Python Homework Help
- 1. For any help regarding Python Homework Help Visit :- https://www.pythonhomeworkhelp.com/ , Email :- support@pythonhomeworkhelp.com or Call us at :- +1 678 648 4277
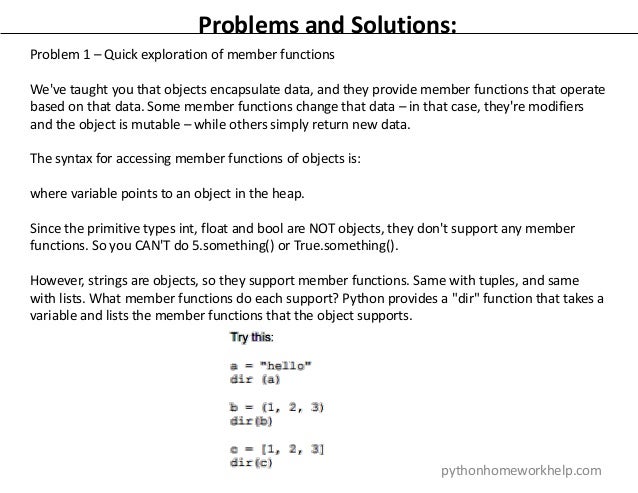
- 2. Problems and Solutions: Problem 1 – Quick exploration of member functions We've taught you that objects encapsulate data, and they provide member functions that operate based on that data. Some member functions change that data – in that case, they're modifiers and the object is mutable – while others simply return new data. The syntax for accessing member functions of objects is: where variable points to an object in the heap. Since the primitive types int, float and bool are NOT objects, they don't support any member functions. So you CAN'T do 5.something() or True.something(). However, strings are objects, so they support member functions. Same with tuples, and same with lists. What member functions do each support? Python provides a "dir" function that takes a variable and lists the member functions that the object supports. pythonhomeworkhelp.com
- 3. You should get out a bunch of what looks like jumbled nonsense. But those things are actually member functions of each object. You'll generally see two types of member functions: __functionname__ functions are generally not meant to be explicitly called. Instead, they're used by Python to do other things. Å "A" comes before "B" alphabetically, so this is True pythonhomeworkhelp.com
- 4. We see the same result. It turns out that whenever you write object1 < object2, Python looks for a __lt__ member function in a and calls it with b as the argument. (In actuality, there is a little more to the story, but we won't worry about that now.) The __functionname__ style exists because it's meant to explicitly make it clear that this function is not meant to be called normally. It's a system function, so in general, we should never be calling functions with names like __functionname__. The rest of the functions are all functions that you can use! For help with any, type: Take a quick look at some of the functions for strings, lists and tuples... we'll be needing them. pythonhomeworkhelp.com
- 5. Let's say there are two methods to find the "distance" of two chromosomes -- that is, how much the two have varied through mutations. One method is to go letter by letter and count the number of discrepancies. Another method is to sum the discrepancies of a's (e.g. chromosome x has 5 a's, chromosome y has 7 a's), c's, g’s, and t’s. Are the two methods the same? We don't know, let's find out. Write a function that uses method 1. It will take two chromosomes, and go letter by letter in each, comparing them. It then returns the total number of discrepancies it finds. Write another function that uses method 2. It will take two chromosomes, and return the sum of 'a' discrepancies, ‘cones, and so on. Then call each function on each of the combinations (A,B), (A,C), (A,D), (B,C), (B, D), and (C, D) and see which methods tell you which pair of chromosomes is "furthest" (i.e. most varied) and which pair is "closest" (i.e. least varied). Remember to use dir()! Important note: From this point on, we are going to stray from interactive programs that use raw_input and go to solving complex problems instead. You should not use a raw_input function anywhere in this program. pythonhomeworkhelp.com
- 6. A = "gtggcaacgtgc" B = "gtagcagcgcgc" C = "gcggcacagggt" D = "gtgacaacgtgc" def method1(c1, c2): discreps = 0 for i in range(len(c1)): if c1[i] != c2[i]: discreps = discreps + 1 return discreps def method2(c1, c2): discreps_a = abs(c1.count('a') - c2.count('a')) discreps_c = abs(c1.count('c') - c2.count('c')) discreps_g = abs(c1.count('g') - c2.count('g')) discreps_t = abs(c1.count('t') - c2.count('t')) return discreps_a + discreps_c + discreps_g + discreps_t pythonhomeworkhelp.com
- 7. def compare(c1, c2, name1, name2): print name1, "and", name2, ":" print "Method 1 says there are", method1(c1, c2), "differences." print "Method 2 says there are", method2(c1, c2), "differences." print compare(A, B, "A", "B") compare(A, C, "A", "C") compare(A, D, "A", "D") compare(B, C, "B", "C") compare(B, D, "B", "D") compare(C, D, "C", "D") pythonhomeworkhelp.com





![A = "gtggcaacgtgc"
B = "gtagcagcgcgc"
C = "gcggcacagggt"
D = "gtgacaacgtgc"
def method1(c1, c2):
discreps = 0
for i in range(len(c1)):
if c1[i] != c2[i]:
discreps = discreps + 1
return discreps
def method2(c1, c2):
discreps_a = abs(c1.count('a') - c2.count('a'))
discreps_c = abs(c1.count('c') - c2.count('c'))
discreps_g = abs(c1.count('g') - c2.count('g'))
discreps_t = abs(c1.count('t') - c2.count('t'))
return discreps_a + discreps_c + discreps_g + discreps_t
pythonhomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonhomeworkhelp-220209090119/95/Python-Homework-Help-6-638.jpg)
