple Measure groups in a single OLAP database They contain field names in multiple languages to enable multi-language report creation Also, when a new OLAP database is created, the necessary Office Data Connections and Excel Reporting templates are created in the Business Intelligence Center in the Reports folder. This data-connected blank template will help you quickly create new reports that are based on the new OLAP database. Create an OLAP Cube OLAP cubes are managed on the OLAP Database Management page in Server Settings on a Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site. To create an OLAP cube, you must have the Manage Cube Building Service Global Permission. Perform the following procedure to create a new OLAP cube. Use the following procedure to create an OLAP cube. To create an OLAP cube 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Database Administration section, click OLAP Database Management. 3. On the OLAP Database Management page, click New. 4. Configure the settings on the OLAP Database Build Settings page. See the following sections for details on each setting. 5. Click Save.
- 126. 118 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Analysis Services Settings Use the Analysis Services Settings area to specify server and database name information along with, optionally, an extranet URL and description. Analysis Services Settings The following table describes the server and network settings for an OLAP cube. Attribute Description Analysis Services Server The name of the instance of Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) where you want to build the cube. Analysis Services Database to The name of the database that you want to create. be created Extranet URL The URL for the extranet site. Description A description of this OLAP cube. Project Department Use the Project Department area to specify which department to use to filter project data in the OLAP cube. OLAP Department settings (example) If you have projects assigned to departments, you can use this setting to specify the department that you want to have included in the cube. If no department is selected, then no departmental filtering occurs.
- 127. Database Administration 119 The selection of departments available is controlled by the Department custom lookup table. To allow multiple selections, modify the Project Departments custom field and select the Allow multiple values to be selected from lookup table check box. Note To deselect a department once selected, click the department again. Resource Department Use the Resource Department area to specify which department to use to filter resource data in the OLAP cube. OLAP Resource settings (example) If you have resources assigned to departments, you can use this setting to specify the department that you want to have included in the cube. If no department is selected, then no departmental filtering occurs. The selection of departments available is controlled by the Department custom lookup table. To allow multiple selections, modify the Resource Departments custom field and select the Allow multiple values to be selected from lookup table check box. Note To deselect a department once selected, click the department again. Database Date Range Use the Database Date Range area to specify the date range of projects, based on project start date, to include in the OLAP cube.
- 128. 120 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide OLAP database date range settings The following table describes the database date range options for an OLAP cube. Attribute Description Use the earliest project start Select this option if you want to base the date range of date and the latest project finish the cube on the earliest start date of any project and the date latest finish date of any project. Use the following last and next Select this option if you want the date range to be time units to calculate the date configured automatically based on a delta from the date range at the time that the OLAP on which the cube is built. In the Last and Next boxes, database is built type the number of days, weeks, or months that you want to use for the delta. Use the fixed date range Select this option if you want to use a fixed date range. specified below In the From and To boxes, type the dates that you want to use. OLAP Database Update Frequency Use the OLAP Database Update Frequency area to specify when and how often you want to build the OLAP cube. We recommend you choose a time of low system use because building cubes can be resource intensive.
- 129. Database Administration 121 OLAP database update settings The following table describes the database update settings for an OLAP cube. Attribute Description Update periodically Select this option if you want to schedule an update frequency. If this option is not selected, the cube is not updated automatically. Immediately retry the OLAP If the scheduled cube build fails because the queue is not database update if available, selecting this option causes the build job to start scheduled time fails because automatically when the queue becomes available instead of of queue down time waiting for the next scheduled time. Update every Select the number of hours, days, weeks, or months for the cube to be rebuilt. Start date Select the start date for the first automated cube build. Start time Select the start time for each automated cube build. Configure an OLAP cube OLAP cubes are managed on the OLAP Database Management page in Server Settings on a Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site. You can configure OLAP cube dimensions and measures, or you can configure the build settings of a cube. To configure an OLAP cube, you must have the Manage Cube Building Service Global Permission. There are two sets of parameters that can be configured on an existing OLAP cube: Dimensions and measures Cube build settings Use the following procedure to configure the build settings of an existing OLAP cube. To configure OLAP cube build settings 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings.
- 130. 122 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Database Administration section, click OLAP Database Management. 3. On the OLAP Database Management page, in the OLAP Database Name column, click the database that you want to configure. 4. Configure the settings on the OLAP Database Build Settings page: 5. Click Save. Use the following procedure to configure the dimensions and measures of an existing OLAP cube. To configure OLAP cube dimensions and measures 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Database Administration section, click OLAP Database Management. 3. On the OLAP Database Management page, select an OLAP database from the list, and then click Configuration. 4. Configure the settings on the Database Configuration page: 5. Click Save. Cube dimensions Use the Cube dimensions area to specify the custom fields that you want to add to the OLAP cube as dimensions. Cube selector Select a cube from the dropdown list to display the available and selected dimensions.
- 131. Database Administration 123 Cube dimension selector Choose the dimensions that you want to include in that cube in the Available fields list and click Add to include them in the cube. Do this for each cube in the Cube dropdown list. Cube measures Use the Cube measures area to specify the custom fields that you want to add to the OLAP cube as measures. Cube selector Select a cube from the dropdown list to display the available and selected measures. Cube measure selector Choose the measures that you want to include in that cube in the Available fields list and click Add to include them in the cube. Do this for each cube in the Cube dropdown list.
- 132. 124 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Built-in measures Use the Built-in measures area to select the build-in measures that you want to include in the OLAP cubes. Cube built-in measure selector The fields that you select will be added to the Project, Task, and Assignment cubes as measures. Inactive tasks Use the Inactive tasks area to specify if you want to include inactive tasks in the OLAP cubes. Inactive tasks selector If you want the cube to include inactive tasks, select the Include Inactive Tasks check box. Calculated measures Use the Calculated measures area to specify an MDX expression to define a calculated measure. Cube selector
- 133. Database Administration 125 Select the cube that you want to define an expression for from the Cube dropdown list. MDX expression tool Click Insert to add a custom MDX expression. For more information about MDX expressions, see Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) Reference (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms145506.aspx). Copy an OLAP cube OLAP cubes are managed on the OLAP Database Management page in Server Settings on a Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site. To copy an OLAP cube, you must have the Manage Cube Building Service Global Permission. Perform the following procedure to copy an existing OLAP Cube. Copying a cube will create a new cube with the same settings and configuration as the cube you copied. Copying a cube does not copy the Analysis Services database, but rather copies all the cube settings from which you can build a new Analysis Services database. Note You must specify a new name for the Analysis Services database after you copy the cube. Copy an OLAP cube Use the following procedure to copy an OLAP cube. To copy an OLAP cube 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Database Administration section, click OLAP Database Management. 3. On the OLAP Database Management page, select the cube that you want to copy, and then click Copy.
- 134. 126 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. On the OLAP Database Build Settings page, type the name of the server and the database that you want created and adjust any other desired settings. 5. Click Save. Delete an OLAP cube OLAP cubes are managed on the OLAP Database Management page in Server Settings on a Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site. To delete an OLAP cube, you must have the Manage Cube Building Service Global Permission. Perform the following procedure to delete an OLAP Cube. Note Deleting an OLAP cube in Project Server does not delete the OLAP database from Analysis Services. Delete an OLAP cube Use the following procedure to delete an OLAP cube. To delete an OLAP cube 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Database Administration section, click OLAP Database Management. 3. On the OLAP Database Management page, select the cube that you want to delete, and then click Delete. Build an OLAP cube OLAP cubes are managed on the OLAP Database Management page in Server Settings on a Microsoft Project Web App (PWA) site. OLAP cubes can be scheduled to be built on a regular basis. For more information, see Configure an OLAP cube (Project Server 2010). You can also start the build process manually. To build an OLAP cube, you must have the Manage Cube Building Service Global Permission. Perform the following procedure to build an existing OLAP cube.
- 135. Database Administration 127 Build an OLAP cube Use the following procedure to build an OLAP cube. To build an OLAP cube 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Database Administration section, click OLAP Database Management. 3. On the OLAP Database Management page, select the cube that you want to build, and then click Build Now.
- 136. 128 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4 Look and Feel Project Server 2010 supports customization of various user interface elements, including: Views Color and text formats of grouping levels within views Color and shape options for Gantt bars Links, or groups of links, included on the Quick Launch in Project Web App The options that are described in this chapter are available under Look and Feel on the Server Settings page in Project Web App. Server Settings page
- 137. Look and Feel 129 Manage Views Team members can view project information by selecting different views from the View list at the top of most pages within Project Web App. As an administrator, you can better meet the information needs of your organization by adding new views and changing the existing views. There are several different kinds of views in Project Web App, as listed in the following table. View Type Example Project Use this type of view to review the task, assignment, and resource details of a specific project when a team member clicks a project in the Project Center. Project Center Use this type of view to review information about all projects in the Project Center.
- 138. 130 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide View Type Example Resource Assignments Use this type of view to review details about specific resource assignments. Resource Center Use this type of view to review and compare all resources in the Resource Center.
- 139. Look and Feel 131 View Type Example My Work Team members use this type of view to review their task assignments. Resource Plan Managers use this type of view to create resource plans for their projects.
- 140. 132 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide View Type Example Team Tasks Team members use this type of view to review the tasks to which their team is assigned as a resource. Team Builder Managers use this type of view to create a team for their project (not a resource plan).
- 141. Look and Feel 133 View Type Example Timesheet Team members use this type of view to report time against the projects to which they are assigned. Portfolio Analyses Portfolio managers use this type of view to compare project proposals and determine which meet organizational goals.
- 142. 134 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide View Type Example Portfolio Analysis Project Selection Portfolio managers use this type of view to choose which proposals to approve as projects. Create a New View Options for creating a new view vary depending on the type of view you are creating. To create a new view 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, click Manage Views. A list of views is displayed. 3. Click New View. 4. In the Name and Type section, in the View Type list, select the type of view you are creating. 5. In the Name box, type the name of the new view.
- 143. Look and Feel 135 6. In the Description box, type a description of the new view. 7. Complete the remaining fields on the New View page. Not all options listed below are available for every view type. Task, Resource, or Assignment Choose the type of information to display in the view. Note These choices are only available when Project is selected as the View Type. Available fields and Displayed fields In the Available fields list, select the fields that you want to include in the view and then click Add. To reorder the fields, click a field name in the Displayed fields box, and then click Up or Down to move it within the list. Field width Click the name of a field in the Displayed fields box, and then type a number of pixels in the Field width box. You can repeat this for each field listed in the Displayed fields box. Setting this value is optional. Custom Label Click the name of a field in the Displayed fields box, and then type a display name in the Custom Label box. You can repeat this for each field listed in the Displayed fields box. Setting this value is optional. Note Custom labels are not available for the Resource Plan, Team Tasks, Team Builder, or Portfolio view. Make column read only Click the name of a field in the Displayed fields box, then select this check box to make that field read-only. Not all fields can be made read-only. Note Only the Timesheet and My Work views have this option. Gantt Chart format Select the type of Gantt chart that you want to use to display information. Note This option is only available for views that can show a Gantt chart. Left offset for the splitter bar Type an offset measurement in pixels to define the placement of the splitter bar in the view. Note This option is only available for views that can show a Gantt chart.
- 144. 136 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Show Select the number of outline levels that you want to display, by default, in this view. People using the view will be able to expand additional outline levels. Grouping format Select the grouping style that you want to use, and then define the order of grouping by using the Group by and Then by lists. For more information on setting up grouping formats, see “Grouping Formats,” later in this chapter. Sort by Select the fields by which you want to sort the view. In the Order list, select Ascending or Descending to define the order in which you want to sort the view. Filter Click this button to create or edit filters that you can apply to this view. For more information, see “To set up a filter for a view Filter Resources to user’s RBS branch Select this check box to display only those resources that fall under the resource breakdown structure branch of the resource looking at the view. Note This option is only available in Resource Center views. Available categories and Categories which access this view Click a category in the Available categories list, and then click Add to make the new view available to users in that security category. Tip If users are unable to see views that they think they should be able to see, a best practice is to first check that the correct categories are added to the view.
- 145. Look and Feel 137 8. After you have set all appropriate options for the new view, click Save. You can apply a filter to a view, so that data in the view is automatically narrowed down based on a set of criteria. To set up a filter for a view 1. On the New View page, in the Filter section, click Filter. The Custom Filter dialog box is displayed. 2. On the Custom Filter dialog box, select a field in the Field Name list and a test in the Test list, and then type a value to test for in the Value box. You can set a range of values by typing two values separated by a comma (,) in the Value box. Tip As you create the filter rules, a green check mark or a red X is displayed to the left of the rule, under the Valid? heading. If you see a red X next to a rule, hover over the X for more information on why the rule is not considered. 3. If the filter contains more than one row, select an operator in the And/Or column to start a new row. 4. Click OK when you have finished setting up filters. Modify a View After you have been using a view in Project Web App, you may find that it needs some fine- tuning. It may need a field added, or some adjustments to the security settings. You can easily modify existing views. To modify an existing view 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Manage Views. 3. Click the name of the view you want to modify, in the Name column.
- 146. 138 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Tip If you know the view type for the view you want to modify, you can collapse the other view types to reduce the number of views to scroll through. 4. Modify the fields and options for the view, and then click Save. Copy a View Sometimes it may be easier to create a new view by basing it on an existing view. You can select a view and copy it to create a new view. To create a new view as a copy of an existing view 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Manage Views. 3. Click a cell in the row for the view you are copying, and then click Copy View. Note Be careful NOT to click the name of the view, in the Name column. This will open that view for editing, instead of selecting it. 4. On the Copy View dialog box, type a name for the new view, and then click OK. The copied view is added to the table on the Manage Views page. 5. Scroll through the list of views to find the view you just created, and then click the name of the new view in the Name column. 6. Modify the fields and options for the new view, and then click Save.
- 147. Look and Feel 139 Delete a View If a view is not meeting your organization’s needs, or is just not being used, you can delete it from Project Web App. To delete a view 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Manage Views. 3. Click a cell in the row for the view you are deleting, and then click Delete View. Note Be careful NOT to click the name of the view, in the Name column. This will open that view for editing, instead of selecting it. 4. When prompted, click OK to delete the view. Grouping Formats You can change how rows (or levels) of information appear when task and resource information is grouped in the Project Center, Resource Center, Project, Task, Timesheet, and Assignment views. By changing the appearance of these grouping levels, you can highlight specific information for your team members. The following figure shows an example of grouping level formatting. The first-level groups are shaded in yellow with bold text, and the second-level groups are shaded in blue with bold text.
- 148. 140 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide To change the appearance of grouping levels 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Grouping Formats. A list of grouping formats appears. 3. In the Grouping format list, above the table, select the grouping level that you want to format. This will refresh the table and narrow down which levels are displayed. 4. To rename the selected grouping level, click Rename. Type the new name in the New name for the grouping format box, and then click OK. If you do not want to rename the selected grouping level, skip this step. 5. Use the lists in the Cell Color, Font Color, and Font Style columns to define the appearance of each grouping level. 6. Click Save, at the bottom of the page.
- 149. Look and Feel 141 After you have created a format for grouped task or resource information, you apply the formatting when a new view is created or modified. See “Manage Views,” earlier in this chapter, for more information. Gantt Chart Formats You can format the color, shape, and pattern of the Gantt bars in Gantt Charts views, Project Center views, and other views. To format a Gantt chart 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Gantt Chart Formats. 3. In the Gantt Chart list, above the table, select the name of the Gantt chart view that you want to format. 4. To rename the selected Gantt chart view, click Rename. Type the new name in the New name for Gantt Chart box, and then click OK. If you do not want to rename the selected Gantt chart view, skip this step. Note You cannot change the names of the individual Gantt bars. 5. For each bar type within the selected Gantt chart view (represented as a row in the table), choose the following: Display Select this check box to display this bar type on the selected Gantt chart view. Middle bar shape Select the shape you want to use for the bar type.
- 150. 142 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Bar Color Choose a color to fill in the selected bar shape. Bar Pattern Choose a pattern to fill in the selected bar shape. Start shape Choose a graphic to display at the start of a Gantt bar of this type. Start color Choose a color to fill in the start shape. End shape Choose a graphic to display at the end of a Gantt bar of this type. End color Choose a color to fill in the end shape. A preview of the resulting Gantt bar is displayed on the right side of the table. 6. Click Save, at the bottom of the page, below the table. Quick Launch The Quick Launch is the left navigation list in Project Web App.
- 151. Look and Feel 143 You can change how links behave on the Quick Launch, add new links or groups of links, reorder the links, or delete links or groups of links. Change Quick Launch Behavior Links on the Quick Launch can be displayed at all times, or you can choose to collapse links based on the context of what a user is currently viewing. You can also choose whether to include links from Microsoft SharePoint Foundation. To change how the Quick Launch displays links 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Quick Launch. 3. In the Edit Quick Launch section, under Expand menu items for, choose from the following options: All sections If you want to display all Quick Launch items at all times, regardless of what view is currently displayed, click All sections. Current section only If you want to collapse the Quick Launch items to just the top- level headings for sections that do not apply to the current view, click Current section only. For example, if you have selected Current section only, when you are looking at the Project Center, you will only see the Quick Launch items under the Projects heading.
- 152. 144 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. Select the Show menu items from Microsoft SharePoint Foundation check box to also show any applicable Quick Launch items that are part of SharePoint Foundation. If you clear this check box, only Project Web App items will be displayed on the Quick Launch. 5. Click Save. Add a New Link You can also add new links to the Quick Launch, to meet your organization’s needs. Links can be to views within Project Web App, intranet sites, or even external Web sites. To add a link to the Quick Launch 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Quick Launch. 3. Under Set Menu Item Details, click New Link. 4. Type a name for the link in the Custom link name box. This is the text that will appear linked on the Quick Launch. 5. Type the URL for the link in the Custom Web address box. 6. In the Heading section, choose the placement for the new link: If you are creating a new heading link for the Quick Launch, similar to the Projects and My Work headings, select New Heading. If you are creating a link to be included below an existing heading, select the existing heading from the list. The link will be indented below the selected heading.
- 153. Look and Feel 145 7. If you want to hide the new link from the Quick Launch, click No in the Display link in Quick Launch list. For example, if you are creating a new group of links below a new heading, you can choose to hide the new heading, then create all of the new links below the heading and set those to display. When you have the group of links ready to go, you can change the Display link in Quick Launch setting for the new heading to Yes, and the group of links is added to the Quick Launch. 8. Click OK to add the link to the Quick Launch. Modify an Existing Link If a link on the Quick Launch is not pointing to the right place, is not categorized under the right heading, or needs to be temporarily hidden, you can easily make those changes. To modify an existing Quick Launch item 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Quick Launch. 3. Under Set Menu Item Details, click the name of the link you want to modify, in the Name column. Tip If you have a long list of Quick Launch items to scroll through, you can collapse the headers to hide the links you do not want to modify. 4. Modify the link name, URL, and/or display option for the link, and then click OK. Reorder Quick Launch Items As you use Project Web App, you may find that the links on the Quick Launch would be more helpful if they appeared in a different order. You can reorder the links to meet your organization’s needs. To reorder the links on the Quick Launch 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Quick Launch.
- 154. 146 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 3. Under Set Menu Item Details, click a cell in the row for the Quick Launch item you are moving, and then click Move Up or Move Down. If you select a heading, all items indented below the heading will move with it. Note Be careful NOT to click the name of the link, in the Name column. This will open that link for editing, instead of selecting it. Delete a Link If you find that your organization is not using a link that is currently included on the Quick Launch, you can easily remove it. To delete a link from the Quick Launch 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Look and Feel, click Quick Launch. 3. Under Set Menu Item Details, click a cell in the row for the Quick Launch item you are deleting, and then click Delete Link. If you select a heading, all items indented below the heading will also be deleted. Note Be careful NOT to click the name of the link, in the Name column. This will open that link for editing, instead of selecting it. 4. When prompted, click OK to delete the link, or group of links, from the Quick Launch.
- 155. Time and Task Management 147 5 Time and Task Management Site administrators and others with appropriate permissions can configure how timesheets and task status are captured and handled in Project Server 2010. This includes: Setting up fiscal periods and time reporting periods Adjusting timesheets Setting up timesheet line classifications Choosing the right timesheet settings Configuring administrative time categories Choosing task status settings Preventing certain tasks from being updated The options that are described in this chapter are available under Time and Task Management on the Server Settings page in Project Web App.
- 156. 148 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Server Settings page Fiscal Periods Fiscal periods define the start and beginning dates of the business calendar. They are used to calculate financial statements on an annual basis. By setting up fiscal periods in Project Server 2010, you provide a way to map project work against your organization’s fiscal planning structure. Once set up, you can use fiscal periods as a dimension in your OLAP cubes. Define Fiscal Periods Using Project Web App, you can easily define the fiscal periods for a specific year. By creating the fiscal periods in bulk, you can base them off of several different models, and Project Server will calculate the dates accordingly. For example, if your organization divides each quarter into three periods—one that is four weeks long, followed by one that is five weeks long, and then another that is four weeks long— you can specify this model in Project Web App, and Project Server will create fiscal periods for the year according to that schedule. So, if the fiscal year begins on January 1, 2011, the first quarter will have three periods: Period 1: 1/1/2011 – 1/28/2011 Period 2: 1/29/2011 – 3/4/2011 Period 3: 3/5/2011 – 4/1/2011
- 157. Time and Task Management 149 To set fiscal periods in Project Web App 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Fiscal Periods. 3. In the Manage Fiscal Period section, click the year that you want to define as the fiscal period, and then click Define. 4. In the Define Fiscal Period Start Date section, type the date on which the fiscal year should begin, or select it using the date picker. 5. In the Set Fiscal Year Creation Model section, select a formatting method for the fiscal period: 4,5,4 Method This fiscal quarter method sets a four-week fiscal period, followed by a five-week fiscal period, and then another four-week fiscal period. 4,4,5 Method This fiscal quarter method sets a four-week fiscal period, followed by another four-week fiscal period, and then a five-week fiscal period. 5,4,4 Method This fiscal quarter method sets a five-week fiscal period, followed by a four-week fiscal period, and then another four-week fiscal period. 13 months This method sets each fiscal period as four weeks. Standard calendar year This method sets each fiscal period according to the standard 12 month year, beginning on January 1. Note If you want to use a different model for your organization’s fiscal year, use the steps in this procedure to choose a model that is closest to what you would like your fiscal year to look like. Once you have saved, you can go back and modify the calendar dates to refine the schedule to meet your organization’s needs. 6. In the Define Period Naming Convention section, create a unique name for the periods by entering: Prefix A prefix of up to 15 characters. Next Sequence Number A sequence number of up to six digits. Suffix A suffix of up to 15 characters. Tip As you enter a naming convention in the Prefix, Next Sequence Number, and Suffix fields, an example of the final naming convention is displayed below the fields, next to Sample.
- 158. 150 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 7. Click Create and Save. On the Fiscal Periods page, the fiscal period will be displayed with the individual periods showing in the Adjust Fiscal Months grid. After defining a fiscal period, you can edit it by using the Adjust Fiscal Months grid. To refine the fiscal period dates 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Fiscal Periods. 3. In the Manage Fiscal Period section, select the year that you want to adjust. 4. In the Adjust Fiscal Months section, in the End Date column, click the end date that you want to modify, and then use the date picker to choose a new end date. Start and end dates for periods following the modified end date will be automatically adjusted so that all periods are contiguous. 5. Click Save.
- 159. Time and Task Management 151 Delete Fiscal Periods After you have initially defined the fiscal periods for your organization, you may decide that a 13 month schedule would work better, or that you would prefer a 5,4,4 schedule over the 4,5,4 schedule that you initially selected. Instead of redefining each date, it may be easier to delete the fiscal periods altogether and start over from scratch. To delete the fiscal period for a specific year in Project Web App 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Fiscal Periods. 3. In the Manage Fiscal Period section, select the year that contains the fiscal periods you want to delete. 4. In the Adjust Fiscal Months section, click Delete. All periods are deleted, and the year returns to an Undefined status. Once you have deleted the fiscal periods for a year, you can redefine them using the process outlined in the “Define Fiscal Periods” section. Time Reporting Periods Time reporting periods define the start and end dates used for each timesheet and task status report. You can create several time reporting periods in bulk to set them up, and then insert or delete individual periods, as necessary. For example, you can create several time reporting
- 160. 152 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide periods for an entire fiscal year, and then modify those periods, as needed, to meet the individual needs of your organization. Create Bulk Time Reporting Periods Rather than creating each time reporting period individually, you will save yourself quite a bit of time if you create them in bulk, using parameters for how many periods to create, when the first period should begin, and how long each period should last. To create several time reporting periods at once 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Time Reporting Periods. 3. In the Define Bulk Period Parameters section, enter the following: Number of periods to be created Type the number of time reporting periods you want to create at one time. If you want to create time reporting periods for each week in a year, leave this set to 52. Date the first period starts Type the date on which you want the first time reporting period to start, or use the date picker to choose a date. Project Server will calculate the dates for all subsequent periods, based on the date selected in this field. Note Be sure to select the correct day of the week, as all time reporting periods will be based on this date. Length of the standard period (days) Type the number of days in each time reporting period. If you want to use one-week time reporting periods, leave this set to 7. 4. In the Define Batch Naming Convention section, create a unique name for each of the periods by entering: Prefix A prefix of up to 20 characters. Next Sequence Number A sequence number of up to six digits. Suffix A suffix of up to 20 characters. Tip As you enter a naming convention in the Prefix, Next Sequence Number, and Suffix fields, an example of the final naming convention is displayed below the fields, next to Sample.
- 161. Time and Task Management 153 5. Click Create Bulk to create the time reporting periods you specified. Note The Status column for all new time reporting periods is set to Open. Only a Project Server administrator can close a period. It is possible to restrict future timesheets from being submitted. See the “Timesheet Settings and Defaults” section for more information. 6. To make changes to a period label, date, or status, click in the grid in the Create Periods section, and then enter the modifications. See “Insert or Delete Time Reporting Periods” for more information. 7. Click Save. Insert or Delete Time Reporting Periods Occasionally, you may need to insert an additional time reporting period. For example, if the current fiscal year uses Monday-Sunday time reporting periods, and you have decided that the next fiscal year will use Sunday-Saturday time reporting periods, you may need to insert a shortened period to transition between the two models. To insert a time reporting period 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Time Reporting Periods. 3. In the Create Periods section, scroll through the list to find where you want to insert a new time reporting period, and then click the nearest existing period. 4. Click Insert Before or Insert After to create a new row for the period you are inserting.
- 162. 154 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 5. In the Period Label column, replace the New Period text with the name of the inserted period. 6. Replace the dates in the Start Date and End Date columns, if necessary. 7. If the inserted period is not currently open for resources to report data, select Closed in the Status column. 8. Click Save. You may also find that you occasionally need to delete existing time periods. For example, if your organization has already set up one-week time reporting periods for the entire year, and partway through the year you decide to switch to two-week time reporting periods, you will need to delete the remaining one-week periods, and recreate the rest of the year as two-week periods. To delete a time reporting period 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Time Reporting Periods. 3. In the Create Periods section, click the row for the time period you want to delete, and then click Delete. Important To protect project data provided by team members, time reporting periods that have associated timesheets cannot be deleted. Because it is common for time reporting periods to have associated timesheets, it is unlikely that you will be able to delete past time reporting periods.
- 163. Time and Task Management 155 4. Click Save. Timesheet Adjustment Occasionally, a resource will identify changes that need to be made to a timesheet after the timesheet has been submitted and approved. People with the appropriate permissions can adjust timesheet data. To adjust timesheets 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Timesheet Adjustment. 3. Choose filter options to help you display the timesheet you want to adjust: Approved by me Choose this option to display only timesheets that you have approved. Available timesheets to adjust Choose this option to display all timesheets available for adjustment. My Resources Unsubmitted Timesheets Choose this option to show all timesheets for resources assigned to your projects. This option may display a very long list of timesheets. You can use the options to the right of the line in the shaded filter section to narrow down the list.
- 164. 156 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Date Use this option in combination with Approved by me, Available timesheets to adjust, or My Resources Unsubmitted Timesheets. Select the Date check box, and then choose whether you want to filter for a specific Fiscal Period, or a Custom Date Range. Resources Use this option in combination with Approved by me, Available timesheets to adjust, or My Resources Unsubmitted Timesheets. Select the Resources check box, and then choose whether you want to filter for a specific Cost Center, and/or a specific Resource Name. 4. Click Apply, on the far right side of the shaded filter section, to filter the list of timesheets using the options you selected. 5. Click the name of the timesheet you want to adjust, in the Timesheet Name column. This opens the timesheet. 6. Make adjustments to the timesheet, as necessary. Rows that you have adjusted will show as Not Submitted in the Process Status column, indicating that the data for those rows was not submitted by the resource. 7. On the Timesheet tab of the ribbon, in the Actions group, click Save. Line Classifications Timesheet line classifications are used to report different types of time against the same task assignment. For example, your organization may have different classifications for Travel, Training and Standard (default) work. Using classifications enables the timesheet user to add the same task assignment once per classification type. Note The Standard line classification is required, even if all work on the task assignment is being reported against timesheet lines with other classifications.
- 165. Time and Task Management 157 By default, all timesheet lines use the Standard (or default) line classification. Resources can manually change a timesheet line to use one of the additional line classifications you have configured. To create a new timesheet line classification 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Line Classifications. 3. In the Edit, Enter Line Classification section, click New Classification. 4. In the grid, type a new name and description that identifies the timesheet line classification for team members. 5. Click Save. If you no longer want resources to be able to use a classification in timesheets, but that classification has been used in previous timesheets, you can make the classification inactive. This will maintain the classification in previous timesheets, for historical reporting purposes, but prevent it from being available in future timesheets. To inactivate an existing timesheet line classification 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Line Classifications. 3. In the Edit, Enter Line Classification section, choose Inactive in the Status column for the line classification you no longer want available to resources. Note The Standard line classification cannot be inactivated. 4. Click Save. If a line classification has never been used on a timesheet, you can delete it from Project Server altogether. To delete an existing timesheet line classification 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Line Classifications. 3. In the Edit, Enter Line Classification section, click the row for the line classification you are deleting, and then click Delete Classification.
- 166. 158 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. Click Save. Timesheet Settings and Defaults Site administrators can choose several different options to control how resources enter time on their timesheets, and whose approval is required. The Timesheet Settings and Defaults page is also where you choose whether your organization will use Single Entry Mode, a feature new to Project Server 2010 that combines task status updates with timesheets in one view. To configure timesheet settings and defaults 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Timesheet Settings and Defaults. 3. In the Project Web App Display section, select the The timesheet will use standard Overtime and Non-Billable time tracking check box to enable team members to submit overtime and non-billable time. If you do not want team members to be able to submit overtime or non-billable time, clear this check box. 4. In the Default Timesheet Creation Mode section, specify which data should be included in the default timesheet: Select Current task assignments to pre-populate timesheets with information about the team members' tasks assignments. Select Current projects to pre-populate timesheets with information about the team members' current projects. Select No prepopulation to create blank timesheets for team members. 5. In the Timesheet Grid Column Units section, specify whether you want timesheet columns to represent Days or Weeks. If you choose Weeks, each column in a timesheet represents 7 days, and the date in the column represents the first day of the week. 6. In the Default Reporting Units section, specify whether team members report time within each timesheet column in Hours or Days. 7. To specify how many hours constitute an entire day's worth of work, type the hours in the The number of hours in a standard timesheet day is box.
- 167. Time and Task Management 159 8. To specify how many hours constitute a standard work week, type the hours in the The number of hours in a standard timesheet work week is box. 9. In the Hourly Reporting Limits section, specify the maximum and minimum hours allowed in a timesheet, as well as the maximum number of hours allowed to be reported in a day. If team members report time beyond these limits, errors will appear on their timesheets when they submit them. Note You may need to put some restrictions on how time is entered based on accounting systems, customers, or internal business policies. Also, if your organization uses team resources, remember this when setting the maximum and minimum values in the Hourly Reporting Limits section. If you don't want to set a maximum or a minimum hourly reporting limit, type 999 in the Maximum Hours per Timesheet box to represent unlimited hours, or type 0 in the Minimum Hours per Timesheet box to represent no minimum time. Typing either of these options effectively turns off reporting limits. 10. In the Timesheet Policies section, specify the following: Select the Allow future time reporting check box to enable team members to record time for periods in the future. Select the Allow new personal tasks check box to enable team members to create as many personal tasks as needed. This time is not mapped to any Project Server project or task. Personal tasks will not show up outside of a team member’s timesheet and/or task status. Select the Allow top-level time reporting check box to enable team members to report time against summary tasks. If this check box is cleared, team members must report time against lower-level tasks, and those values will roll up to the summary level. Under Task Status Manager Approval, click Enabled to allow project managers to coordinate or approve/reject timesheet lines on a per-line basis. If you select Enabled, you can choose to select the Require line approval before timesheet approval check box, if you want each line approved before the entire timesheet can be approved. If you only want to approve entire timesheets (no line-by-line approval), select Disabled. Note If you are using Single Entry Mode, you must enable task status manager approval.
- 168. 160 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 11. In the Auditing section, select the Enable Timesheet Auditing check box to create a detailed record of all changes made to a timesheet. Tip Click Purge Log to clear the auditing log. 12. In the Approval Routing section, select the Fixed Approval Routing check box to prevent team members from manually specifying the next approver when they submit their timesheet. 13. In the Single Entry Mode section, select the Single Entry Mode check box if you want to enable team members to report task progress, as well as actual work, on their timesheets. 14. Click Save. Administrative Time Time spent on things other than project work can be classified as administrative time. Administrative time may include vacation, sick leave, organizational meetings, training, or travel. Site administrators can set up different categories for administrative time, so that resources can capture those hours on their timesheets to accurately represent what they have done during a given reporting period. To add an administrative time category 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Administrative Time. 3. Click New Category. A row is added to the table.
- 169. Time and Task Management 161 4. Type a name for the new administrative time category in the Categories column. 5. In the Status column, choose whether the category is currently Open for use on timesheets, or Closed. 6. In the Work Type column, choose whether the category captures Working time, such as training or travel, or Non Work time, such as vacation or sick leave. 7. In the Approve column, choose whether you want time reported in this category to require approval from a manager. 8. Select the check box in the Always Display column if you want to display a row for this category, by default, on every timesheet for every user. For example, you might choose to always display a timesheet row for the Sick time category, so that team members are reminded to report those hours. 9. Click Save. Tip Before clicking Save, be sure you have the right set of categories listed. Once you click Save, any new categories you have added cannot be deleted. As you create administrative time categories, you may decide that you do not actually need a category and would rather delete it. If you have not yet saved the new categories, you can easily delete the category you do not need. Tip If you want to make it so that a category that has been saved is no longer available for selection in a timesheet, change the Status column for that category to Closed, and be sure the check box in the Always Display column is cleared. To delete an administrative time category 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Administrative Time. 3. Click the row header for the category you are deleting, and then click Delete Category. The category is removed.
- 170. 162 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Note You can only delete categories that are not yet saved. For example, say you have created several new categories on the Administrative Time page, but have not yet clicked Save on that page. You can delete any of the new categories you created while on that page. Once you click Save on the Administrative Time page, the categories you added can no longer be deleted. 4. Click Save. Task Settings and Display Site administrators can use the Task Settings and Display page to change how resources report task progress, how actual work can be updated, and other task settings. To configure task settings and display options 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Task Settings and Display. 3. In the Tracking Method section, select the tracking method that best represents how you want team members to report their progress on project tasks. Options in this section can only be modified if you are not using Single Entry Mode. If you are using Single Entry Mode, the Hours of work done per period and Force project managers to use progress reporting method specified above for all projects options are automatically selected and cannot be modified. Tip If you want project managers to have the option of displaying different reporting methods for their projects, clear the Force project managers to use the progress reporting method specified above for all projects check box. However, requiring the same reporting method provides a consistent user experience throughout all projects in your organization, and may make it easier for team members to report progress. 4. In the Reporting Display section, choose whether you want resources to report their hours daily or weekly. If you choose the Resources should report their total hours worked for a week option, select the appropriate day from the Week starts on list. 5. In the Protect User Updates section, specify how you want updates on actuals to occur:
- 171. Time and Task Management 163 To prevent the project manager from updating a team member's actual time worked, select the Only allow task updates via Tasks and Timesheets check box. To import actual work from all timesheet lines, regardless of line classification, select the Import all timesheet line classifications check box. If this check box is cleared, only actual work from timesheet lines that have a standard classification will be imported into task status. To enable users to provide task updates using periods that they define, select the Allow users to define custom periods for task updates check box. 6. In the Define Near Future Planning Window section, type the number of reporting periods you want to include in the Near Future Planning Window on the Tasks page. Close Tasks to Update If you have the appropriate permissions, you can lock project tasks in order to prevent people from submitting task updates. Note Changes to task updating will not take effect until the next time that the project is published. To prevent updates to a task 1. On the Quick Launch, under Settings, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Time and Task Management, click Close Tasks to Update. 3. On the Close Tasks to Update page, in the Select a project list, click the project that contains that task you want to close for updating. 4. In the Select Tasks section, in the Lock column, select the check box for each task that you want to close to updating. Tip If you want to prevent updates to all tasks in a project, click Select All, below the table in the Select Tasks section. You can also click Clear All to remove all current selections in the Lock column.
- 172. 164 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 5. Do one of the following: To publish your project and close the selected tasks to updating, click Publish. Note Publishing your project to close tasks to updating will also publish all applied task updates and any other changes that were made to the plan. If you are not ready to publish that information, click Submit instead, to save your task closure settings. When you are ready to publish other changes to your project, the task closure settings will also be published. To save your changes without publishing the project, click Submit. Tasks that you selected to be closed for updating will remain open until you publish the project.
- 173. 165 6 Queue Management This chapter describes the Microsoft Project Server 2010 Queuing System. This chapter provides an overview of the Queuing System, which describes the queuing process and architecture, the methods in which queuing jobs are grouped, states that queuing jobs can be in, and how multithreading works in the queue. This chapter also describes how to manage queuing through the Microsoft Project Web App Server Settings page. Queue System Overview A queue is a waiting line that becomes a necessity when the number of service requests becomes greater than the optimum serving capacity. In an Enterprise Project Management System, there are several instances when this is true. For example:
- 174. 166 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide At the end of the workday on Friday, nearly all 500 employees of a small company submit their timesheets. A few hours before their team status meeting, nearly all project managers publish their projects. The purpose of the Project Server 2010 Queuing System is to handle these abrupt changes in demand gracefully and reliably. The Project Server 2010 Queuing System takes all the users' input, records entries for the requests in Microsoft SQL Server, and then processes the data asynchronously on a first-come, first-served basis. Having a queue ensures that the Project Server 2010 EPM solution does not stop working when a spike in demand occurs. Nearly all critical operations in the Project Server 2010 system go through the Project Server 2010 Queuing System. These include: Project Save Project Publish Timesheet Save Timesheet Submit Project Backup/Recovery Report Data Service operations Cube Building Service operations Server Side Scheduling The Project Server Queuing System provides the following advantages: Reliability o Data integrity: There is a well-defined protocol to save any job in the queue. If a job is just half-saved, it is not processed. Also, all jobs are saved into SQL Server (not the file system) and take advantage of SQL Server transactions. o In-order delivery: If a user of Project Professional clicks Save and then Publish, the Project Queuing System ensures that the Save job is processed first and is then followed by a Publish job. o Fault tolerance: Failed jobs in the queue can be retried. Also, when more than one instance of the Queue NT Service is running, if one of them stops responding, the other one picks up the extra load automatically. (This process is called transparent failover.) Scalability
- 175. Queue Management 167 o Multithreading: The Project Server 2010 Queuing System can process multiple jobs at the same time. For example, Project 1 Save, Project 2 Publish, and a cube building job can be processed simultaneously. o You can simply add more middle-tier servers to handle load better. Each middle-tier server will have a Project Queuing Service, and the loads will be balanced automatically. o The number of jobs in the queue is limited only by the scale limitations of SQL Server. Manageability Queuing process The following illustration shows the queuing process: Queuing Process
- 176. 168 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 1. The user makes a server request from a client application (for example, publishing a project from Project Professional). The user passes a Job ID (a unique identifier that tracks the request) as part of the request. 2. The Project Web service takes the request and puts it in the queue. 3. A Job ID is issued to the user as an acknowledgement. 4. The user queries to check the status of the request through the issued Job ID. 5. The Project Server 2010 Queuing System returns the status of the request to the user. Queuing architecture This section describes: Queuing modules How the Queuing modules work together Queuing modules The Queue NT Service is installed on every Project Server application server computer as part of provisioning. It starts one "Queue Worker Process" per Service Application defined in the farm. The Queue Worker Process services all the instances of Project Web App (PWA) that are associated with its Service Application, and it runs under the "Service Application Administrator" identity. For example, if two Project Web App sites are defined for the Service Application, the Queue Worker Process will service both of them. Remember this deployment model when going through the rest of this section. The Project Server Queuing System is composed of the following four modules, and is dependent on how the four modules work together: 1. Job Storage: Queue jobs are stored in the Draft and Published Project Server databases. In this manner, the jobs are backed up and restored as part of the normal Project Server database backup and recovery routines.
- 177. Queue Management 169 2. Job Polling: Job storage is polled at regular intervals by a Job Polling thread to check for new jobs. Polling intervals are configured by administrators in the Project Web App Server Settings Queue Management pages. The Queue Worker process starts the Job Polling threads for each instance of PWA that it services. The Job Polling thread runs inside the "Queue Worker Process" process and under the "Queue Worker Process" identity. The Job Polling thread has two main properties: o Type - A given job polling thread could be a "project job polling thread" (looking for project-related jobs) or a "timesheet job polling thread" (looking for timesheet- related jobs). o Project Web App instance - Every job polling thread looks for jobs originating from a specific instance of Project Web App.
- 178. 170 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 3. Job Processing: The Job Polling thread spawns one Job Processing thread for each job that it finds. The maximum number of Job Polling threads can be configured by administrators. Note that the job processing threads run under the "Microsoft Project Server Queue Service 2010" identity. 4. Job Status Check and Management: This is the module of the Project Server Queue that the end user sees. Project Web App Manage Queue page: Administrators use this to see the status of any job in the queue. They can also cancel or retry failed jobs. This feature is part of PWA — there is no need to download a special tool.
- 179. Queue Management 171 Job Grid on the Manage Queue page Project Web App Queue Settings page: Administrators can view or change the settings of a queue, such as the polling interval and the maximum number of job processor threads. This feature is part of PWA — there is no need to download a special tool. Queue Settings page Project Web App My Queued Jobs page: Any user can check the status of a job using this interface. This feature is part of PWA — there is no need to download a special tool.
- 180. 172 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Queue Status PSI: Software developers can use these APIs to get the status of any queue job. There are several powerful filters to narrow the search. How it all works together The Project Server Queuing System modules must interact and work as a whole when the system is tasked with requests, such as adding jobs, processing jobs, and retrieving job status. Adding Jobs There are many ways in which jobs can be added to the queue. For example, a project manager can save a project from Project Professional, a team member can submit a timesheet, or a third- party application can publish a project. Each of these actions causes a call to an element in the Project Server Interface (PSI), which in turn adds the appropriate jobs to the queue. Job Processing Job processing occurs in different phases and involves interaction between various modules: 1. Start Queue Worker Process: When the Queue NT Service starts, it starts one child Queue Process per PWA instance. The Queue NT Service should always be running for the Project Queuing System to work.
- 181. Queue Management 173 2. Start Job Polling threads: When the Queue Worker Process starts, it starts the job polling threads, which are specific to instances of Project Web App. 3. Pick up new jobs: The polling thread looks for new jobs in the project databases. 4. Create job processing threads: If there are new jobs, job processing threads are created. 5. Write status: Once a job processing thread finishes, the status of the job (success or failure) is written back to the database.
- 182. 174 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Retrieving status Job status can be checked in various ways. Administrators can use the Project Web App Queue Management pages, team members can use the My Queued Jobs page, or software developers can programmatically get status using the Queue PSI methods. The Project and Timesheet queues The Project Server 2010 Queuing System is composed of two separate queues: Project Queue Primarily used for project-related messages such as Saving, Publishing, Reporting, and Cube Building, although other types of messages may be sent to this queue as well. Its tables and stored procedures are stored in the Project Server 2010 Draft database.
- 183. Queue Management 175 Timesheet Queue Primarily used for timesheet-related messages such as Timesheet Save and Timesheet Submit, although other types of messages may be sent to this queue as well. Its tables and stored procedures are stored in the Project Server 2010 Published database. The two queues are designed the same way, except that their jobs reside in different databases. The advantages in having two types of queues include: Performance: Storing queue job data in the same database as the core data saves the queue from making expensive cross-database calls during job processing. Let us look at an example: When a Timesheet Submit job occurs, the data entered by the user (for example, hours worked) is packaged as part of the submitted queue job and put into the SQL Server job store. Also, there is already existing information about a timesheet (duration, name, and so forth), and this information is available in the "Published" database. To process the Timesheet Submit job, both sets of data are necessary. Performance is improved if both these sets of data reside in the same database. That is why Timesheet queue jobs are stored in the "Published" database (where all timesheet core data resides) and Project queue jobs are stored in the "Draft" database (where most of the project core data resides). Fine-tuning: Every setting in the queue can be specified separately for the Project and Timesheet queues. This gives administrators flexibility in configuration. For example, if a customer is using Project Server 2010 primarily for timesheets and there are very few projects, the polling interval of the timesheet queue can be set to 10 seconds, and the project queue could be set to a slightly higher time interval. Note The polling interval specifies the frequency with which the queuing service checks either of the queues for new jobs. This setting can be specified in the Project Web App Queue Settings page. How the Project and Timesheet queues are used The following image shows how the modules in the Project Server Queuing System work with the project and timesheet queues.
- 184. 176 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 1. Start Job Polling threads: For every instance of Project Web App serviced by the queue (the queue can service more than one instance of Project Web App), a polling thread pair is launched — one thread to service the project queue, another to service the timesheet queue. Both of these threads reside within the "Queue Worker Process" process space and run under the "Queue Worker Process" identity (which is the Service Application Administrator identity). 2. Job Storage: As mentioned above, the project-related jobs (Project Save, Publish, Reporting, Cube Building, and so on) are stored in the "Draft" database. The timesheet-related jobs (Timesheet save, Timesheet submit, and so on) are stored in the "Published" database. 3. Job processing: When the "job polling threads" discover new jobs, new job processing threads are created. Note that the job processing threads still reside within the "Queue Worker Process" process space and run under the "Queue Worker Process" identity (which is the Service Application Administrator identity). Status-checking modules will continue to check for status of a job; they do not care which queue the job is part of. Queue management is always done on a per-queue basis — in the
- 185. Queue Management 177 Project Web App Queue Management pages, administrators have to select which queue (project or timesheet) they are changing the settings for. Queue groupings There are three distinct levels of grouping for queued data: 1. Jobs A job is a trackable packet of work that gets executed by Project Server (for example, project save, project publish, timesheet submit). Some jobs are not explicitly initiated by the user (for example, email notifications, reporting data synch-up). Jobs are the level at which queuing is tracked (using a Job ID). 2. Correlated Job Group A correlated job group is a categorization of jobs imposed by internal rules of Project Server. Jobs within a correlated job group are always processed together and in order (with some exceptions). In the example below, Project 1 is edited and saved from Project Professional and then checked in. Project 1 is then checked out by another user, who then publishes it. Publishing Project 1 triggers Reporting and a Reporting job is added to the queue as well. Project Server assembles a correlation group comprised of the four jobs related to Project 1. It then will attempt to process the jobs in sequence since the Project Server internal rules dictates that there is a dependency between the jobs. The dependency that exists is that the Project 1 publish and the Reporting database update cannot occur until Project 1 is saved. Also, if any of the jobs in the correlation fail, the other jobs after it in the correlation group will be blocked. For example, if the Save Project 1 job (job ID 12) fails, the Checkin Project 1 job (job ID 13) should get blocked. If the Checkin Project 1 job were executed, this would lead to problems because someone else may then checkout Project 1 and then attempt to modify it which may be in an inconsistent state due to the failed save. 3. Sub-jobs Each job can be broken down further into smaller segments called sub-jobs. If a job is very large (such as saving a 10 MB project) it will be broken into multiple sub-jobs. Sub-jobs are not exposed to the PSI or the Project Web App user. However, sub-jobs may be noted in ULS logs (depending on the verbosity option that is selected).
- 186. 178 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Parent/Child Relationships between submitted Jobs It is important to realize that parent/child relationships can exist for submitted jobs which require that further processing be done. For example, if a user publishes Project 1, a reporting request for Project 1 will be generated, as well as notification requests regarding Project 1. Note that Notifications for Project 1 will always be generated, but since Reporting Project 1 is generated only if the Publish of Project 1 is successful, should the publish job fail, the Reporting Project 1 job will not be generated. Similarly, a child job may fail without any effect to the parent job. For example, if Notification Project 1 should fail, there will be no effect on Publish Project 1 since it will have already occurred. It is important to note that although the user may be aware that the publish of Project 1 was processed through the queue, he/she may not be aware that a child job may have failed. If you would like to verify what child jobs were spawned from a parent job that they had entered into the queue as well as their status, you can do this through the My Queued Jobs page in Project Web App. Administrators can use the Queue Management UI and see all jobs in the queue.
- 187. Queue Management 179 Queuing states When a job is submitted to the queue it can transition through various states. The table below describes each of these states: State Description Getting queued Job is put into the queue. A job ID is issued. Waiting to be Job is in the queue and is waiting to be processed. Processed Processing Job is being processed. Success Job has been successfully processed. This is a terminating state in which the job can go no further. Blocked Job has been blocked by failure of another job before it in the same correlation group. The user will need to retry or cancel. Failed and Not Job has failed, but is not blocking any other jobs in its group. This is a Blocking terminating state in which the job can go no further. Correlation Failed and Job has failed and may be blocking one or more dependent jobs. Blocking Correlation Skipped for Job has been skipped because a duplicate job has been found after it within optimization the group. For example, a project manager may attempt the following in sequence when working with a project: 1. Saves Project 1 2. Publishes Project 1 3. Changes a task in Project 1 4. Save Project 1 5. Publishes Project 1 6. Changes the start date of Project 1 7. Save Project 1 8. Publishes Project 1 All three incremental saves to Project 1 will be processed. However, all three publish attempts do not need to be processed. If the last publish job is processed, it would produce the same results as if all three publish jobs were processed. For optimization, the first two publish attempts are skipped.
- 188. 180 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide State Description Cancelled Job has been cancelled. A job can be cancelled from any state except the two terminating states (Success, Failed and Not Blocking Correlation). Sleeping Job could not process immediately because of another conflicting job and is temporarily in an inactive mode. The job will be retried. Changes in queue state As jobs are entered into the queue and processed, it is important to understand the possible changes in queue state that can occur. The following flowchart describes the possible paths through each state. State Next Possible State Getting Queued Waiting to be Processed Cancelled
- 189. Queue Management 181 State Next Possible State Waiting to be Processed Processing Cancelled Blocked Skipped for optimization Processing Success Failed and Not Blocking Correlation Failed and Blocking Correlation Cancelled Success End Blocked Processing Cancelled Failed and Not Blocking End Correlation Failed and Blocking Cancelled Correlation Processing Skipped for Optimization Blocked (due to a failed job) Cancelled Success Failed and Not Blocking Correlation Failed and Blocking Correlation Processing Cancelled End Queue Administration Settings Queue management and administration can be done through the Project Web App Server Settings page. In the Queue section of the Server Settings page there are two options to administer the queue:
- 190. 182 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Manage Queue Jobs You can use this page to view jobs in the queue. You can use the configuration options to filter jobs and only see the ones you are interested in viewing. You can also retry or cancel jobs through this page. Queue Settings You can set configuration options that control the way by which jobs are pulled from the Project and Timesheet queues and processed. These settings get applied without the need to restart the Queue Service. You must have the Manage Queue permission in order to access the Queue Administration settings pages. Manage Queue Jobs The Manage Queue Jobs page allows you to view jobs in the queue through the jobs grid. Viewable jobs are displayed according to the following filter options Filter Type Job History Job Types Job Completion States Columns Advanced Options Filter Type This configuration option allows you to select filters to query for specific types of jobs that will display in the Job Grid. The filters available in the Filter Type drop-down menu are: By Status- Displays jobs in the queue in order by status. This is the default setting.
- 191. Queue Management 183 My Jobs – Displays only jobs initiated by you. By Project – Displays jobs in the queue in order by project. By ID – Displays jobs in the queue in order by Job ID. Active – Displays all jobs that have a status of Active. Blocked- Displays all jobs that have a status of Blocked. Job History This configuration option enables you to select the date range of jobs that display in the Job Grid. Use the From and To fields to select a beginning and end data. The default selection is to select the one-day date range for the present date. You can use the Maximum Number of Jobs field to limit the number of jobs that display for a given date range. If the selected date range contains a huge number of jobs that need to display in the Job Grid, the load time for the Manage Queue Jobs page can be very long. The Maximum Number of Jobs field allows you to limit the jobs that display. The default setting is 500. Job Types The Job Types configuration option enables you to select the type of job (for example, Project Create, Timesheet Submit, Notifications etc.) that you want to appear in the Job Grid. By default, all job types will be listed in the Selected Jobs list.
- 192. 184 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Job Completion States The Job Completion States configuration option enables you to select the job states (for example, Success, Blocked Due to a Failed Job, Processing, etc. ) of the jobs that you want to appear in the Job Grid. By default, all job state types except Success will be listed in the Selected Jobs list. Success is not available by default because we assume Project Server Administrators would be more interested about problems that can be caused by non-successful jobs rather than successful one. This setting can be helpful for troubleshooting jobs that are not completing successfully in the queue. For example, some of your users might be experiencing problems over the past few days. You can see specifically which jobs are not completing successfully by going to the Job Completion States setting and adding all job states except Success. You can also select a Job History date range for that corresponds to when shortly before the problems occurred (for example, seven days). The Job Grid should display information about all jobs that are in a non- successful job status that have occurred over the past week. Columns The columns configuration option allows you to select the columns that will appear in the Jobs Grid section.
- 193. Queue Management 185 Advanced Options The Advanced Options queue settings both apply to the way that jobs in the queue are cancelled: Cancel jobs getting enqueued: Selecting this option will cancel all jobs that remain in a “getting enqueued” state for a prolonged period of time. When a job is in this state, it means that the queue has been told to start receiving a job that will be processed later, but it has not received a tag telling it that all the data for the job has been received. Until the full job has been received, the job will remain in the getting queued state. If a job remains in the getting queued state for a prolonged period of time, it is likely that something is preventing the job from finishing. If the job continues to remain in this state after rerunning it, review your ULS logs to troubleshoot why they problem is occurring. Saving a project from Project Professional to Project Server is a job that typically enqueues. When you save a project from Project Profession to the Project Server, the job synchronizes with the server. If the synchronization does not complete, then the job remains in the enqueued state. This setting is enabled by default. Cancel subsequent jobs in the correlation: When you cancel a job that spawns additional jobs, this option will automatically cancel those jobs as well. For example, a Project 1 Publish job that is cancelled will also cancel the Project 1 Reporting job that was automatically created. This setting is also enabled by default.
- 194. 186 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Jobs Grid The Jobs Grid provides a view the jobs that meet the criteria listed in the Manage Queue Jobs page. Options within this section enable you to select a job or group of jobs and to apply the following options to them, if applicable: Retry Job: Allows you to try to rerun selected jobs in the queue that did not complete successfully. Cancel Job: Allows you to selected jobs in the queue that did not complete successfully. View Related Jobs: Allows you to view jobs that have a dependency relationship (for example, jobs in the same correlation) with a selected job in the queue. Refresh Status: Allows you to update the jobs in your job grid with the latest status. Queue Settings Queue Settings options allow you to configure the way the queue does operates. The Queue Settings page contains the following configuration options: Queue Type Maximum Number of Job Processor Threads Polling Interval (in milliseconds) Retry Interval (in milliseconds) Retry limit SQL retry interval (in milliseconds) SQL retry limit SQL Timeout (in seconds) Cleanup Interval (in hours) Cleanup Interval Offset (in minutes) Cleanup Age Limit for Successful Jobs (in hours)
- 195. Queue Management 187 Cleanup Age Limit for Non-Successful Jobs (in hours) Bookkeeping Interval (in milliseconds) Queue Timeout (in minutes) Fast Polling Queue Type The Queue Type setting allows you to select the queue (either Project or Timesheet) to which the settings on the page will apply. Maximum Number of Job Processor Threads The Maximum Number of Job Processor Threads setting determines how many job processor threads are available for use for the selected queue type (Project or Timesheet).
- 196. 188 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide As a starting point, we recommend that you set the maximum number of processor threads settings based on the number of available processors (or cores). For example, if the Project Server application server uses a single dual-core processor, configuring the settings for two threads per queue is a good starting point. If your application server uses a quad dual-core processor, you might be able to use eight threads per queue. You can adjust these settings accordingly based not only on the volume of transactions, but also the average size of the transactions (for example, publishing 10-line projects versus 1000-line projects). You should also take into account the farm topology and other applications that are running on the farm. For example, if you have four application servers on the farm and each server has two cores, a setting of “4” gives you the potential for 32 threads to be operating. Adjust the setting accordingly if your application server is also serving as a front-end Web server or running search or other processor-intensive activities. It is also important to consider the throughput of the SQL Server hosting the Project Server databases. For instance, suppose you have eight application servers that can process threads and the Maximum Number of Job Processor Threads setting is at “4” (potential for 32 threads all processing jobs). The SQL Server may start having contention issues simply because all the threads are operating on the same table. Additionally, you can monitor performance counters, application logs, and ULS logs to guide you in fine-tuning the queue to work with your normal server loads. Polling Interval The Polling Interval setting allows you to specify the time interval (in milliseconds) in which the Queue NT Service polls the project or timesheet database (depending what you selected for Job Type) for new jobs. The valid range is 500 through 300000, with a default value of 1000.
- 197. Queue Management 189 Retry Interval The Retry Interval setting allows you to set the length of time (in milliseconds) between retries for jobs that have failed through SQL-related issues, such as SQL deadlocks. The valid range is 0 (immediate retry) to 300000, with a default value of 1000. Retry Limit The Retry Limit setting allows you to set the limit on retries on a failed polling query. The Project Server Queuing System polls the databases on a regular basis to retrieve jobs that need processing. If this query should fail for an SQL-related reason, the system will attempt to poll the database again after a period of time.
- 198. 190 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide SQL Retry Interval The queue polls the database at regular intervals for jobs that need processing. If the query fails, the SQL Retry Interval setting allows you to set the length of time (in milliseconds) before the query is retried. The valid range is 0 (immediate retry) to 60000, with a default value of 1000. SQL Retry Limit The queue polls the database at regular intervals for jobs that need processing. If the query fails, the SQL Retry Limit setting allows you to set the number of times the query will be retried. The valid range is 0 (no retries) to 100, with a default value of 5.
- 199. Queue Management 191 SQL Timeout The queue makes SQL calls for retrieving and executing jobs. This SQL Timeout setting allows you to set the timeout value (in seconds) for these calls. If any job fails due to an SQL Timeout error, you can increase the value for this setting and retry the job. The valid range is 30 to 86400 (one day), with a default value of 1800 (30 minutes). Cleanup Interval This Cleanup Interval setting allows you to configure the frequency (in hours) with which the Queue Cleanup job runs. The valid range is 1 to 100000, with a default value of 24 (one day). For example, if the cleanup interval is set to the default value of “24”, the Queue Cleanup job will run every 24 hours. You can set the time which the Queue Cleanup job will run with the Cleanup Interval Offset setting.
- 200. 192 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Cleanup Interval Offset The Cleanup Interval Offset setting determines the time at which the Queue clean up job will run. The default value is 0, which sets the cleanup to occur at 12:00AM. The valid range is 0 (12:00 a.m.) to 1439 (11:59 p.m.). Use this in conjunction with the Cleanup Interval setting. For example, if the Cleanup Interval Offset value is set to “180”, and the Cleanup Interval value is set to “24”, the Queue Cleanup job will run daily at 3:00AM. You may want to use the Cleanup Interval Offset to run after the Cube service is scheduled to run. In this situation, if the Cube service starts at midnight, you may want to postpone the cleanup to occur a couple of hours after midnight. Cleanup Age Limit for Successful Jobs The Cleanup Age Limit for Successful Jobs setting allows you to configure when a job that has been completed successfully will be removed from the system. You can configure this setting by entering the value (in hours) in the Cleanup Age Limit for Successful Job field. The value you enter configures the queue to delete the job during the cleanup interval, only if the age of the successfully created job is equal to or greater than that value.
- 201. Queue Management 193 For example, you configure the Cleanup Age Limit for Successful Jobs value to be 24 (default value). Cleanup Interval Offset is configured to clean up jobs at 12:00AM daily. If you have a publish job that completed successfully on 11:55PM on Sept 1, it will not be removed from the system until September 3 at 12:00AM when it will be over 24 hours old. The Sept 2 12:00AM cleanup will not remove the job since it will only be five minutes old. Note Typically the number of successful jobs in comparison to non-successful jobs is very high. Therefore, Cleanup Age for Successful Jobs is usually set to a lower value in comparison to the Cleanup Age Limit for Non-Successful Jobs value. Note Default Project Server categories cannot be deleted. Cleanup Age Limit for Non-Successful Jobs The Cleanup Age Limit for Non-Successful Jobs setting allows you to configure when a job that has completed in an unsuccessful state will be removed from the system. You can configure this setting by entering the value (in hours) in the Cleanup Age Limit for Non- Successful Job field. The value you enter configures the queue to delete the job during the cleanup interval, only if the age of the unsuccessful job is equal to or greater than that value. The method in which unsuccessful jobs are removed from the system is identical to the way successfully completed jobs are removed from the system.
- 202. 194 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Note Jobs that are in an “Unsuccessful and blocking correlation” state will stay in the history until they are successfully retried or cancelled. The cleanup for non-successful jobs does not affect jobs in this state. The default value of this setting is 168 hours (7 days). Since job status information is important in helping to troubleshoot problems when a job has not completed successfully, it is recommended to not set this value to less than the default setting. Bookkeeping Interval There are a number of "bookkeeping" tasks that are run by the Queuing System. For example, these include awakening jobs in a "sleeping" state, updating the heartbeat timestamp, or checking if the Queue Cleanup job needs to be run. The Bookkeeping Interval setting controls the time interval (in milliseconds) at which these tasks are run. The valid range is 500 to 300000, with a default value of 10000 (ten seconds).
- 203. Queue Management 195 Queue Timeout In a farm containing multiple Application servers, if the Queue Service fails on one of the servers, jobs are automatically distributed the remaining Application servers on which the Queuing service is active. A Queue Service is considered to have timed out if it has not updated its heartbeat for longer than the Queue Timeout value (in minutes). The heartbeat is updated by the Queue in all the Project Web App databases that it touches (for example, each time the Published and Draft databases are polled for jobs). The valid range is 2 to 20, with a default value of 3. Note The Queue Timeout value cannot be less than four times the Bookkeeping Interval at any time. If the Queue Timeout value will automatically be changed to four times the Bookkeeping value if the rule is violated. Note Default Project Server categories cannot be deleted.
- 204. 196 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Fast Polling The Fast Polling setting is enabled by default and allows the Queue to process all jobs in a Waiting to be Processed state to be processed as soon as possible. However, if this fast processing overwhelms the server and the Queue needs to slow down, this setting can be disabled. If Fast Polling is disabled, the Queue will check if there are any free threads to process jobs. If there are, the free threads will be loaded with jobs in a Waiting to be Processed state. It will then wait for the polling interval, and repeat the process. If Fast Polling is enabled, the Queue will not wait for the polling interval if there are pending jobs. As jobs get processed, all pending jobs will start getting processed immediately.
- 205. Operational Policies Management 197 7 Operational Policies Management This chapter about Operational Policies Management contains the following sections: Alerts and Reminders Additional Server Settings Server-Side Event Handlers Active Directory Resource Pool Synchronization Project Sites Project Site Provisioning Settings Bulk Update Project Sites Alerts and Reminders
- 206. 198 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Project Server 2010 generates e-mail notifications and reminders for each user whenever new, overdue, rejected, or forthcoming events occur. Administrators can configure alerts for their reminders from the Alerts and Reminders page in the Additional Settings page of your Project Web App Server Settings. Before e-mail notifications and reminders can be used by members of your organization, the appropriate server and account information must be identified. As a Project Web App administrator, you can configure the following settings in the Alerts and Reminders page: Notification E-mail Settings Schedule E-mail Reminder Service Notification E-mail Settings The Notification E-mail Settings allows the Project Server Administrator to maintain the default sender e-mail address and message information that is automatically included with each email notification or reminder sent by Project Server. It also allows you to specify the SMTP server and associated port number. To configure the Notification E-mail setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies page, click Alerts and Reminders. 2. On the Alerts and Reminders page, in the Notification E-mail Settings section, enter the following information: a. Select Turn on notifications with the following settings check box to maintain all of your Notification email settings, but turn off notifications globally. Note This setting was not available in Project Server 2007. In Office Project Server 2007, you had to remove the SMTP server details to stop notifications and reminders from being sent. b. In the SMTP mail server box, type the name of your SMTP server. Verify the port number in the Port box.
- 207. Operational Policies Management 199 c. In the From address box, enter the default email address. This address is the reply-to address for all notification and reminder e-mails. d. In the Company domain box, enter the domain name of your company (for example, Contoso.com). e. In the E-mail foot box, type the default message you want appended to all notification emails. For example: This email message may contain confidential information and is intended only for the recipients named above. 3. Click Save. Schedule E-Mail Reminder Service The Schedule E-mail Reminder Service allows a Project Server Administrator to set the time of day at which the e-mail reminder service scans the Project Server databases to determine who should receive e-mail reminders (users with upcoming or overdue tasks and status reports). Depending on the volume of notification and reminder e-mails, you should consider setting the service to run at a time when the overall load on the server is low. To configure the Schedule E-mail Reminder service: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies page, click Alerts and Reminders. 2. On the Alerts and Reminders page, in the Schedule E-Mail Reminder Service section, click the Schedule e-mail reminder service to run every day at drop-down menu and select the time at which you want the service to run. 3. Click Save. Additional Server Settings The Alerts and Reminders page allows you to configure settings for: Project 2007 Compatibility Mode Project Professional Versions Enterprise Settings
- 208. 200 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Currency Settings Resource Capacity Settings Resource Plan Work Day Exchange Server Details Task Mode Settings Project 2007 Compatibility Mode The Project 2007 Compatibility Mode setting allows an upgraded Project Server 2010 instance to accept client connections from Project Professional 2007 with Service Pack 2 (SP2) as well as Project Professional 2010. This setting is only configurable if your deployment has been upgraded from Office Project Server 2007 (it is enabled by default after the upgrade). This feature in Project Server 2010 is also referred to as Backward Compatibility Mode (BCM). Note Project Server 2010 will not accept connections from Project Professional 2003, even if BCM in enabled. Backward compatibility mode (BCM) is a feature in Project Server 2010 that assists in the upgrade of your Enterprise Project Management environment. Project Server 2010 accepts connections from the Microsoft Project Professional 2010 client, but it can also accept connections from Microsoft Office Project Professional 2007 with Service Pack 2 (SP2) if BCM is enabled in Project Server 2010. BCM is enabled automatically after you upgrade to Project Server 2010. After you upgrade to Project Server 2010 (by either the in-place or database-attach upgrade method), BCM allows you to avoid having to upgrade your Office Project Professional 2007 client computers at the same time. Because Project Server 2010 accepts connections from both Office Project Professional 2007 SP2 and Project Professional 2010 clients when BCM is enabled, you can decide to upgrade your clients later, and in batches (running in a mixed environment), if you want. When you have finished upgrading the clients to Project
- 209. Operational Policies Management 201 Professional 2010, you can turn off BCM in Project Server 2010 server settings, which then allows for only Project Professional 2010 connections. Important Once the Project 2007 Compatibility Mode is disabled, it cannot be re-enabled. Verify that you want to disable BCM if you are going to make the change. We recommend that BCM be enabled only as a temporary measure to help in the upgrade process. When Project Server 2010 is configured in backward compatibility mode, Project Professional 2010 clients that connect with Project Server 2010 have certain features that are disabled. These include the following: Manually scheduled tasks are not available on the server or client. Tasks cannot be set to inactive. Font strikethrough is not available. All departmental custom fields are enforced in Office Project Professional 2007. All new features that are available in Project Professional 2010 (for example, Timeline, Team Planner, 32-bit colors) are available to Project Professional 2010 users, but not to Office Project Professional 2007 SP2 users. Office Project Professional 2007 SP2 connecting to Project Server 2010 in BCM mode is blocked from providing functionality that requires loading a Microsoft Project Web App page in the client. This includes doing approvals and opening enterprise resources. As a workaround, you can use Project Web App on a Web browser to do these functions until you are ready to upgrade to Project Professional 2010. Additionally, workflow-controlled custom fields are not available in Office Project Professional 2007 SP2. Project Server 2010 prevents you from creating cross-project type links (resource sharing, cross- project dependencies, and master/subproject) on mixed Project file versions. For example, you cannot create a cross-project link from a project that is in Compatibility mode (Office Project 2007 format) with one that is in the Native mode (Project 2010 format). What this means is that after you disable backward compatibility mode, as you open and save projects, they are converted to Native mode. However, projects that have not been opened and saved remain in Compatibility mode. Project Server 2010 does not allow you to create or even connect projects that are in different modes. Therefore, your cross-project links do not fully function until all of the related projects are opened and saved so that they are all in Project 2010 format. When BCM is disabled in Project Server 2010, Project Server is running in Native mode. In Native mode, only Project Professional 2010 clients are able to connect to Project Server 2010. However, Project Professional 2010 features that were not available in BCM (such as manually scheduled tasks), become available in Native mode.
- 210. 202 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide To disable Project 2007 Compatibility Mode (Backward Compatibility Mode): 1. Verify that all projects are checked in to Project Server 2010. You can verify this by 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies page, click Additional Server Settings. 3. On the Additional Settings page, in the Project 2007 Compatibility Mode section, clear the Enable Project 2007 Compatibility Mode check box. 4. Click OK. 5. After making the change, you must check out and open the Enterprise Global file in Microsoft Project Professional 2010. In the Enterprise Global file, make a very minor change (for example, dragging the splitter bar on the screen), save the file, and then check it back in. This is required to upgrade the Enterprise Global file to the newer version of the Microsoft Project Professional client. Important The Enterprise Global file must be upgraded to the Project Professional 2010 client after BCM is disabled (step 5 in the procedure above). This step ensures that all new projects are in native mode with all Project Professional 2010 features enabled. (All new projects are based on the Enterprise Global file). Neglecting to upgrade the Enterprise Global file with the Microsoft Project Professional client can lead to serious problems. Objects in the file (for example, views, tables, filters) will remain in Office Project 2007 format and they will be expected to be in Project 2010 format when new projects are created. Project Professional Versions The Project Professional Versions setting allows you to specify which versions (build numbers) of Project Professional client will be able to connect to your Project Server 2010 environment. This setting allows you to ensure that Project Professional client connections to the server are all at a required base level. For example, if you recently updated both Project Server 2010 and Project Professional 2010 to the October 2010 Cumulative Update, you can verify that all clients connecting to the server are at least at this level by entering the build number (14.0.5128.5000). All
- 211. Operational Policies Management 203 Project Professional 2010 clients that have not been updated to the October 2010 Cumulative Update or later will not be able to connect. Note If Backward Compatibility Mode (BCM) is enabled, you do not need to make any additional changes to this setting to allow Project Professional 2007 SP 2 clients to connect to the server. However, you can enter a build number for the Office Project Server 2007 client if you require a minimum build. For example, BCM is enabled and you only want the following two builds (and higher) to connect to Project Server 2010: Project Professional 2007 with Service Pack 3 (SP3) Project Professional 2010 with the December 2010 Cumulative update In the above example, for the Project Professional Versions setting you would enter the build number for each version, separated by a comma. To configure the Project Professional Versioning Settings: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings. 2. On the Additional Server Settings page, in the Project Professional Versions section, type the build number of each Project Professional version that you want to connect to Project Server 2010. Versions older than the build number you enter will not be able to connect. 3. Click Save. Enterprise Settings The Enterprise Settings setting allows you to determine whether or not Project Server 2010 allows projects to have the following capabilities: Allow master projects to be saved and published to Microsoft Project Server 2010 (enabled by default) – Enabling this setting allows master projects to be used in Project Server 2010. Master projects are projects that contain sub-projects, and usually contain tasks that are dependent on each other. Check with your Project Management Office to see if your organization prohibits the use of master projects. Allow projects to use local base calendars – Enabling this settings allows users to not only use enterprise base calendars that are on the system for their enterprise
- 212. 204 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide projects, but to also use base calendars local base calendars that your users create. Disabling this setting (default) will restrict users to using only enterprise base calendars that are on the system for their projects. Restricting your users to use only enterprise calendars gives you more control by preventing problems that can occur when projects use local base calendars that contain conflicting data. For example, a project using a local base calendar that differs from an enterprise calendar (for example, July 4th as a working day versus a holiday) can lead to faulty calculations and other issues. To configure the Enterprise Settings: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings. 2. On the Additional Server Settings page, in the Enterprise settings section: a. Select Allow master projects to be saved and published to Microsoft Project Server 2010 if you to enable this setting (enabled by default). b. Select Allow projects to use local base calendars if you want to enable this setting (cleared by default). 3. Click Save. Currency Settings Through the currency setting you can select the default currency setting for projects that are published to the server (used for reports and the default view for new projects). The default value will be based on the default currency of the language used for the Project Web App instance. You can also select the currency settings for publishing: Allow projects to be published in various currencies – Select this option if your company uses multiple currencies for costs within projects (this is the default setting). Enforce that projects are published in the server currency – Select this option if your company only uses a single currency for costs within projects. The currency used will be the one selected as the default server currency.
- 213. Operational Policies Management 205 To configure the Currency settings: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings. 2. On the Additional Server Settings page, in the Currency Settings section, select one of the following currency options: Allow projects to be published in various currencies (default). Enforce that projects are published in the server currency 3. You will see the following message box if you selected Enforce that projects are published in the server currency: This message box warns you that the change will only be enforced on all subsequent projects that are published to the server. All projects that are not using the default server currency must be changed to the default currency and republished. Click OK. 4. All projects published to the server that are using a currency that is in conflict with the server currency will be displayed in the Currency Settings section: You can use this as a reference to note which projects need to have their currency changed to the server currency. 5. Click Save.
- 214. 206 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Change currency option for a project Use the following procedure in Project Professional 2010 to change the currency settings for a project. You can use this procedure to: Select the currency for a specific project if the currency setting allows you to use multiple currencies. Change the currency setting on a project to the server currency if the currency setting allows you to only use the server currency. To change the currency for a project in Project Professional 2010: 1. Open Project Professional 2010 and log on to Project Server 2010. 2. Check out and open a project from Project Server 2010. 3. Click File, and then click Options. 4. On the Project Options page, click Display. 5. On the Display page, in the Currency options for this project section, select the Currency that you want to use for this project. 6. Click OK. 7. Click File, and then click Save to save the project. 8. Click File, and then click Publish to publish the project. Resource Capacity Settings The Resource Capacity Settings are used to calculate your resources availability for work over a specified time range. Your resources capacity data for the specified time range is stored on the Reporting database, and is updated daily through a timer job which is run at a time you specify in the settings. You are able to set the Active capacity view by entering a time range in relative terms - months in the past, and months in the future – using the
- 215. Operational Policies Management 207 current date as a relative date point. You can use the Resource Capacity report or create a custom report to view this data from the Reporting database. The default Active capacity view settings are “1” month behind and “12” months ahead. This means that when you view the data in the Reporting database, you can view a resources future availability for up to 12 months from the current date, as well as utilization over the last month. By increasing the Month Ahead setting, you will get more capacity computed for future periods. For example, a company is planning for new projects later in the year and wants to forecast the capacity for resources from 12 months to 24 months. Some customers might want to increase the months behind value if they want to get an accurate report of work completed in the past (for example, to account for any users who might report time long after work in completed). Note that increasing either value will also increase the amount of time it will take for the daily timer job to run. The data from the timer job is stored on the Reporting database on a day-to-day basis, and can be configured to run at a specific time through the “Scheduled Time” setting. The default value for the Scheduled Time setting is 1:00 AM. To configure the Resource Capacity setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings. 2. On the Additional Server Settings page, in the Resource Capacity Settings section, for Active capacity view, enter the following: a. In the Months behind field, enter the number of months in the past that you want resource data to be calculated from. b. In the Months ahead field, enter the number of months in the future that you want resource data to be calculated from. c. For Scheduled time, enter the time at which you would like latest resource capacity information to be processed (the default value is 1:00 AM). 3. Click Save.
- 216. 208 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Resource Plan Work Day The Resource Plan Work Day setting allows you to specify the length of a work day (full- time equivalents or FTE) for all resources in your resource plan. This value can be calculated from either the resource’s base calendar, or can be manually entered in as a value. To configure the Resource Plan Work Day setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings. 2. On the Additional Server Settings page, in the Resource Plan Work Day section, for Calculate resource full-time equivalent from, select one of the two options: a. Resource base calendars – Use this option if you want the full-time equivalents to be calculated from each resources base calendar. This is the default option. b. Hours per day – Use this option if you want to specify the full-time equivalents for your resources in the resource plan. After selecting this option, enter the value (in hours) of the standard work day you would like to use for your organization. Note that this value will be used for all resources in the resource plan. 3. Click Save. Exchange Server Details In Office Project Server 2007, users could view their tasks in Microsoft Outlook with the use of an Outlook Add-in that had to be downloaded and installed to each user’s computer. In Project Server 2010, Exchange Server can be integrated with Project Server 2010 to provide task synchronization with Outlook 2007 or Outlook 2010. For more information about how to configure task integration with Exchange Server, see the
- 217. Operational Policies Management 209 TechNet article set “Deploy Project Server 2010 with Exchange Server” (http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff793353.aspx). To configure the Exchange Server Details setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings. 2. On the Additional Server Settings page, in the Exchange Server Details section, click Synchronize Tasks if you want to automatically synchronize tasks from Project Server 2010 with Outlook 2007 or Outlook 2010. 3. Click Save. Task Mode Settings The Task Mode Settings allow you to select the default mode in which tasks are scheduled (manually or automatically). Additionally, if you select the default setting (Manually Scheduled), you can also configure if you want task to be published to team members. Manually scheduled tasks (also referred to as “User-Controlled Scheduling”) is a new feature available in Project Server 2010. When a new project is using the manually scheduled task mode, when a new task is created it ignores the scheduling engine and creates the task without a duration, start date, or finished date (can be entered manually). It can be useful for scheduling tasks with hard dates that are difficult to move (for example, training). For more information about the Manually Scheduled task feature, see the MSDN article “Project 2010: Introducing User-Controlled Scheduling” (http://blogs.msdn.com/b/project/archive/2009/10/23/project-2010-introducing-user- controlled-scheduling.aspx). To configure the Task Mode setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Additional Server Settings.
- 218. 210 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 2. In the Task Mode Settings section: a. Select Manually Scheduled tasks can be published to team members (enabled by default) if you want to allows project managers to publish their manually scheduled task to team members. b. For Default task mode in new projects, select one of the two following settings: Manually Scheduled – You need to enter duration, start, and finish dates for your tasks. This is selected by default. Automatically Scheduled: Scheduling engine will automatically calculate durations, start, and finish dates for your tasks. c.Select Users can override the default selection in Project Professional (enabled by default) if you want to allow your Project Professional users to override your default task mode settings you selected. 3. Click Save. Server Side Event Handlers Similar to Office Project Server 2007, Project Server 2010 provides public events that enable development of custom processes such as adding and enforcing business rules, validation, data processing, notification services, and workflow. These custom processes are written as server side event handlers by developers in an organization and can be associated to Project Server 2010 events through the Server Side Event Handlers page in Project Web App Server Settings. For example, developers in your organization can create an event handler that starts a custom workflow. Through the Server Side Event Handlers page, you can associate that event handler with the Project Published event so that a workflow starts whenever the event occurs. For more information about Project Server Events, see the MSDN article “Project Server Events” (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms481079(v=office.12).aspx) For more information about Project Server Event Handlers, see the MSDN article “How to Write and Debug a Project Server Event Handler” (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en- us/library/ms469450(office.12).aspx).
- 219. Operational Policies Management 211 To associate an event handler with a server side event: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Server Side Event Handlers. 2. On the Server Side Event Handlers page, in Events list, find the event that you want to associate your new event with, and then click the Event Source listed next to the Event Name (for example, click the Project Event Source for the Published Event Name). 3. In the Event Handlers section, the Event Source and Event Name should populate with the Event you selected. Any event handlers that are currently associated with the event will display in the Event Handlers list. Click New Event Handler. 4. In the New Event Handler page, enter the following information for the event handler you want to associate with the selected event: a. In the Display Information section, enter the Event Handler name. You can also optionally enter a description of the Event Handler. b. In the System Information section, in the Assembly Name field, enter the full name of the strongly named event handler assembly. c. In the Class Name field, enter the fully qualified name of the class the implements the event handler functionality.
- 220. 212 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide d. In the Order field, provide the order number of the event handler. If it is the only event handler associated with the event, enter “1”. If there are multiple event handlers associated with the event, enter the order number in which this event handler will be executed. 5. Click Save. Active Directory Resource Pool Synchronization Project Server 2010 Active Directory Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization is used to create or update multiple Project Server enterprise resources at once. Project Server enterprise resources can also be automatically activated and deactivated based on group membership in the Active Directory directory service. For example, new employees in your department can automatically be added as Project Server enterprise resources as long as they are in the Active Directory group selected for synchronization. Conversely, employees who are removed from the Active Directory group have their Project Server accounts deactivated upon synchronization. Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization also updates enterprise resource properties with the most current data from Active Directory. For example, an employee's name and e-mail address may change due to marriage. As long as the change is made in Active Directory and the user is in the linked group, the change occurs in the user’s Enterprise Resource properties when synchronization occurs. The Enterprise Resource Pool can be mapped to a single Active Directory group for synchronization. This Active Directory group can, however, contain nested groups whose members are also synchronized. The following actions can occur during the Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization process: A new Project Server enterprise resource and corresponding user account can be created based on an Active Directory account. An active Project Server resource/user account can be deactivated.
- 221. Operational Policies Management 213 An existing Project Server user account’s metadata (for example, name, e-mail address, and so on) can be updated if it has changed in Active Directory. A previously inactive Project Server resource/user account can be reactivated. Before you perform this procedure, confirm that: You have access to Project Server through Project Web App with an account with the Manage Active Directory Settings and the Manage users and groups global settings. The Service Application (SA) service account for the Project Server instance has Read access to all Active Directory groups and user accounts involved in the synchronization. You can verify this account in the SA's properties on the Service Application Administration page on the SharePoint Central Administration Web site. To configure Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization Use this procedure to configure Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization in Project Server 2010. The following table describes possible scenarios and corresponding actions that occur when Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization takes place: Scenario Action The user exists in Active Directory and is a A new corresponding Project Server user and member of the Active Directory group enterprise resource is created in Project Server mapped to the Enterprise Resource Pool. and added to the Team Members Project Server The user does not exist in Project Server. security group. The user exists in Project Server, but does If Prevent Active Directory synchronization not exist in Active Directory or is not a for this user is not enabled for the user account member of the Active Directory group in Project Server, the corresponding Project mapped to the Enterprise Resource Pool. Server user account status is set to inactive. Otherwise the account will stay active. The user exists in Active Directory and is a The corresponding Project Server enterprise member of the Active Directory group resource and user information is updated (if mapped to the Enterprise Resource Pool. applicable). The user exists in Project Server as an enterprise resource and a user. The user's information has been updated in Active Directory. The user exists in Active Directory and is a If the Automatically reactivate currently
- 222. 214 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Scenario Action member of the Active Directory group inactive users if found in Active Directory mapped to the Enterprise Resource Pool. during synchronization resource option is The user exists in Project Server, but as an selected in Project Server, the account is inactive account. reactivated. If the option is not selected, the account remains inactive in Project Server. Configure Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Active Directory Resource Pool Synchronization. 2. On the Active Directory Enterprise Resource Pool Synchronization page, in the Active Directory Group section, under Active Directory Group to Synchronize, click Find Group. 3. On the Find Group in Active Directory — Webpage Dialog page, in the Group Name field, enter all or part of the name of the Active Directory group which you want to synchronize with the Enterprise Resource Pool. Click the button next to the field to search the Active Directory forest based on your search criteria. 4. To select a group from a remote forest, type the fully qualified domain name of the group (for example, group@corp.contoso.com). You can synchronize to a security or distribution group of any scope (Local, Global, or Universal). Note The Active Directory forest that is searched is shown at the top of the Find Group in Active Directory — Webpage Dialog page. The forest is defined by the fully qualified domain name of the account for the Shared Services Provider on which the Project Server instance is running.
- 223. Operational Policies Management 215 5. From the Group Name list, select the group with which you want to synchronize your Enterprise Resource Pool. Click OK. When you do so, the Active Directory group membership of the selected group is put into memory. This includes all users who are members of nested active directory groups across domains and forests. 6. On the Active Directory Enterprise Resource Pool Synchronization page, you should see the Active Directory group you selected next to Active Directory Group to Synchronize: in the Active Directory Group section. 7. If you want to configure synchronization to occur on a scheduled basis, in the Scheduling Options section, select Schedule Synchronization. Alternatively, you can choose to manually run Active Directory Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization. If you prefer the manual option, skip the following step and continue to step 8. 8. In the Frequency fields, define the frequency at which you want synchronization to occur between the Enterprise Resource Pool and the Active Directory group. This can be scheduled over a defined period of days, weeks, or months. Select a start date and time.
- 224. 216 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 9. You can enable inactive accounts to be reactivated if they are found in the Active Directory group during synchronization. To do so, in the Resource Option section, select Automatically reactivate currently inactive users if found in Active Directory during synchronization. (For example, enabling this option would ensure that if an employee were rehired, the employee's user account would be reactivated). 10. Click Save to save the settings. Click Save and Synchronize Now if you want to synchronize your Enterprise Resource Pool immediately. If you choose not to schedule Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization, you can rerun it manually when needed by returning to this page and clicking Save and Synchronize Now. 11. You can check the status of the Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization by returning to the Active Directory Enterprise Resource Pool Synchronization page and reviewing the information in the Synchronization Status section. It contains information such as when the last successful synchronization occurred. Project Sites Project Sites were referred to as Project Workspaces in previous versions of Project Server. The Project Sites page in Server Settings allows you to manage Project Sites for your projects in Project Server 2010. You can do the following through the Project Sites page: Create a new Project Site Edit a Project Site Address Synchronize Delete a Project Site Go to Project Site Settings
- 225. Operational Policies Management 217 Create Site The Create Site setting allows you to create a new Project Site for your project if you did not originally create one when the project was originally published to Project Server 2010. You can view the Project Sites list to determine if a project does not have an existing Project. All projects without project sites will not have a corresponding URL next to it in the Site Address column. To create a Project site for a project: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Sites. 2. From the Project Name list, select a project for which you want to create the project site. 3. Click Create Site. 4. The Create Project Site message box appears.
- 226. 218 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 5. In the Web Application list, select the Web Application you want for the Project Site. 6. In the Site Application field, verify the site URL for the project site. You can edit the Site URL information if needed. The site URL will be appended to the Web Application to provide you with the Destination URL (as seen in the Destination URL field). 7. Click OK. The project site you created will now display next to the project name you selected in step 2. Edit Site Address The Edit Site Address setting allows you to edit the destination URL for a project site to point to a new site address. Changing the site address information breaks the existing link between the project and the existing Project Site. You can then enter the information to the new Project Site. Note Before changing the Project Site URL for a project, be sure to provision a new Project Site with a new site template. To edit a site address for a Project site: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Sites. 2. From the Project Name list, select a project for which you want to edit the Project site information. 3. Click Edit Site Address. 4. The Edit Site Address dialog box appears.
- 227. Operational Policies Management 219 5. Type a new SharePoint site URL will be selected by default. Change the project site URL information to the new URL. 6. Click Test URL to verify if the new project site URL can be opened. 7. Click OK. The project site URL for the project you selected in step 2 will be changed to the new URL. Synchronize The Synchronize button allows you to manually synchronize the Project Site’s users, permissions, and other Project Server-related information between Project Server 2010 and the Web Server that is running SharePoint Foundation. If you want to automatically run synchronization for your Project Sites, see the Project Site Provisioning Settings Automatic Provisioning setting. To synchronize your Project Site information between Project Server and SharePoint Foundation Server: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Sites. 2. From the Project Name list, select a project for which you want to synchronize your Project site information between Project Server 2010 and SharePoint Foundation. 3. Click Synchronize. Note To view a confirmation that Synchronization occurred, you can go to the Manage Queue Job Server Settings and verify that the synchronization job completed successfully.
- 228. 220 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Delete Site The Delete Site setting allows you to permanently remove a Project Site and its content. Important Verify that you truly want to permanently remove a site and its content before you proceed with this procedure. Deleted Project Sites are not recoverable. To delete a Project site: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Sites. 2. From the Project Name list, select a project for which you want to delete a Project Site. 3. Click Delete Site. 4. A message box appears that will ask you to confirm if you want to delete the Project Site. It will also warn you that Click OK to proceed with deleting the site. Click Cancel if you no longer want to delete the site. 5. If you clicked OK, the Project Site will be deleted and will no longer display next to the project it was associated with in the Project Sites page. Go to Project Site Settings The Go to Project Site Settings setting allows you to go directly to a Project Site’s site settings page. From the Site Settings page, you can make changes to the site, such as add or remove users to the site, add Web Parts to the site, customize the site’s look and feel, and many others.
- 229. Operational Policies Management 221 To go to the Site Settings page for a Project site: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Sites. 2. From the Project Name list, select a project for which you want to view the Project Site settings page. 3. Click Go to Project Site Settings. 4. The Site Settings page for the selected Project Site will open. You can make changes to the Project Sites site settings from this page. Project Site Provisioning Settings The Project Site Provisioning Settings page allows you to configure settings for the Project Sites that are created for projects. You can configure the following settings: Site URL Default Site Properties Automatic Provisioning Project Site Permissions
- 230. 222 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Site URL The Site URL settings allow you to change the default Web application in which your Project Sites are created. The default Site URL information on this page is based on the information provided during the provision of the Project Web App instance. To specify Site URL information: 1. On the Project Web App Home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Site Provisioning Settings. 3. On the Project Site Provisioning Settings page, in the Site URL section, select the Web application you want to be the default Web Application that your Project Sites will be created in from the Default Web application drop-down menu. 4. In the Site URL field, type the URL path (for example, PWA). 5. Click Save. Default Site Properties The Default Site Properties settings allow you select the default site template language and the default Project Site template that will be used to create your Project Sites. When selecting a Project Site template, you can only use the “Microsoft Project Site” template that installs with Project Server 2010, or a template that is derived from it. The
- 231. Operational Policies Management 223 Microsoft Project Site template is built to supports features and functionality in SharePoint Server 2010. Important Project Server 2010 and Office Project Server 2007 do not support the use of the Project Tracking Workspace template from the SharePoint Server 2010 “Fab 40” templates to create project sites. For more details, see Project Server 2010 –The Fab 40 Strikes Again! on the Microsoft Project Support Weblog (http://blogs.msdn.com/b/brismith/archive/2010/12/06/project-server-2010-the-fab-40-strike- again.aspx). To configure default site properties for your Project Sites: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Site Provisioning Settings. 2. On the Project Site Provisioning Settings page, in the Default Site Properties section, select the default language for your Project Sites from the Default site template language drop-down menu. 3. In the Default Project Site template drop-down menu, select the Project Site template that will be used to create your Project Sites. 4. Click Save. Automatic Provisioning The Automatic Provisioning setting allows you to indicate whether you want to have Project Server 2010 create Project Sites for projects when the projects are newly published to the server. Alternatively, the settings can be configured to allow the Project Server Administrator to create Project Sites manually after projects have been published, if desired. Note If you have a group of Project Managers who will not need to create Project sites, you can set the provision mode to Allow users to manually crate project sites in Project Server as noted above. Additionally, denying this group of users the “Manage SharePoint Foundation” global permission will eliminate the display of a Publish Project Site dialog box that typically displays whenever a project is created.
- 232. 224 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide To configure the Automatic Provisioning setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Site Provisioning Settings. 2. On the Project Site Provisioning Settings page, in the Automatic Provisioning section, under Provisioning Mode select one of the two options: Automatically create a project site for each project when first published to Project Server Allow users to manually create project sites in Project Server 3. Click Save. Project Site Permissions The Project Site Permissions setting allows you to specify access is granted to Project sites in Project Server 2010. This setting allows you to automatically synchronize Project Web App users with Project Sites over the following circumstances: When Project Sites are created When project managers publish projects When user permissions change in Project Server 2010 When the Project Site Permissions setting is enabled, the following occur automatically when any of the circumstances above occur: Project managers who have published a project or who have Save Project permissions on a project are added to the Project Managers (Microsoft Project Server) site group. Team members with assignments in a project are added to the Team Members (Microsoft Project Server) site group. Other Project Server users who have View Project Site permission on a project are added to the Readers (Microsoft Project Server) site group.
- 233. Operational Policies Management 225 To enable the Project Site Permissions setting: 1. On the Project Web App Home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Project Site Provisioning Settings. 3. On the Project Site Provisioning Settings page, in Project Site Permissions section, click Check to automatically synchronize Project Web App users with Project Sites when they are created, when project managers publish projects, and when user permissions change in Project Server. When the check box is cleared, Project Server users are never synchronized with Project Sites. 4. Click Save. When the check box is cleared, users are not automatically added to their respective Web sites. To add or update users to their sites, click the Synchronize button on the Project Sites page of the Operational Policies section of Project Web App Server Settings. Bulk Update Project Sites The Bulk Update Project Sites page allows you to change site path information for Project Sites in one Web application to a different one (for example, when migrating). It allows you to break the original links between Project and their corresponding Project Sites in one site collection, and then relinking to the new Project Sites in the new site collection. Update Site Paths Update Content Types Project Site Permissions
- 234. 226 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Update Site Paths The Update Site Paths setting allows you break links between projects and Project Sites contained in one site collection and relink with the new Project Sites in a different site collection. To update Project Site paths to a new site collection: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Bulk Update Project Sites. 2. On the Bulk Update Project Sites page, in the Update Site Paths section, for Previous Site Paths: Select the Web Application for your Project Sites that you want to break the link to. If you are migrating project sites on the same server, the Web Application you need to select may display as a URL. If you are migrating projects sites from a different server, the Web Application you need to select may display as a GUID. In the Site URL field, type the site URL information (for example, PWA). 3. In the New Site Paths: Select the Web Application that contains the Project Sites that you want to link to (for example, http://hr1.contoso.com). In the Site URL field, type the site URL information (for example, PWA). 4. Click Save.
- 235. Operational Policies Management 227 Update Content Types The Update Content Types setting allows you to ensure that when migrating content from one farm to another, that the content types of Project Issues, Risks, and Documents are updated in the new location so that item links will remain functional. To enable the Update Content Types setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Bulk Update Project Sites. 2. On the Bulk Update Project Sites page, in the Update Content Types section, click Update Content Types. 3. Click Save. Project Site Permissions The Project Site Permissions setting allows you to synchronize permissions to the Project Sites while updating the site paths. This allows users to immediately access their Project Sites. Note For the Project Site Permissions site permissions setting to be enabled, the Project Site Permissions setting must also be enabled on the Project Site Provisioning page. To enable the Synchronize Site Permissions setting: 1. On the Server Settings page, in the Operational Policies section, click Bulk Update Project Sites. 2. On the Bulk Update Project Sites page, in the Project Site Permissions section, click Synchronize site permissions. 3. Click Save.
- 236. 228 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 8 Workflow and Project Detail Pages This chapter about Project Server 2010 Workflow and Project Detail Pages contains the following sections: Enterprise Project Types Workflow Phases Workflow Stages Change or Restart Workflows Project Detail Pages Project Workflow Settings
- 237. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 229 Enterprise Project Types An enterprise project type represents a wrapper that encapsulates phases, stages, a single workflow, and PDPs. Each EPT represents a single project type. Normally, project types are aligned with individual departments, for example, marketing projects, IT projects, or HR projects. Using project types helps to categorize projects within the same organization that have a similar project life cycle. For a user, the EPTs appear in a drop-down list of project types when the user clicks New Project on the Ribbon in Project Web App. Create New Enterprise Project Type To create a new enterprise project type 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Workflow and Project Detail Pages, click Enterprise Project Types 3. Click New Enterprise Project Type. In the Name box, enter a name for the type, and then provide a brief description in the Description box.
- 238. 230 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 4. Select a workflow from the Site Workflow Association list. Once you associate a site workflow with a project type and save the type, you cannot go back and update the type to use a different workflow. Note If you're not seeing any workflows in this list, be sure that your server administrator has installed and configured workflows on the Microsoft Project Server 2010 machine. The Project Server 2010 workflow platform is built on the SharePoint workflow platform, which, in turn, is built on the Windows workflow platform. 5. Select a project detail page from the New Project Page list. 6. If you selected No Workflow from the Site Workflow Association list, select the project detail pages that you want to include in this project type from the Available Project Detail Pages box, and then click Add to move them to the box on the right. 7. If the enterprise project type that you are creating is the one that all new projects should use by default, select the Use this as the default Enterprise Project Type during Project Creation check box. 8. Click the button next to the Departments field to select the departments you want to associate with this project type, if appropriate. 9. If you want to associate an image with this project type, provide the URL for the image in the Type the URL box. 10. In the Order section, choose whether you want this project type to appear at the end of the list of project types, or if you want to control its placement in the list. 11. To include this type at the end of the list, select the Position this type at the end check box. 12. To control the placement of this type in the list, clear the Position this type at the end check box, and then choose the type that you want to appear just before the type you're creating from the Choose the type before which the current type should be positioned list. 13. Select a template from the Project Plan Template list, if appropriate. 14. Select a template from the Project Site Template list, if appropriate. 15. Click Save to save this enterprise project type to the server, making it available for new project or proposal creation.
- 239. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 231 Workflow Phases A phase represents a collection of stages grouped to identify a common set of activities in the project life cycle. Examples of phases are project creation, project selection, and project management (shown as Create, Select, and Manage Phases). Phases do not have any direct technical effect on the behavior of an Enterprise Project Type. That is, changing the order of phases does not affect how the system reacts. The primary purpose of demand management phases is to provide a smoother user experience where users have the option of organizing stages into logical groups. Default Workflow Phases New Workflow Phase To create a new workflow phase 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Workflow and Project Detail Pages, click Workflow Phases 3. Click the New Workflow Phase button on the toolbar. 4. Under Name enter the name of the desired phase and optionally enter a description of the phase in the Description text box. 5. Click Save. Add Workflow Phase
- 240. 232 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide To edit an existing workflow phase 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Workflow and Project Detail Pages, click Workflow Phases 3. Click the existing workflow phase in the Workflow Phases column that you wish to modify. 4. Under Name change the name to the desired phase name and optionally enter a description of the phase in the Description text box. 5. Click Save.
- 241. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 233 Workflow Stages A stage represents one step within a project life cycle. A stage is composed of one or more Project Detail Pages linked by common logic or theme. Stages at a user level appear as steps within a project. At each step, data must be entered, modified, reviewed, or processed. Workflow Stages New Workflow Stages To create a new workflow stage 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Workflow and Project Detail Pages, click Workflow Stages. 3. Click the New Workflow Phase button on the toolbar. 4. Under Name enter the name of the desired stage and optionally enter a description of the stage in the Description text box. 5. Under Description for Submit type the description that will be displayed to end-users when submitting to workflow. By default, this description will be displayed in the following places: a. As a Tool Tip when users rest the pointer on the 'Submit' button in a Project Detail Page b. As part of the confirmation dialog shown to users when they click the 'Submit' button in a Project Detail Page
- 242. 234 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide 6. Under Workflow Phase choose the Workflow Phase to correspond with this Workflow Stage. 7. Under Workflow Stage Status Project Detail Page choose the Workflow Stage Status Project Detail Page from the dropdown. This page will be displayed as the introduction page when the project enters this workflow stage. 8. In Visible Project Detail Pages select the Project Detail Pages you wish to be visible for this workflow stage by selecting them from the Available column and clicking the Add button to put them in the Selected Project Detail Pages column. Note By default no PDPs are visible for workflow stages but at least one page should be selected for a workflow stage. 9. Under Additional Settings for the Visible Project Detail Page you may edit the specific description of the Visible PDPs by selecting them in the right column from the previous step and then editing the description in the text box. You may also check the Project Detail Page requires attention check box to highlight the PDP on the Workflow Status page. 10. Under Required Custom Fields select the Custom Fields that are required for the Workflow to enter this Workflow Stage and click the Add button. Take note that these Custom Fields are 'Required' just for this Workflow Stage, not for all the subsequent Workflow Stages in the Workflow. 11. Under Read Only Custom select the Custom Fields that are read only for this Workflow Stage and click the Add button. 12. Under Strategic Impact Behavior select the radio button to specify whether the Strategic Impact values for the project are Read Only, Read Write or Required in this workflow stage. If Strategic Impact behavior is set to Required then a strategic impact value needs to be specified for every business driver. This is typically accomplished by using the Strategic Impact Web part on a project detail page. 13. Under Project Check In Required select whether this Workflow Stage requires the project to be checked in. If project checkin is required for the current workflow stage, the user cannot Submit the Project to Workflow without checking in the Project. This option is typically selected if any project updates occur in this Workflow Stage (which will be blocked if the project is not checked in). 14. Click Save. The Project Workflow Stage is now saved.
- 243. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 235
- 244. 236 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Add a Workflow Stage Details Page Change or Restart Workflows The Change or Restart Workflow section allows you to change a project’s in-progress workflow or change a project’s current stage in a workflow. Restart Enterprise Project Type Change or Restart a Workflow To Change or Restart a Workflow 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings.
- 245. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 237 2. On the Server Settings page, under Workflow and Project Detail Pages, click Change or Restart a Workflow. 3. Under Choose Enterprise Project Type choose the Enterprise Project Type that needs to be changed or restarted. 4. Under Choose Projects select the project with the workflow instances that need to be changed or restarted and add it to the Target List. Note Only projects that are not checked out or are checked out to you are shown in the Choose Projects section. If a project is checked out to another user the workflow cannot be changed or restarted on that project. 5. Under Choose new Enterprise Project Type or restart workflow for current Enterprise Project Type select whether to restart the current workflow for the selected projects or to associate the projects with a new Enterprise Project Type. If a new Enterprise Project Type is selected, you must then choose from the drop down menu the new Enterprise Project Type you wish to use. 6. Under Choose Workflow Stage to Skip to you can select the target workflow stage this workflow will skip to. 7. Click OK. Choose Workflow Stage to Skip Project Detail Pages Project Detail Pages (PDPs) represent a single Web Part Page in Project Web App. PDPs can be used to display or collect information from the user. You can create PDPs in much the same way you create any Web Part Page in a SharePoint site, where you can add Web Parts that provide the experience you want. You can add individual Web Parts from the standard Web Part galleries or create custom Web Parts. Project Server Web Parts and custom Web Parts used in demand management all contain custom fields. Web Parts can make calls to the Project Server Interface (PSI), query the Reporting database, or integrate with external systems. Create or Edit Project Detail Pages There are three types of Project Detail Pages that can be created:
- 246. 238 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide project template that has a workflow for portfolio analysis. diting To create a project detail page 1. On the PWA home page, click Server Settings. 2. On the Server Settings page, under Workflow and Project Detail Pages, click Project Detail Pages. 3. Click on the Documents tab. 4. Select New Document on the ribbon. 5. On the newly created blank page, select Add a Web Part. 6. In Categories select Project Web App and then select the web part you would like to add.
- 247. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 239 7. The newly selected Web Part is displayed. Now you must select the project fields used to populate the web part. From the top right menu select Edit Web Part. 8. In the Edit Web Part pane click the Modify button. 9. Select the project data you wish the web part you selected to display and then click OK. 10. In the Edit Web Part pane under Appearance enter a title and then click OK. 11. Select the Page Tools tab on the ribbon and click Stop Editing. 12. Now select Edit Properties on the ribbon and update the Display Name and Page Type for your newly created Project Detail Page.
- 248. 240 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Project Workflow Settings Project Server 2010 workflows are built from SharePoint Server 2010 Site Workflows which are built off of Windows Workflow Foundation, which in turn is built off of Windows .NET Framework 3.5. The workflows are made up of workflow activities that are objects with code within it. Project Server 2010 Workflow Hierarchy The Project Workflow Settings page designates the Workflow Proxy User account so that the Project Server Interface (PSI) calls within a workflow can be performed. By default, all PSI calls within a workflow will be made under the context of the Workflow Proxy User Account. For these PSI calls to be successful the Workflow Proxy User Account should have appropriate permissions in Project Server, therefore the only item to be set on this page is to make sure that the Workflow Proxy User account text box contains a logon account with sufficient permissions.
- 249. Workflow and Project Detail Pages 241 Project Workflow Settings
- 250. 242 Appendices
- 251. Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 243 A Project Server 2010 Category Permissions The following is a list of category permissions for Microsoft Project Server 2010. The table includes columns with the following information: Description Describes what the permission lets you do. Dependencies Lists any other permissions (global or category) or requirements to allow the permission to function. Previous name, if renamed from Office Project Server 2007 Specifies the Microsoft Office Project Server 2007 permission name if the permission was renamed from Office Project Server 2007 but provides the same functionality. New for Project Server 2010 Displays an X symbol if the permission is new for Project Server 2010. Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Accept Task Allows a user to accept Update updates on projects without Requests requiring that the user have the Save Project to Project Server permission
- 252. 244 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Adjust Allows a Project Web App User must have the Timesheet user to adjust a team View Resource member’s submitted Timesheet timesheet entries. Grant this permission to use this permission to any member permission. of your organization who requires the ability to adjust a resource’s timesheet entry after that resource has submitted the entry. Approve Allows a user to approve a User must have Timesheets team member’s submitted the Approve timesheet entries. Grant this Timesheets permission to any member permission of your organization who through a requires the ability to category which approve a resource’s contains the timesheet. resources which they want to approve timesheets on. Assign Allows a user to assign or User must have Resources allocate a given resource to the View Team projects. This permission Builder global controls the list of available permission in resources in Team Builder order to use the in both Project Web App Build Team page and Project Professional. in Project Web Grant this permission to all App or Project project managers and Professional. resource managers who
- 253. Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 245 Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 have to assign, manage, or User must have allocate resources. For the Build Team example, if you want to add on Project resource R to project P, category then you must have permission in permission to assign order to assign a resource R (Assign resource in an Resources) plus permission existing to build the team on Project enterprise P (Build Team on Project). project. In addition, you must have access to the Team Builder User must have page through either Project the Build Team Web App or Project on New Project Professional (Assign global permission Resources to Project Team). in order to assign a resource in a new enterprise project. Build Team Allows a user to add User must have On Project resources to a project that the View has already been saved to Enterprise the Project Server database. Resource Data Grant this permission to and Assign project managers who want Resources to use the Build Team category feature in Project permissions in Professional to staff their order to see projects before they save resources that are (and publish) them to the part of the Project Server database. Or, Enterprise grant this permission to Resource Pool in
- 254. 246 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 resource managers who the Build Team want to use the Build Team feature in Project feature in the Project Center Professional and of Project Web App to add Project Web resources to a project that App. has already been saved to the Project Server database. User must have permission (at the category level) to access the specific projects and resources that have to be accessed to build the project team or assign resources. Create New Determines which projects User must be granted Task or are available when you are the New Task Assignment creating new tasks. Grant Assignment global this permission to any permission in order to group of projects that access the New task individual users will be able page in Project Web to create new tasks in by App. using the Create a new task page in Project Web App. Create When allowed, this Object Links permission enables a user to create, modify, or delete links between Project Tasks
- 255. Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 247 Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 and items in the Project Workspace (documents, issues, deliverables or risks). Delete Allows users of Project Project Professional to delete a project saved to the Project Server database from the Open from Microsoft Project Server dialog box in Project Professional. Grant this permission to members of your organization to enable them to more closely manage the projects he or she has saved to the Project Server database from Project Professional or by using the "Delete Enterprise Objects" link in Project Web App. Before letting users delete projects, you should consider how your organization will recover those projects, if you have to do so. Edit Allows a project manager to User must be granted Enterprise edit enterprise resource data the View Enterprise Resource by using Project Resource Data Data Professional (checked-out category permission. Enterprise Resource Pool) or a resource manager to
- 256. 248 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 edit enterprise resources using Project Web App (Resource Center). Grant this permission to project managers and resource managers who have to make updates to resources that belong to the Enterprise Resource Pool. Resource managers with this permission are able to edit enterprise resource data in the Resource Center in Project Web App, and they can make updates to cost data, custom outline code data, custom field data, and other static information related to resources. Resource managers cannot add or delete resources from the Enterprise Resource Pool in Project Web App. Project managers can add or delete resources from the Enterprise Resource Pool in Project Professional if they have the New Resource global permission (to add resources) or the Clean Up Project Server Database global permission (to delete resources). These
- 257. Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 249 Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 permissions are required in addition to the Edit Enterprise Resource Data category permission. Note The Project Server Interface (PSI) can also be used to create or delete resources in the Enterprise Resource Pool and to edit enterprise resource data. Edit Project Allows a user to edit only Edit Project X Summary the enterprise project fields Properties Fields shown in the new project in Project fields Web Part. If you do Center not have this permission, but have "Save Project to Project Server" you can still edit project-level fields/custom fields in the project field Web Part. Manage Controls whether a specific X Basic Project Project Permission can be Security set on a single project through the new Project Permissions feature. Manage Allows a user to see other X Resource users whom he or she
- 258. 250 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Delegates manages and to set delegates for them. Manage Allows a user to edit a Resource resource plan. Plan Open Project Allows a user to open a project from the Project Server database in read-only mode using Project Professional. Grant this permission to any member of your organization who has to use the Open from Microsoft Project Server dialog box in Project Professional or in the Project Center in Project Web App to open projects that have been saved to the Project Server database. If users are not assigned the Save Project to Project Server permission, then the project will only be open in read-only mode. Publish Allows a user to Publish User must be granted Project projects to the Project the Open Project Server Published database category permission using Project Professional on any project that has and Project Web App. to be checked out Grant this permission to all from the Project
- 259. Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 251 Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 members of your Server database. If the organization who will be project has changed publishing projects. since opening, the user will be required to have the Save Project to Project Server permission on that project. If not, when a publish occurs, it will only publish the outdated version. Save Project Allows a user to save User must be to Project projects to the Project granted the New Server Server database using Project Project Professional. Also permission in gives Project Web App order to create users the permission to save the project. schedules and strategic impact data. Grant this User must be permission to all members granted the of your organization who Open Project will be saving projects from category Project Professional to the permission on Project Server database any project that using the Save to Project has to be Server dialog box or checked out through Server-side from the Project projects. Server database. Save Allows a user to save a User must be granted Protected protected baseline or clear a the Save Project to Baseline protected baseline Project Server
- 260. 252 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 associated with an category permission. enterprise project published to the Project Server database. Grant this permission to project managers who have to save baselines in their projects. Baselines are saved by using the Set Baseline functionality accessed from the Project Professional ribbon on the Project tab in the Schedule group. Click the Set Baseline button and then select Save Baseline or Clear Baseline. Protected Baselines are in the range of Baseline 0-5 inclusive. Only users who have Save Unprotected Baseline, Open Project and Save Project Category permissions are able to save Baselines in Baseline 6-10. View Project Allows a user to access a Users also must be Summary in specific project in the granted the View Project Project Center from Project Project Center View Center Web App. Grant this permission in order to permission to any member see the Project Center. of your organization who has to view projects summaries in the Project
- 261. Project Server 2010 Category Permissions 253 Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Center. View Project Allows a user to view View X Schedule in project information for a Project Project Web specific project from the Details in App Project Center in Project Project Web App. Grant this Center permission to users who have to view project details in the Project Center. View Allows a user to view Resource assignment details using Assignments assignment views in the in Resource Center. Grant this Assignment permission to project Views managers and resource managers who have to view resource assignment details in the Resource Center from Project Professional or Project Web App. View Allows a user to view Enterprise resources and resource data Resource that is stored in the Data Enterprise Resource Pool. Grant this permission to any user who has to view resources and resource data that is stored in the Enterprise Resource Pool. View Project Allows users to view Risks, View X
- 262. 254 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if New renamed for from Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Site Issues, and Documents Project areas in Project Web App Workspace and Project Professional. Grant this permission to any user of Project Professional who has to select Project site, Documents, Issues, or Risks from the Info page in the Backstage or any user of Project Web App who has to access the Project site, Documents, Issues, or Risks top-level navigation links.
- 263. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 255 B Project Server 2010 Global Permissions The following is a list of global permissions for Microsoft Project Server 2010. The columns in the table include the following: Description Describes what the permission enables you to do. Dependencies Lists any other permissions (global or category) or requirements necessary for the permission to function. Previous name, if renamed from Project Server 2007 Specifies the Office Project Server 2007 permission name if the permission was renamed from Office Project Server 2007 but provides the same functionality. New for Project Server 2010 Displays an X symbol if the permission is new for Project Server 2010. Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 About Allows a user to access the Microsoft About Project Server page Project Server through Project Web App Server Settings.
- 264. 256 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Accept Allows a user to accept but Users have access Timesheets not approve a timesheet. An to the Approval example would be where an Center if they have administrative assistant would either the Accept view the timesheets to make Timesheets or the sure that there were no View Approvals inaccuracies in them. When it permission. is accepted then a manager with Approve Timesheets permission will approve the timesheets. Build Team Allows a user to add resources User has to be On New to a project that has not been granted the Assign Project saved to Project Server. Grant Resources and this permission to project View Enterprise managers who want to use the Resource Data Build Team feature in category Microsoft Project Professional permissions in to staff their projects before order to see they save (and publish) them resources that are to Project Server. part of the Enterprise Resource Pool in the Build Team feature in Microsoft Project Professional. Can be Specifies whether a user can X Delegate be a delegate. Change Allows a user to change their
- 265. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 257 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Password Forms user account password from Project Web App. Forms-based authentication is provided through a membership provider and individual membership providers may prevent the changing of passwords. Please verify this with your membership provider if you intend to use this permission. Change Allows a user to change a X Workflow project's Enterprise Project type. (Change Project Type). Clean up Allows a user to access the Project Server Delete Enterprise Objects database page available through the Server Settings page in Project Web App. Grant this permission to users who have to delete timesheets, status reports responses, projects, resources, users, and user delegates from Project Server. Close Task to Allows a user to close tasks to Updates Time Reporting. It gives access to the Close Tasks to Update Project Web App page.
- 266. 258 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Contribute to Allows users to edit items Contribute Project Web within lists in Project Web to Project App App project sites. Web App Edit Status Allows a user to access the Report Request a status report link on Requests the Project Web App Status Reports center and to view team reports. Grant this permission to any member of your organization who has to create status report requests and view team reports, usually project managers, resource managers, team leads, and members of your organization’s PMO. Edit Status Allows a user to access the Report Submit a status report link on Responses the Status Reports center in Project Web App. Grant this permission to any user of Project Web App who must be able to submit status reports. Log on Allows a user to connect to Project Server from Microsoft Project Professional or to log on to Project Web App. Grant this permission to any user who is authorized to connect
- 267. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 259 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 to Project Server from Microsoft Project Professional or log on to Project Web App. Log on to Allows a user to load the Project Server Enterprise Global Template from Project when he or she connects Professional Microsoft Project Professional to Project Server. Grant this permission to all users in your organization who will be using Microsoft Project Professional to connect to Project Server. Manage Allows users to modify any Active Active Directory Directory Synchronization settings Settings within the Project Web App Administration. If the user is denied this permission then they cannot modify settings for any of the following: Enterprise Resource Pool synchronization settings. Project Web App Security Groups synchronization settings. Choose an Active Directory Group to synchronize against a specific Security Group within the Add/Modify Group page.
- 268. 260 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Manage Allows a user to access the Check-Ins Forced Check-in Enterprise Objects page in Project Web App. This page lets users force check-in projects, resources, custom fields, calendars, lookup tables and resource plans. Manage Cube Allows a user to the set and Building modify the settings for OLAP Service cube creation. Manage Allows a user to access the X Drivers drivers.aspx page to create drivers for Portfolio Analysis. Manage Allows a user to create, modify Enterprise and delete Enterprise Calendars Calendars within Project Web App. Manage Allows a user to modify the Enterprise definitions of Enterprise Custom Fields Custom Fields and lookup table from Project Web App. Manage Allows administrators to X Exchange enable the synchronization of Integration project tasks with Exchange Server. Manage Gantt Allows a user to access the Chart and Gantt chart and grouping
- 269. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 261 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Grouping formats customization options Formats in the Project Server Administration page for Project Web App views. Manage Lists Allows a user to create, in Project modify, and delete lists within Web App the Project Web App project site. This permission is used when synchronizing a user against the Project Web App project site. Manage Allows a user to manage the X Notification Notification and Reminders and settings. Reminders Manage My Allows users to see the X Delegates "Manage Delegates" link and to set a delegate on the "Add/Modify Delegation" page. Manage My Allows users to set a user who X Resource requires a substitute on the Delegates Add/Modify Delegation page. Manage Allows a user to access the Personal Manage My Alerts and Notifications Reminders page in Project Web App. Grant this permission to any user that
- 270. 262 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 you want to be able to sign up for e-mail notifications and reminders related to tasks and status reports. Manage Allows a user to create, read, X Portfolio update, and delete Portfolio Analyses analyses. Manage Allows a user to create, read, X Prioritizations update, and delete driver prioritizations. Manage Allows a user to schedule the Project Server backup or immediately back Backup up several entities on Project Server, including the following: Projects The Enterprise Resource Pool Calendars Custom fields The Enterprise Global template Views System settings Categories Group settings. Manage Allows a user to immediately Project Server restore several entities on Restore Project Server, including the
- 271. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 263 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 following: Projects The Enterprise Resource Pool Calendars Custom fields The Enterprise Global template Views System settings Categories Group settings Note Similar to Server Backup except that the permission does not let you schedule a recovery. Manage Allows a user to access the Project Web Manage Views page in the App Views Server Settings page in Project Web App. Users with permission to access this page are able to add, modify, or delete Project, Project Center, Resource Center, Assignment, or Portfolio Analyzer views, and they are able to modify Timesheet views. Grant this permission to project managers, resource managers,
- 272. 264 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 and members of your organization’s PMO so they can create project data views for users to access in Project Web App and Microsoft Project Professional. It is important to remember that if your organization is allowing project managers to create custom fields at the project level, then each project may require its own unique view. The number of projects in this kind of environment may be too many for the IT administrator team; offloading this work to the people in your organization that work at the project level on a day-to-day basis is one way to distribute the workload of managing views. Manage Allows the user to read or set Queue queue configuration settings and retry, cancel, and unblock jobs in the queue. Manage Allows a user to access the Resource Alert me about my resources Notifications on tasks and status reports link on the Project Web App home page. Grant this permission to
- 273. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 265 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 any resource manager or project manager you want to be able to sign up for e-mail notifications and reminders related to their resource’s tasks and status reports. Manage Rules Allows a user to access the Rules page from the Approval Center in Project Web App and set rules on how update transactions will be automatically processed. Grant this permission to project managers, resource managers, or members of your organization’s PMO so they can define how they will automatically receive and accept changes to transactions by their resources. Manage Allows a user to access the security Manage security page in Project Web App to define security categories, security templates, and user authentication settings. Grant this permission to Project Server administrators or a very small and closely managed group of people. This page lets users change Project Server
- 274. 266 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 security settings, create security categories and security templates. Changes to settings on this page, once you have begun using Project Server in your organization, should be carefully managed and (ideally) infrequent. Manage Allows a user to register event X Server Events handlers for specific Project Server server-side events. The Manager Server Events page requires the event handler to be registered by the server as defined in the Project Server SDK. Manage Allows a user to access the Server Project Web App Permissions Configuration page in Project Web App. Users with permission to access the Project Web App Permissions page can enable or disable enterprise features, manage organizational permissions, and create custom menus (both top-level and side-pane) in Project Web App. Grant this permission to Project Server administrators or a very small and closely managed group of people.
- 275. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 267 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Manage Allows a user to create and Users with this Manage X SharePoint delete project sites, whether or permission should Windows Foundation not sites are created on project be granted SharePoint publish, permission administrative Services synchronization settings, and privileges to all of site path updates. Grant this the servers that are permission to members of running Project your organization who are Server 2010 and administrators for Project SharePoint Server Web App or administrators 2010 for the servers that are running SharePoint Server 2010. Manage Site Allows users or groups the X Services ability to manage Queue Settings, Active Directory Synchronization, and Event handlers. Manage Time Allows a user to create and Manage X Reporting and modify Timesheet and Fiscal Timesheet Financial period definitions. and Periods Financial Periods Manage Time Allows a user to be forwarded Tracking timesheets for review. After reviewing the timesheet, the user will be required the following permissions: Accept Timesheet
- 276. 268 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Approve Timesheet Manage Users Allows a user to access the and Groups Manage Users and Groups page in the Server Settings page in Project Web App. Users with this permission will be able to add, modify, or delete Project Server users and manage Project Server security groups. Grant this permission to members of your organization who are Project Server administrators. Only a small group of people should have permission to access this set of pages. Manage Allows a user to manage and X Workflow and view workflow and Project Project Detail Detail Pages (PDPs). Pages New Project Allows a user to add a new project to Project Server using Microsoft Project Professional, Project Web App, or the Project Server Interface (PSI). New functionality in Project Server
- 277. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 269 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 2010 for this permission: If you do not also have the Open Project permission, after you create a project, you are taken back to the Project Center. New Resource Allows a project manager to add new resources to the Enterprise Resource Pool using Microsoft Project Professional, the Project Web App Resource Center, or the Project Server Interface (PSI). Grant this permission to any member of your organization who has to create new enterprise resources in Project Server. Note If your organization is using the Active Directory synchronization feature, you may want to consider denying this permission to all non-IT administrators in your organization. New Task Allows users to access the Assignment Create a New Task and Add Yourself to a Task links from the Insert Row button found
- 278. 270 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 on the Tasks page of Project Web App. Grant this permission to any member of your organization who has to create new assignments on existing tasks in projects that have been published to Project Server. Users with this permission will also be able to use the Create a New Task link to create new tasks in Project Web App for any project to which the user has access. The list of available projects for a user to create new tasks is determined by the Create New Tasks or Assignment category permission. A user who has the New Task Assignment permission must also have access to the projects to which they want to assign themselves to a task. Open Project Allows a user to open an User must be Template Enterprise Project Template granted the New from Project Server using Project global Microsoft Project permission in order Professional. Grant this to save the project permission to all users in your to the Project organization who will be using Server database as Microsoft Project Professional an actual project.
- 279. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 271 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 to create and manage projects that are based on Enterprise Project Templates. Reassign Task Allows a user to delegate an assigned task to another (existing) user. Grant this permission to members of your organization who need the ability to delegate task assignments to other resources. For example, a large project may be run by a single project manager, but actually implemented by several teams, each with their own team lead. A project manager could assign the team leads in the project plan, and then the team leads could in turn delegate each task to individual members of their teams. This example creates an additional layer of task management within the larger organization, but it can also simplify resource allocation within projects themselves and make it easier for a project manager to manage large projects. Or, if you have a resource that is about to leave on a three-week vacation, and this resource had
- 280. 272 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 this permission, they would be able to assign their tasks directly to other resources instead of having the project manager check out the project and reassign resources. Save Allows a user to check out, Enterprise modify, and save the Global Enterprise Global Template to the Project Server database from Microsoft Project Professional. This permission should only be granted to a small group of people in your organization; either project managers, members of your organization’s PMO, or Project Server administrators. Save Project Allows a user to create and User needs to be Template save a project as an Enterprise granted the Assign Project Template from Resources and Microsoft Project Professional View Enterprise to the Project Server database. Resource Data Grant this permission to category members of your organization permissions in who are tasked with creating addition to this Enterprise Project Templates. permission if they When a user saves a project to are also responsible Project Server for the first for adding Generic time, the option to select resources to the Template (as opposed to Enterprise Project
- 281. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 273 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Project) from the Type drop- Template. down list in the Save to Project Server dialog box is enabled. Save Allows a user to save a non- User needs to be Unprotected protected baseline or clear a granted the Save Baseline non-protected baseline Project category associated with an enterprise permission. project published to the Project Server database. Baselines are saved by using the Set Baseline functionality accessed from the Microsoft Project Professional ribbon on the Project tab in the Schedule group. Click the Set Baseline button and then select Save Baseline or Clear Baseline. Unprotected Baselines are in the range of Baseline 6-10 inclusive. Self-Assign Resources can be members of Team Tasks a Team Assignment Pool. With this permission, it is possible for users to assign tasks, which have been assigned to their Team Assignment Pool, to themselves through the Team Tasks page in Project Web App.
- 282. 274 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Status Broker Allows API updates to occur X Permission for a user from places like Microsoft Exchange Server. View Allows a user to view the Users have access Approvals Approval Center. to the Approval Center if they have either the Accept Timesheets or the View Approvals permission. View Business Allows a user to see the X Intelligence Business Intelligence link in Link Quick Launch. However, it has no impact on Report Center Security. View OLAP Allows a user to read from the Data output for the OLAP cube. This permission is only checked when the OLAP cube is built. View Project Allows users to access the User needs to be Center Project Center from Project granted the View Web App or Microsoft Project Project Summary Professional. in Project Center category permission. View Project Allows a user to access project View views in Project Web App.
- 283. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 275 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Grant this permission to users who need to drill down into project details using the Project Center in Project Web App or Microsoft Project Professional. View Project Allows a user to see the link in X Schedule the Quick Launch. However, Views it has no impact on Report Center Security. View Project Allows a user to approve X Timesheet timesheets on a line-by-line Line basis. Approvals View Allows a user to access the Resource View Resource Availability Availability page to view resource allocation data in Project Web App. Grant this permission to users in your organization who need to view resource availability in Project Web App. View Allows users to access the User needs to be Resource Resource Center from Project granted the View Center Web App or Microsoft Project Enterprise Professional and view resource Resource Data allocation data. Grant this category permission to users who need permission.
- 284. 276 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 to view the Resource Center in Project Web App by clicking the Resources link in the top- level navigation, or in Microsoft Project Professional by selecting Resource Center on the Collaborate menu. View Allows a user to access the X Resource Plan Resource Plan page within Project Web App. View Allows users to view the Users must be Resource timesheets, regardless of their granted the Accept Timesheet state or ownership, for Timesheet global resources identified in the permission to use category selection criteria. this permission. View Task This permission when denied Center prevents users from seeing the Task Center link on the Project Web App Quick Launch menu. Note This permission does not lock down access to the Task Center page. It is still possible for users to navigate to this page. View Team Allows a user to use Build User needs to Builder Team in Project Web App and be granted the
- 285. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 277 Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Microsoft Project Assign Professional, as well as Resources determine the list of available category resources. Grant this permission in permission to resource addition to managers to allow them to use the View Build Team in Project Web Team App to add resources to Builder projects that have been saved global to the Project Server database. permission. Project Managers can also use The Assign this permission to allow them Resources to use Build Team in category Microsoft Project Professional permission to add resources to projects. determines the list of resources available in Build Team in both Microsoft Project Professional and Project Web App. User needs to be granted the Build Team on Project category permission. The Build
- 286. 278 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Previous name, if renamed New from for Office Project Project Server Permission Description Dependencies Server 2007 2010 Team on Project permission determines with which projects Build Team can be used. This applies to using Build Team in both Microsoft Project Professional and Project Web App. View When this permission is View X Timesheets denied it prevents users from Timesheet seeing the Timesheet Center Center link on the Project Web App Quick Launch menu Note This permission does not lock down access to the Timesheet page. It is still possible for users to navigate to this page
- 287. Project Server 2010 Global Permissions 279
- 288. 280 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide C Project Server 2010 Default Security Groups This article describes the default permissions that are given to the default templates and user groups in Microsoft Project Server 2010. Project Server 2010 creates seven default groups during installation: Administrators Executives Portfolio Managers Project Managers Resource Managers Team Leads Team Members Each group is given a default set of permissions (global and category). Templates are also included to allow these default permissions to be assigned to new groups created by the administrator. After using the template to create a new group, you can then choose to customize the new group to better suit your users by editing the permission for the group. Global permissions differ from category permissions in that they apply to functionality that the user is allowed to use in Project Server 2010. Category permissions apply to what users are allowed to do with specific projects, resources, and views as defined by the category that the group is associated with. For more information about groups and categories, see the Microsoft TechNet article “Plan groups, categories, and RBS in Project Server 2010” (http://technet.microsoft.com/en- us/library/cc197354.aspx).
- 289. Project Server 2010 Default Security Groups 281 Default global permissions The following table contains a list of the default global permissions for each of the default user groups. Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members About Microsoft X Project Server Accept X X X Timesheets Build Team On X X X X New Project Can Be Delegate X Change X X X X X X X Password Change X Workflow Clean Up X Project Server Database Close Tasks To X X X Updates Contribute to X X X X Project Web App Edit Status X X X X X X Report Requests Edit Status X X X X X X X Report Responses Log On X X X X X X X Log on to X X X X Project Server
- 290. 282 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members from Project Professional Manage Active X Directory Settings Manage Check- X X Ins Manage Cube X X Building Service Manage Drivers X X X Manage X X Enterprise Calendars Manage X X Enterprise Custom Fields Manage X Exchange Integration Manage Gantt X Chart and Grouping Formats Manage Lists in X X X X Project Web App Manage My X X Delegates Manage My X X Resource Delegates Manage X X Notification and Reminders
- 291. Project Server 2010 Default Security Groups 283 Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Manage Personal X X X X X X X Notifications Manage X X X Portfolio Analyses Manage X X X Prioritizations Manage Project X Server Backup Manage Project X Server Restore Manage Project X X Web App Views Manage Queue X X Manage X X X X Resource Notifications Manage Rules X X Manage Security X Manage Server X Configuration Manage Server X Events Manage X SharePoint Foundation Manage Site X Services Manage Time X Reporting and Financial Periods
- 292. 284 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Manage Time X Tracking Manage Users X and Groups Manage X Workflow Project Detail Pages New Project X X X X X X X New Resource X X X New Task X X X X Assignment Open Project X X X Template Reassign Task X X X Save Enterprise X X Global Save Project X X X Template Save X X X Unprotected Baseline Self-assign Team X X X X X Tasks Status Broker X Permission View Approvals X X X X View Business X X X X Intelligence Link View OLAP X X X X Data
- 293. 285 Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members View Project X X X X X X X Center View Project X X X X X X X Schedule Views View Project X X X X Timesheet Line Approvals View Resource X X X X X Availability View Resource X X X X X Center View Resource X X X X X Plan View Resource X Timesheet View Task X X X X X X X Center View Team X X X X Builder View Timesheets X X X X X X X Default category permissions The following table contains a list of the default category permissions for each of the default user groups. Use the following legend for the table below. My Org = My Organization My Dir = My Direct Reports My Proj = My Projects
- 294. 286 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide My Res = My Resources My Tsks = My Tasks For example, a user in the default Administrators group (who is associated to the My Organization category by default) has permissions allowed in the Administrators column in the table. These category permissions only apply to all projects, resources, and views selected for the My Organization category. However, a user in the default Project Managers group (who is associated to the My Organization and My Projects categories) has a different set of category permissions for the objects in the My Organization category. This allows you to conveniently set a more or less restrictive set of permissions for different types of users to a group of projects, resources, and views. For more information about groups and categories, see the Microsoft TechNet article “Plan groups, categories, and RBS in Project Server 2010” (http://technet.microsoft.com/en- us/library/cc197354.aspx). Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Accept Task My Org My Proj Update Requests Adjust My Org Timesheet Approve My Org My Org My Dir, Timesheets My Res Assign My Org My Org My Org My Res Resource Build Team My Org My Org My Proj My Org On Project Create New My Org My Proj My Proj My My Tsks Task or Proj Assignment Create My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Org, My My Tsks Object My Proj, Proj Links My Res
- 295. 287 Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Delete My Org My Org My Proj Project Edit My Org My Org My Res Enterprise Resource Data Edit Project My Org My Proj Summary Fields Manage My Org My Org My Proj Basic Project Security Manage My Org My Res Resource Delegates Manage My Org My Org My Org My Res Resource Plan Open My Org My Org My Proj My Tsks Project Publish My Org My Org My Proj Project Save Project My Org My Org My Proj to Project Server Save My Org My Proj Protected Baseline View My Org My Org My Org My Org, My Res Enterprise My Proj Resource
- 296. 288 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Data View My Or My Org My Org My Proj My My Tsks Project Proj Schedule in Project Web App View My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Proj My My Tsks Project Site Proj View My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Proj My My Tsks Project Proj Summary in Project Center View My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Res My My Tsks Resource Proj Assignments in Assignment Views
- 297. Project Server 2010 Default Categories 289 D Project Server 2010 Default Categories Microsoft Project Server 2010 creates seven default categories during installation. Each of the categories is configured to be accessed by specified default user groups. Each category has a predefined set of category permissions for default user groups that have access to that category. The following sections list the default settings for each category for Project Server 2010. In this article: Categories Category permissions Categories Specific default groups are already associated with each of the default categories. The following table shows the default categories and the default groups that can access each of them. Note For more information about the relationship between groups and categories, see the TechNet article “Plan groups, categories, and RBS in Project Server 2010” (http://technet.microsoft.com/ro-ro/library/cc197354(en-us).aspx). Category Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members My Direct X Reports My X X X X X
- 298. 290 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Category Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Organization My Personal X X X X X X Projects My Projects X X X My X Resources My Tasks X Category permissions The following table describes the default category permissions for each default group. For example, a user in the default Administrators group (who is associated to the My Organization category by default) has the permissions allowed in the Administrators column in the table. These category permissions only apply to all projects, resources, and views selected for the My Organization category. However, a user in the default Project Managers group (who is associated to the My Organization and My Projects categories) has a different set of category permissions for the objects in the My Organization category. This allows you to conveniently set a more or less restrictive set of permissions for different types of users to a group of projects, resources, and views. Note For more information about category permissions, see Appendix A: Project Server 2010 category permissions. For more information about the relationship between groups and categories, see the TechNet article “Plan groups, categories, and RBS in Project Server 2010” (http://technet.microsoft.com/ro-ro/library/cc197354(en-us).aspx). Use the following legend for the table below. My Org = My Organization My Dir = My Direct Reports My Proj = My Projects My Res = My Resources My Tsks = My Tasks
- 299. Project Server 2010 Default Categories 291 Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Accept Task My Org My Proj Update Requests Adjust My Org Timesheet Approve My Org My Org My Dir, Timesheets My Res Assign My Org My Org My Org My Res Resource Build Team My Org My Org My Proj My Org On Project Create New My Org My Proj My Proj My My Tsks Task or Proj Assignment Create My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Org, My My Tsks Object My Proj, Proj Links My Res Delete My Org My Org My Proj Project Edit My Org My Org My Res Enterprise Resource Data Edit Project My Org My Proj Summary Fields Manage My Org My Org My Proj Basic Project Security
- 300. 292 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members Manage My Org My Res Resource Delegates Manage My Org My Org My Org My Res Resource Plan Open My Org My Org My Proj My Tsks Project Publish My Org My Org My Proj Project Save Project My Org My Org My Proj to Project Server Save My Org My Proj Protected Baseline View My Org My Org My Org My Org, My Res Enterprise My Proj Resource Data View My Or My Org My Org My Proj My My Tsks Project Proj Schedule in Project Web App View My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Proj My My Tsks Project Site Proj View My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Proj My My Tsks Project Proj Summary in Project Center
- 301. Project Server 2010 Default Categories 293 Permission Portfolio Project Resource Team Team Name Administrators Executives Managers Managers Managers Leads Members View My Org My Org My Org My Proj My Res My My Tsks Resource Proj Assignments in Assignment Views
- 302. 294 Project Server 2010 Administrator's Guide







































































![Enterprise Data 63
Attribute Description
Test Choose the operator (equals, less than, etc.) to apply to the field
value to determine the image to use.
Values Type the field value or a field reference (e.g., [cost]) that, combined
with the operator in the test column, determines when to use the
image in the Image column.
Image Choose the image to display when the test/value combination is
true.
Move Use the move buttons to move a row up or down in the table.
Show data values in Select the Show data values in ToolTips to show the field value in
ToolTips the tool tip associated with the image.
When using graphical indicators for summary rows, you can choose to inherit the graphical
indicator settings that you have defined for non-summary rows.
Graphical indicators – summary rows
If you select the Inherit criteria from non-summary rows check box when configuring
graphical indicators for summary rows, the graphical indicator parameters you configured for
the non-summary rows will be used.
Graphical indicators – project summary
If you select the Inherit criteria from summary rows check box when configuring graphical
indicators for project summary, the graphical indicator parameters you configured for the
summary rows will be used.
Behavior
You can configure a custom field to be controlled by workflow or to require a value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftprojectserver2010administratorsguide-121017074124-phpapp02/85/Microsoft-project-server-2010-administrators-guide-71-320.jpg)