Module 2 Database ICTL Form 2
- 1. Students Profile Create a table, define primary key & insert data
- 2. fields records The table content eleven records. Each records have five fields.
- 3. Format Use to display Text Short, alphanumeric values, such as a last name or a street address. Number Numeric values, such as distances Currency Monetary values. Yes/No Yes and No values and fields that contain only one of two values. Date/Time Date and Time values for the years 100 through 9999. Rich Text Text or combinations of text and numbers that can be formatted using color and font controls. Calculated Field Results of a calculation. The calculation must refer to other fields in the same table. Attachment Attached images, spreadsheet files, documents, charts, and other types of supported files to the records in your database, similar to attaching files to e-mail messages. Hyperlink Text or combinations of text and numbers stored as text and used as a hyperlink address. Memo Long blocks of text. Lookup Displays either a list of values that is retrieved from a table or query, or a set of values that you specified when you created the field.
- 4. 1. The primary key of a relational table uniquely identifies each record in the table. 2. It can either be a normal attribute that is guaranteed to be or it can be generated by the DBMS. 3. Primary keys may consist of a single attribute or multiple attributes in combination. 4. A good candidate for a primary key has several characteristics: It uniquely identifies each row It is never empty or null — it always contains a value The values it contains rarely (ideally, never) change Note : Take care in choosing a primary key because it is difficult to change the primary key in a production table. 5. Examples of poor primary keys Here are a few examples, along with reasons why they would be poor choices. Poor primary key : Reason Personal name Phone number Might not be reliably unique, and Likely to change.
- 5. Primary key
- 6. Number Format Use to display General Numbers without additional formatting exactly as it is stored. Currency General monetary values. Euro General monetary values stored in the EU format. Fixed Numeric data. Standard Numeric data with decimal. Percentage Percentages. Scientific Calculations.
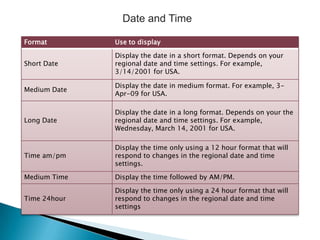
- 7. Date and Time Format Use to display Short Date Display the date in a short format. Depends on your regional date and time settings. For example, 3/14/2001 for USA. Medium Date Display the date in medium format. For example, 3Apr-09 for USA. Long Date Display the date in a long format. Depends on your the regional date and time settings. For example, Wednesday, March 14, 2001 for USA. Time am/pm Display the time only using a 12 hour format that will respond to changes in the regional date and time settings. Medium Time Display the time followed by AM/PM. Time 24hour Display the time only using a 24 hour format that will respond to changes in the regional date and time settings
- 8. Yes/No Data Type Use to display Check Box A check box. Yes/No Yes or No options True/False True or False options. On/Off On or Off options.
- 9. Quick Start Data Type Use to display Address Fields for the entire postal address. Phone Fields for the Home Phone, Mobile Phone, and the Work Phone. Priority A drop-down box with the following priority options: Low, Medium, High. Status A drop-down box with the following options: Not Started, In Progress, Completed, Cancelled. Tags Displays up to three tags.