PHP data structures (and the impact of php 7 on them), phpDay Verona 2015, Italy
- 1. PHP Data Structures (and the impact of PHP 7 on them) Patrick Allaert phpDay Verona 2015, Italy
- 2. About me ● Patrick Allaert ● Founder of Libereco and co-founder of catchy.io ● Playing with PHP/Linux for +15 years ● eZ Publish core developer ● Author of the APM PHP extension ● @patrick_allaert ● patrickallaert@php.net ● http://github.com/patrickallaert/ ● http://patrickallaert.blogspot.com/
- 3. PHP native datatypes ● NULL ● Booleans ● Integers ● Floating point numbers ● Strings ● Arrays ● Objects ● Resources
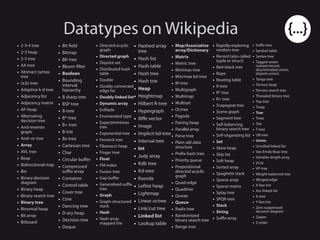
- 4. Datatypes on Wikipedia ● 2-3-4 tree ● 2-3 heap ● 2-3 tree ● AA tree ● Abstract syntax tree ● (a,b)-tree ● Adaptive k-d tree ● Adjacency list ● Adjacency matrix ● AF-heap ● Alternating decision tree ● And-inverter graph ● And–or tree ● Array ● AVL tree ● Beap ● Bidirectional map ● Bin ● Binary decision diagram ● Binary heap ● Binary search tree ● Binary tree ● Binomial heap ● Bit array ● Bitboard ● Bit field ● Bitmap ● BK-tree ● Bloom filter ● Boolean ● Bounding interval hierarchy ● B sharp tree ● BSP tree ● B-tree ● B*-tree ● B+ tree ● B-trie ● Bx-tree ● Cartesian tree ● Char ● Circular buffer ● Compressed suffix array ● Container ● Control table ● Cover tree ● Ctrie ● Dancing tree ● D-ary heap ● Decision tree ● Deque ● Directed acyclic graph ● Directed graph ● Disjoint-set ● Distributed hash table ● Double ● Doubly connected edge list ● Doubly linked list ● Dynamic array ● Enfilade ● Enumerated type ● Expectiminimax tree ● Exponential tree ● Fenwick tree ● Fibonacci heap ● Finger tree ● Float ● FM-index ● Fusion tree ● Gap buffer ● Generalised suffix tree ● Graph ● Graph-structured stack ● Hash ● Hash array mapped trie ● Hashed array tree ● Hash list ● Hash table ● Hash tree ● Hash trie ● Heap ● Heightmap ● Hilbert R-tree ● Hypergraph ● Iliffe vector ● Image ● Implicit kd-tree ● Interval tree ● Int ● Judy array ● Kdb tree ● Kd-tree ● Koorde ● Leftist heap ● Lightmap ● Linear octree ● Link/cut tree ● Linked list ● Lookup table ● Map/Associative array/Dictionary ● Matrix ● Metric tree ● Minimax tree ● Min/max kd-tree ● M-tree ● Multigraph ● Multimap ● Multiset ● Octree ● Pagoda ● Pairing heap ● Parallel array ● Parse tree ● Plain old data structure ● Prefix hash tree ● Priority queue ● Propositional directed acyclic graph ● Quad-edge ● Quadtree ● Queap ● Queue ● Radix tree ● Randomized binary search tree ● Range tree ● Rapidly-exploring random tree ● Record (also called tuple or struct) ● Red-black tree ● Rope ● Routing table ● R-tree ● R* tree ● R+ tree ● Scapegoat tree ● Scene graph ● Segment tree ● Self-balancing binary search tree ● Self-organizing list ● Set ● Skew heap ● Skip list ● Soft heap ● Sorted array ● Spaghetti stack ● Sparse array ● Sparse matrix ● Splay tree ● SPQR-tree ● Stack ● String ● Suffix array ● Suffix tree ● Symbol table ● Syntax tree ● Tagged union (variant record, discriminated union, disjoint union) ● Tango tree ● Ternary heap ● Ternary search tree ● Threaded binary tree ● Top tree ● Treap ● Tree ● Trees ● Trie ● T-tree ● UB-tree ● Union ● Unrolled linked list ● Van Emde Boas tree ● Variable-length array ● VList ● VP-tree ● Weight-balanced tree ● Winged edge ● X-fast trie ● Xor linked list ● X-tree ● Y-fast trie ● Zero suppressed decision diagram ● Zipper ● Z-order
- 5. Game: Can you recognize some structures?
- 10. Array: PHP's untruthfulness PHP“Arrays”are not true Arrays!
- 11. Array: PHP's untruthfulness PHP“Arrays”are not true Arrays! An array typically looks like this: Data DataDataData Data Data 0 1 2 3 4 5
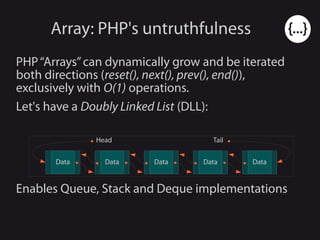
- 12. Array: PHP's untruthfulness PHP“Arrays”can dynamically grow and be iterated both directions (reset(), next(), prev(), end()), exclusively with O(1) operations.
- 13. Array: PHP's untruthfulness PHP“Arrays”can dynamically grow and be iterated both directions (reset(), next(), prev(), end()), exclusively with O(1) operations. Let's have a Doubly Linked List (DLL): Data Data Data Data Data Head Tail Enables Queue, Stack and Deque implementations
- 14. Array: PHP's untruthfulness PHP“Arrays”elements are always accessible using a key (index).
- 15. Array: PHP's untruthfulness PHP“Arrays”elements are always accessible using a key (index). Let's have an Hash Table: Data Data Data Data Data Head Tail Bucket Bucket Bucket Bucket Bucket Bucket pointers array Bucket * 0 Bucket * 1 Bucket * 2 Bucket * 3 Bucket * 4 Bucket * 5 ... Bucket * nTableSize -1
- 16. Array: PHP's untruthfulness http://php.net/manual/en/language.types.array.php: “This type is optimized for several different uses; it can be treated as an array, list (vector), hash table (an implementation of a map), dictionary, collection, stack, queue, and probably more.”
- 17. Optimized for anything ≈ Optimized for nothing!
- 18. Optimized for anything ≈ Optimized for nothing!
- 19. Array: PHP's untruthfulness ● In C: 100 000 integers (using long on 64bits => 8 bytes) can be stored in 0.76 MiB. ● In PHP 5: ● it will take 13.97 MiB!≅ ● A variable (containing an integer) takes 48 bytes. ● The overhead for every“array”entries is about 96 bytes.
- 20. Array: PHP's untruthfulness ● In C: 100 000 integers (using long on 64bits => 8 bytes) can be stored in 0.76 MiB. ● In PHP 5 7: ● it will take ≅ 13.97 4 MiB! ● A variable (containing an integer) takes 48 16 bytes. ● The overhead for every“array”entries is about 96 20 bytes.
- 21. Data Structure
- 22. Structs (or records, tuples,...)
- 23. Structs (or records, tuples,...) ● A struct is a value containing other values which are typically accessed using a name. ● Example: Person => firstName / lastName ComplexNumber => realPart / imaginaryPart
- 24. Structs – Using array $person = [ "firstName" => "Patrick", "lastName" => "Allaert", ];
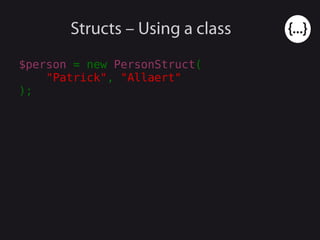
- 25. Structs – Using a class $person = new PersonStruct( "Patrick", "Allaert" );
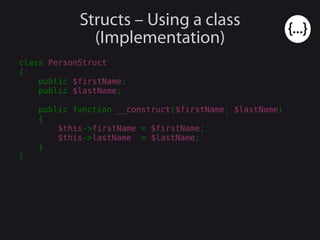
- 26. Structs – Using a class (Implementation) class PersonStruct { public $firstName; public $lastName; public function __construct($firstName, $lastName) { $this->firstName = $firstName; $this->lastName = $lastName; } }
- 27. Structs – Using a class (Implementation) class PersonStruct { public $firstName; public $lastName; public function __construct($firstName, $lastName) { $this->firstName = $firstName; $this->lastName = $lastName; } public function __set($key, $value) { // a. Do nothing // b. trigger_error() // c. Throws an exception } }
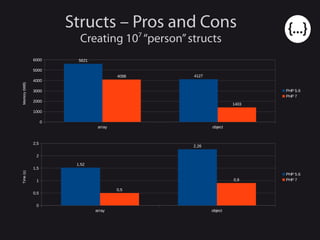
- 28. Structs – Pros and Cons Creating 107 “person”structs array object 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 5621 41274098 1403 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Memory(MiB) array object 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 1,52 2,26 0,5 0,9 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Time(s)
- 29. Structs – Pros and Cons Using a class implementation + Type hinting possible + Rigid structure + More OO + Uses ~ 26% less memory - Slower to create by ~ 50% Starting PHP 7: + Uses ~ 66% less memory - Slower to create by a factor 2!
- 30. (true) Arrays
- 31. (true) Arrays ● An array is a fixed size collection where elements are each identified by a numeric index.
- 32. (true) Arrays ● An array is a fixed size collection where elements are each identified by a numeric index. Data DataDataData Data Data 0 1 2 3 4 5
- 33. (true) Arrays – Using SplFixedArray $array = new SplFixedArray(3); $array[0] = 1; // or $array->offsetSet() $array[1] = 2; // or $array->offsetSet() $array[2] = 3; // or $array->offsetSet() $array[0]; // gives 1 $array[1]; // gives 2 $array[2]; // gives 3
- 34. (true) Arrays – Pros and Cons Creating/iterating 104 arrays of 1000 elements array SplFixedArray 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1378 539 353 159 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Memory(MiB) array (create) array (iterate) SplFixedArray (create) SplFixedArray (iterate) 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 2,49 0,2 0,92 0,360,33 0,09 0,24 0,19 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Time(s)
- 35. (true) Arrays – Pros and Cons Using SplFixedArray + Uses much less memory + Takes less time at creation - Takes a bit more time to iterate
- 36. Queues
- 37. Queues ● A queue is an ordered collection respecting First In, First Out (FIFO) order. ● Elements are inserted at one end and removed at the other.
- 38. Queues ● A queue is an ordered collection respecting First In, First Out (FIFO) order. ● Elements are inserted at one end and removed at the other. Data DataDataData Data Data Data Data Enqueue Dequeue
- 39. Queues – Using array $queue = []; $queue[] = 1; // or array_push() $queue[] = 2; // or array_push() $queue[] = 3; // or array_push() array_shift($queue); // gives 1 array_shift($queue); // gives 2 array_shift($queue); // gives 3
- 40. Queues – Using SplQueue $queue = new SplQueue(); $queue[] = 1; // or $queue->enqueue() $queue[] = 2; // or $queue->enqueue() $queue[] = 3; // or $queue->enqueue() $queue->dequeue(); // gives 1 $queue->dequeue(); // gives 2 $queue->dequeue(); // gives 3
- 41. Stacks
- 42. Stacks ● A stack is an ordered collection respecting Last In, First Out (LIFO) order. ● Elements are inserted and removed on the same end.
- 43. Stacks ● A stack is an ordered collection respecting Last In, First Out (LIFO) order. ● Elements are inserted and removed on the same end. Data DataDataData Data Data Data Data Push Pop
- 44. Stacks – Using array $stack = []; $stack[] = 1; // or array_push() $stack[] = 2; // or array_push() $stack[] = 3; // or array_push() array_pop($stack); // gives 3 array_pop($stack); // gives 2 array_pop($stack); // gives 1
- 45. Stacks – Using SplStack $stack = new SplStack(); $stack[] = 1; // or $stack->push() $stack[] = 2; // or $stack->push() $stack[] = 3; // or $stack->push() $stack->pop(); // gives 3 $stack->pop(); // gives 2 $stack->pop(); // gives 1
- 46. Stack/Queue – Pros and Cons Creating 104 stacks/queues of 103 elements array Spl(Queue|Stack) 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1378 920 353 541 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Memory(MiB) array (create) array (iterate) Spl(Stack|Queue) (create) Spl(Stack|Queue) (iterate) 0 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1 1,2 1,4 1,6 1,8 0,57 0,2 1,62 0,27 0,17 0,09 1,22 0,18 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Time(s)
- 47. Queues/Stacks – Pros and Cons SplQueue / SplStack + Uses less memory + Type hinting + More OO - A bit more cpu intensive Starting PHP 7 (comparatively to arrays): - Uses more memory - Much more cpu intensive => They haven't received as much attention as arrays did (yet?).
- 48. Sets People with strong views on the distinction between geeks and nerds Geeks Nerds
- 49. Sets ● A set is a collection with no particular ordering especially suited for testing the membership of a value against a collection or to perform union/intersection/complement operations between them.
- 50. Sets ● A set is a collection with no particular ordering especially suited for testing the membership of a value against a collection or to perform union/intersection/complement operations between them. Data Data Data Data Data
- 51. Sets – Using array $set = []; // Adding elements to a set $set[] = 1; $set[] = 2; $set[] = 3; // Checking presence in a set in_array(2, $set); // true in_array(5, $set); // false array_merge($set1, $set2); // union array_intersect($set1, $set2); // intersection array_diff($set1, $set2); // complement
- 52. Sets – Using array $set = []; // Adding elements to a set $set[] = 1; $set[] = 2; $set[] = 3; // Checking presence in a set in_array(2, $set); // true in_array(5, $set); // false array_merge($set1, $set2); // union array_intersect($set1, $set2); // intersection array_diff($set1, $set2); // complement True performance killers!
- 53. Sets – Mis-usage if (in_array($value, ["val1", "val2", "val3"])) { // ... }
- 54. Sets – Mis-usage if ($value === "val1" || $value === "val2" || $value === "val3"))) { // ... }
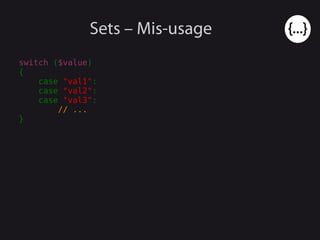
- 55. Sets – Mis-usage switch ($value) { case "val1": case "val2": case "val3": // ... }
- 56. Sets – Mis-usage Testing 5 * 107 membership against set of 3 elements in_array compare switch optimized way ;) 0 5 10 15 20 25 19,59 3,15 5,2 1,97 3,43 2,34 1,53 0,75 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Time(s)
- 57. Sets – Using array (simple types) $set = []; // Adding elements to a set $set[1] = true; // Any dummy value $set[2] = true; // is good but NULL! $set[3] = true; // Checking presence in a set isset($set[2]); // true isset($set[5]); // false $set1 + $set2; // union array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement
- 58. Sets – Using array (simple types) $set = []; // Adding elements to a set $set[1] = true; // Any dummy value $set[2] = true; // is good but NULL! $set[3] = true; // Checking presence in a set isset($set[2]); // true isset($set[5]); // false $set1 + $set2; // union array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement ● Remember that PHP Array keys can be integers or strings only!
- 59. Sets – Using array (objects) $set = []; // Adding elements to a set $set[spl_object_hash($object1)] = $object1; $set[spl_object_hash($object2)] = $object2; $set[spl_object_hash($object3)] = $object3; // Checking presence in a set isset($set[spl_object_hash($object2)]); // true isset($set[spl_object_hash($object5)]); // false $set1 + $set2; // union array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement
- 60. Sets – Using array (objects) $set = []; // Adding elements to a set $set[spl_object_hash($object1)] = $object1; $set[spl_object_hash($object2)] = $object2; $set[spl_object_hash($object3)] = $object3; // Checking presence in a set isset($set[spl_object_hash($object2)]); // true isset($set[spl_object_hash($object5)]); // false $set1 + $set2; // union array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement Store a reference of the object!
- 61. Sets – Using SplObjectStorage (objects) $set = new SplObjectStorage(); // Adding elements to a set $set->attach($object1); // or $set[$object1] = null; $set->attach($object2); // or $set[$object2] = null; $set->attach($object3); // or $set[$object3] = null; // Checking presence in a set isset($set[$object2]); // true isset($set[$object5]); // false $set1->$addAll($set2); // union $set1->removeAllExcept($set2); // intersection $set1->removeAll($set2); // complement
- 62. Sets – Using QuickHash (int) ● No union/intersection/complement operations (yet?) ● Yummy features like (loadFrom|saveTo)(String|File) $set = new QuickHashIntSet(64,QuickHashIntSet::CHECK_FOR_DUPES); // Adding elements to a set $set->add(1); $set->add(2); $set->add(3); // Checking presence in a set $set->exists(2); // true $set->exists(5); // false isset($set[2]);
- 63. Sets – Using bitsets function remove( $path, $files = true, $dir = true, $links = true, $exec = true ) { if (!$files && is_file($path)) return false; if (!$dir && is_dir($path)) return false; if (!$links && is_link($path)) return false; if (!$exec && is_executable($path)) return false; // ... }
- 64. Sets – Using bitsets (example) remove("/tmp/removeMe", true, false, true, false);
- 65. Sets – Using bitsets (example) remove("/tmp/removeMe", true, false, true, false); // WTF ?!
- 66. Sets – Using bitsets
- 67. Sets – Using bitsets E_ERROR E_WARNING E_PARSE E_NOTICE
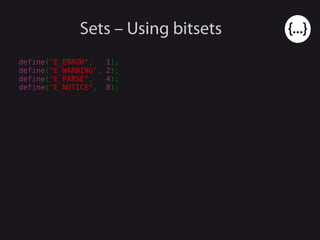
- 68. Sets – Using bitsets define("E_ERROR", 1); define("E_WARNING", 2); define("E_PARSE", 4); define("E_NOTICE", 8);
- 69. Sets – Using bitsets define("E_ERROR", 1); define("E_WARNING", 2); define("E_PARSE", 4); define("E_NOTICE", 8); E_ERROR E_PARSE E_NOTICE 10000000 00100000 00010000
- 70. Sets – Using bitsets define("E_ERROR", 1); define("E_WARNING", 2); define("E_PARSE", 4); define("E_NOTICE", 8); E_ERROR E_PARSE E_NOTICE E_ERROR | E_PARSE | E_NOTICE 10000000 00100000 00010000 10110000
- 71. Sets – Using bitsets define("E_ERROR", 1 << 0); define("E_WARNING", 1 << 1); define("E_PARSE", 1 << 2); define("E_NOTICE", 1 << 3); E_ERROR E_PARSE E_NOTICE E_ERROR | E_PARSE | E_NOTICE 10000000 00100000 00010000 10110000
- 72. Sets – Using bitsets define("E_ERROR", 1 << 0); define("E_WARNING", 1 << 1); define("E_PARSE", 1 << 2); define("E_NOTICE", 1 << 3); // Adding elements to a set $set = 0; $set |= E_ERROR; $set |= E_WARNING; $set |= E_PARSE; // Checking presence in a set $set & E_ERROR; // true $set & E_NOTICE; // false $set1 | $set2; // union $set1 & $set2; // intersection $set1 ^ $set2; // complement
- 73. Sets – Using bitsets (example) define("REMOVE_FILES", 1 << 0); define("REMOVE_DIRS", 1 << 1); define("REMOVE_LINKS", 1 << 2); define("REMOVE_EXEC", 1 << 3); define("REMOVE_ALL", ~0); // Setting all bits function remove($path, $options = REMOVE_ALL) { if (~$options & REMOVE_FILES && is_file($path)) return false; if (~$options & REMOVE_DIRS && is_dir($path)) return false; if (~$options & REMOVE_LINKS && is_link($path)) return false; if (~$options & REMOVE_EXEC && is_executable($path)) return false; // ... }
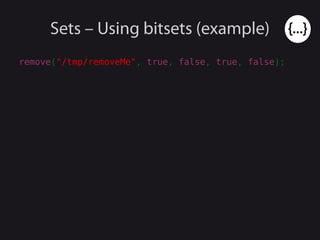
- 74. Sets – Using bitsets (example) remove("/tmp/removeMe", REMOVE_FILES | REMOVE_LINKS);
- 75. Sets – Using bitsets (example) remove("/tmp/removeMe", REMOVE_FILES | REMOVE_LINKS); // Much better :)
- 76. Sets: Conclusions ● Use the key and not the value when using PHP Arrays. ● Use QuickHash for set of integers if possible. ● Use SplObjectStorage as soon as you are playing with objects. ● Use bitsets when playing with finite number of elements (and known in advance). ● Avoid array_unique() / in_array() at all price!
- 77. Maps ● A map is a collection of key/value pairs where all keys are unique.
- 78. Maps – Using array ● Don't use array_merge() on maps. $map = []; $map["ONE"] = 1; $map["TWO"] = 2; $map["THREE"] = 3; // Merging maps: array_merge($map1, $map2); // SLOW! $map2 + $map1; // Fast :)
- 79. Maps – Using array Testing 107 merges against 2 maps of 5 elements array_merge + 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 4 4,5 5 4,74 2,77 1,42 1,09 PHP 5.6 PHP 7 Time(s)
- 80. Multikey Maps – Using array $map = []; $map["ONE"] = 1; $map["UN"] =& $map["ONE"]; $map["UNO"] =& $map["ONE"]; $map["TWO"] = 2; $map["DEUX"] =& $map["TWO"]; $map["DUE"] =& $map["TWO"]; $map["UNO"] = "once"; $map["DEUX"] = "twice"; var_dump($map); /* array(6) { ["ONE"] => &string(4) "once" ["UN"] => &string(4) "once" ["UNO"] => &string(4) "once" ["TWO"] => &string(5) "twice" ["DEUX"] => &string(5) "twice" ["DUE"] => &string(5) "twice" } */
- 81. Heap ● A heap is a tree-based structure in which all elements are ordered with largest key at the top, and the smallest one as leafs.
- 82. Heap ● A heap is a tree-based structure in which all elements are ordered with largest key at the top, and the smallest one as leafs.
- 83. Heap – Using Spl(Min|Max)Heap $heap = new SplMinHeap; $heap->insert(30); $heap->insert(20); $heap->insert(25); var_dump($heap->top()); /* int(20) */
- 84. Heaps: Conclusions ● MUCH faster than having to re-sort() an array at every insertion. ● If you don't require a collection to be sorted at every single step and can insert all data at once and then sort(). Array is a much better/faster approach. ● SplPriorityQueue is very similar, consider it is the same as SplHeap but where the sorting is made on the key rather than the value.
- 85. Bloom filters ● A bloom filter is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure used to test whether an element is member of a set. ● False positives are possible, but false negatives are not!
- 86. Bloom filters – Using bloomy $bloom = new BloomFilter( 10000, // capacity 0,001 // (optional) error rate // (optional) random seed ); $bloom->add("An element"); $bloom->has("An element"); // true for sure $bloom->has("Foo"); // false, most probably
- 87. Other related projects ● SPL Types: Various types implemented as object: SplInt, SplFloat, SplEnum, SplBool and SplString http://pecl.php.net/package/SPL_Types
- 88. Other related projects ● SPL Types: Various types implemented as object: SplInt, SplFloat, SplEnum, SplBool and SplString http://pecl.php.net/package/SPL_Types ● Judy: Sparse dynamic arrays implementation http://pecl.php.net/package/Judy
- 89. Other related projects ● SPL Types: Various types implemented as object: SplInt, SplFloat, SplEnum, SplBool and SplString http://pecl.php.net/package/SPL_Types ● Judy: Sparse dynamic arrays implementation http://pecl.php.net/package/Judy ● Weakref: Weak references implementation. Provides a gateway to an object without preventing that object from being collected by the garbage collector.
- 90. Conclusions ● Use appropriate data structure. It will keep your code clean and fast.
- 91. Conclusions ● Use appropriate data structure. It will keep your code clean and fast. ● Think about the time and space complexity involved by your algorithms.
- 92. Conclusions ● Use appropriate data structure. It will keep your code clean and fast. ● Think about the time and space complexity involved by your algorithms. ● Name your variables accordingly: use“Map”,“Set”, “List”,“Queue”,... to describe them instead of using something like: $ordersArray.
- 93. Questions?
- 94. Thanks Don't forget to rate this talk on https://joind.in/14535 Stay in touch! @patrick_allaert patrickallaert@php.net
- 95. Photo Credits ● Tuned car: http://www.flickr.com/photos/gioxxswall/5783867752 ● London Eye Structure: http://www.flickr.com/photos/photographygal123/4883546484 ● Heap structure: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Max-Heap.svg ● Drawers: http://www.flickr.com/photos/jamesclay/2312912612 ● Stones stack: http://www.flickr.com/photos/silent_e/2282729987 ● Tree: http://www.flickr.com/photos/drewbandy/6002204996




















![Structs – Using array
$person = [
"firstName" => "Patrick",
"lastName" => "Allaert",
];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-24-320.jpg)





![(true) Arrays – Using SplFixedArray
$array = new SplFixedArray(3);
$array[0] = 1; // or $array->offsetSet()
$array[1] = 2; // or $array->offsetSet()
$array[2] = 3; // or $array->offsetSet()
$array[0]; // gives 1
$array[1]; // gives 2
$array[2]; // gives 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-33-320.jpg)





![Queues – Using array
$queue = [];
$queue[] = 1; // or array_push()
$queue[] = 2; // or array_push()
$queue[] = 3; // or array_push()
array_shift($queue); // gives 1
array_shift($queue); // gives 2
array_shift($queue); // gives 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-39-320.jpg)
![Queues – Using SplQueue
$queue = new SplQueue();
$queue[] = 1; // or $queue->enqueue()
$queue[] = 2; // or $queue->enqueue()
$queue[] = 3; // or $queue->enqueue()
$queue->dequeue(); // gives 1
$queue->dequeue(); // gives 2
$queue->dequeue(); // gives 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-40-320.jpg)



![Stacks – Using array
$stack = [];
$stack[] = 1; // or array_push()
$stack[] = 2; // or array_push()
$stack[] = 3; // or array_push()
array_pop($stack); // gives 3
array_pop($stack); // gives 2
array_pop($stack); // gives 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-44-320.jpg)
![Stacks – Using SplStack
$stack = new SplStack();
$stack[] = 1; // or $stack->push()
$stack[] = 2; // or $stack->push()
$stack[] = 3; // or $stack->push()
$stack->pop(); // gives 3
$stack->pop(); // gives 2
$stack->pop(); // gives 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-45-320.jpg)





![Sets – Using array
$set = [];
// Adding elements to a set
$set[] = 1;
$set[] = 2;
$set[] = 3;
// Checking presence in a set
in_array(2, $set); // true
in_array(5, $set); // false
array_merge($set1, $set2); // union
array_intersect($set1, $set2); // intersection
array_diff($set1, $set2); // complement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-51-320.jpg)
![Sets – Using array
$set = [];
// Adding elements to a set
$set[] = 1;
$set[] = 2;
$set[] = 3;
// Checking presence in a set
in_array(2, $set); // true
in_array(5, $set); // false
array_merge($set1, $set2); // union
array_intersect($set1, $set2); // intersection
array_diff($set1, $set2); // complement
True
performance
killers!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-52-320.jpg)
![Sets – Mis-usage
if (in_array($value, ["val1", "val2", "val3"]))
{
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-53-320.jpg)


![Sets – Using array (simple types)
$set = [];
// Adding elements to a set
$set[1] = true; // Any dummy value
$set[2] = true; // is good but NULL!
$set[3] = true;
// Checking presence in a set
isset($set[2]); // true
isset($set[5]); // false
$set1 + $set2; // union
array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection
array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-57-320.jpg)
![Sets – Using array (simple types)
$set = [];
// Adding elements to a set
$set[1] = true; // Any dummy value
$set[2] = true; // is good but NULL!
$set[3] = true;
// Checking presence in a set
isset($set[2]); // true
isset($set[5]); // false
$set1 + $set2; // union
array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection
array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement
● Remember that PHP Array keys can be integers or
strings only!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-58-320.jpg)
![Sets – Using array (objects)
$set = [];
// Adding elements to a set
$set[spl_object_hash($object1)] = $object1;
$set[spl_object_hash($object2)] = $object2;
$set[spl_object_hash($object3)] = $object3;
// Checking presence in a set
isset($set[spl_object_hash($object2)]); // true
isset($set[spl_object_hash($object5)]); // false
$set1 + $set2; // union
array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection
array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-59-320.jpg)
![Sets – Using array (objects)
$set = [];
// Adding elements to a set
$set[spl_object_hash($object1)] = $object1;
$set[spl_object_hash($object2)] = $object2;
$set[spl_object_hash($object3)] = $object3;
// Checking presence in a set
isset($set[spl_object_hash($object2)]); // true
isset($set[spl_object_hash($object5)]); // false
$set1 + $set2; // union
array_intersect_key($set1, $set2); // intersection
array_diff_key($set1, $set2); // complement
Store a
reference of
the object!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-60-320.jpg)
![Sets – Using SplObjectStorage
(objects)
$set = new SplObjectStorage();
// Adding elements to a set
$set->attach($object1); // or $set[$object1] = null;
$set->attach($object2); // or $set[$object2] = null;
$set->attach($object3); // or $set[$object3] = null;
// Checking presence in a set
isset($set[$object2]); // true
isset($set[$object5]); // false
$set1->$addAll($set2); // union
$set1->removeAllExcept($set2); // intersection
$set1->removeAll($set2); // complement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-61-320.jpg)
![Sets – Using QuickHash (int)
● No union/intersection/complement operations
(yet?)
● Yummy features like (loadFrom|saveTo)(String|File)
$set = new QuickHashIntSet(64,QuickHashIntSet::CHECK_FOR_DUPES);
// Adding elements to a set
$set->add(1);
$set->add(2);
$set->add(3);
// Checking presence in a set
$set->exists(2); // true
$set->exists(5); // false
isset($set[2]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-62-320.jpg)













![Maps – Using array
● Don't use array_merge() on maps.
$map = [];
$map["ONE"] = 1;
$map["TWO"] = 2;
$map["THREE"] = 3;
// Merging maps:
array_merge($map1, $map2); // SLOW!
$map2 + $map1; // Fast :)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-78-320.jpg)

![Multikey Maps – Using array
$map = [];
$map["ONE"] = 1;
$map["UN"] =& $map["ONE"];
$map["UNO"] =& $map["ONE"];
$map["TWO"] = 2;
$map["DEUX"] =& $map["TWO"];
$map["DUE"] =& $map["TWO"];
$map["UNO"] = "once";
$map["DEUX"] = "twice";
var_dump($map);
/*
array(6) {
["ONE"] => &string(4) "once"
["UN"] => &string(4) "once"
["UNO"] => &string(4) "once"
["TWO"] => &string(5) "twice"
["DEUX"] => &string(5) "twice"
["DUE"] => &string(5) "twice"
}
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpdatastructuresandtheimpactofphp7onthemphpdays2015-150516112832-lva1-app6892/85/PHP-data-structures-and-the-impact-of-php-7-on-them-phpDay-Verona-2015-Italy-80-320.jpg)














