NEURALGIA
- 1. NEURALGIA ARATHY R NATH NEHRU COLLEGE
- 4. Occurs as a complication of shingles and may be anywhere on the body. Shingles is a viral infection characterized by a painful rash and blisters. Neuralgia can occur wherever the outbreak of shingles was. The pain can be mild or severe and persistent or intermittent. last for months or years. In some cases, the pain may occur before the rash. It will always occur along the path of a nerve, so it’s usually isolated to one side of the body. Postherpetic neuralgia
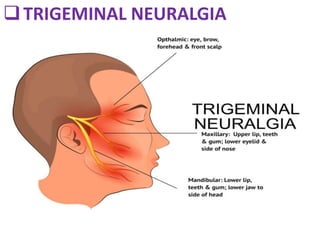
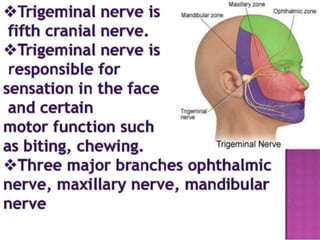
- 5. Trigeminal neuralgia It is associated with pain from the trigeminal nerve, which travels from the brain and branches to different parts of the face. The pain can be caused by a blood vessel pressing down on the nerve where it meets with the brainstem. It can also be caused by multiple sclerosis, injury to the nerve, or other causes. Trigeminal neuralgia causes severe, recurrent pain in the face, usually on one side. It’s most common in people who are older than 50 years.
- 6. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia Pain from the glossopharyngeal nerve, which is in the throat, is not very common. This type of neuralgia produces pain in the neck and throat.
- 8. Infection An infection can affect your nerves. For example, the cause of postherpetic neuralgia is shingles, an infection caused by the chickenpox virus. The likelihood of having this infection increases with age. An infection in a specific part of the body may also affect a nearby nerve. For example, if you have an infection in a tooth, it may affect the nerve and cause pain. Multiple sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease caused by the deterioration of myelin, the covering of nerves. Trigeminal neuralgia may occur in someone with MS.
- 9. Pressure on nerves Pressure or compression of nerves may cause neuralgia. The pressure may come from a: bone, ligament , blood vessel , tumor The pressure of a swollen blood vessel is a common cause of trigeminal neuralgia. Diabetes Many people with diabetes have problems with their nerves, including neuralgia. The excess glucose in the bloodstream may damage nerves. This damage is most common in the hands, arms, feet, and legs.
- 10. Less common causes If the cause of neuralgia isn’t infection, MS, diabetes, or pressure on the nerves, it may be from one of many less- common factors. These include: chronic kidney disease ,medications prescribed for cancer,fluoroquinolone antibiotics, used to treat some infections , trauma, such as from surgery ,chemical irritation
- 14. Trigeminal neuralgia is sudden, severe facial pain. It's often described as a sharp shooting pain or like having an electric shock in the jaw, teeth or gums. It usually occurs in short, unpredictable attacks that can last from a few seconds to about two minutes. The attacks stop as suddenly as they start. In most cases trigeminal neuralgia affects part or all of one side of the face, with the pain usually felt in the lower part of the face. Very occasionally it can affect both sides of the face, although not usually at the same time. People with the condition may experience attacks of pain regularly for days, weeks or months at a time. In severe cases attacks may occur hundreds of times a day.
- 15. It's possible for the pain to improve or even disappear altogether for several months or years at a time (remission), although these periods tend to get shorter with time. Some people may then go on to develop a more continuous aching, throbbing and burning sensation, sometimes accompanied by the sharp attacks. Living with trigeminal neuralgia can be very difficult. It can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, resulting in problems such as weight loss, isolation and depression
- 22. MANAGEMENT 1) Pharmacological 2) Surgical 3) others Pharmacological • 1ST line : Carbamazepine 100,200mg • 2nd line : phenytoin 100 mg Baclofen 5 – 80 mg/day Lamotrigine 25mg/day • 3rd line : Clonazepam 4 – 8mg valproic acid 250 – 500mg oxacarbazepine 1200mg/day
- 23. SURGICAL Glycerol rhizolysis Baloon microcompression Microvasculature decompression (MVD) Peripheral neurectomy Linear accelerator radiosurgery Cryotherapy Stereiolactic radiosurgery (SRS) Radiofrequency gangliolysis
- 26. BRACHIAL NEURALGIA (Shoulder to elbow ) They may follow injury , operation, inoculation or fever. Recovery – low symptoms: : shoulder,arm , forearm , or hand. Causes :- 1) neck – viloent exercise, tumors,degeneration. 2) Arm- due to infections , injury 3) forearm - fractures 4) shoulder – due to arrthritis, frozen shoulder Symptoms : - tightness,shifteenss of shoulder,arm,forearm - difficulty in stretching, lifting the arm. - altered sensation / numbness.
- 27. TREATMENT 1) Tricyclic antidepressants – nortriptylline 2) Amitriptyline (75 – 150mg) & desipramine 3)Carbamazepine (600mg/dl) 4) Gabapentin (300mg TID) 5) phenytoin & sodium valproate 6) Topical agents - lidocaine
- 28. THANK YOU