Python Introduction 2 Deep Learning.pptx
- 2. The indentation matters… First line with less indentation is considered to be outside of the function definition. Defining Functions No header file or declaration of types of function or arguments def get_final_answer(filename): “““Documentation String””” line1 line2 return total_counter Function definition begins with “def.” Function name and its arguments. The keyword ‘return’ indicates the value to be sent back to the caller. Colon.
- 3. Python and Types Dynamic typing: Python determines the data types of variable bindings in a program automatically Strong typing: But Python’s not casual about types, it enforces the types of objects For example, you can’t just append an integer to a string, but must first convert it to a string x = “the answer is ” # x bound to a string y = 23 # y bound to an integer. print x + y # Python will
- 4. Calling a Function The syntax for a function call is: >>> def myfun(x, y): return x * y >>> myfun(3, 4) 12 Parameters in Python are Call by Assignment • Old values for the variables that are parameter names are hidden, and these variables are simply made to refer to the new values •
- 5. Functions without returns All functions in Python have a return value, even if no return line inside the code Functions without a return return the special value None • None is a special constant in the language • None is used like NULL, void, or nil in other languages • None is also logically equivalent to False • The interpreter’s REPL doesn’t print None
- 6. Function overloading? No. There is no function overloading in Python • Unlike C++, a Python function is specified by its name alone The number, order, names, or types of arguments cannot be used to distinguish between two functions with the same name • Two different functions can’t have the same name, even if they have different arguments But: see operator overloading in later slides (Note: van Rossum playing with function overloading for the
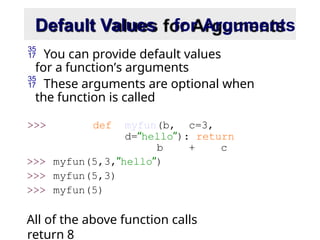
- 7. Default Values for Arguments You can provide default values for a function’s arguments These arguments are optional when the function is called >>> def myfun(b, c=3, d=“hello”): return b + c >>> myfun(5,3,”hello”) >>> myfun(5,3) >>> myfun(5) All of the above function calls return 8
- 8. Keyword Arguments Can call a function with some/all of its arguments out of order as long as you specify their names >>> def foo(x,y,z): return(2*x,4*y,8*z) >>> foo(2,3,4) (4, 12, 32) >>> foo(z=4, y=2, x=3) (6, 8, 32) >>> foo(-2, z=-4, y=-3) (-4, -12, -32) Can be combined with defaults, too >>> def foo(x=1,y=2,z=3):
- 9. Functions are first-class objects Functions can be used as any other datatype, eg: • Arguments to function • Return values of functions • Assigned to variables • Parts of tuples, lists, etc >>> def square(x): return x*x >>> def applier(q, x): return q(x) >>> applier(square, 7) 49
- 10. Lambda Notation Python’s lambda creates anonymous functions >>> applier(lambda z: z * 42, 7) 14 Note: only one expression in the lambda body; its value is always returned Python supports functional programming idioms: map, filter, closures, continuations, etc.
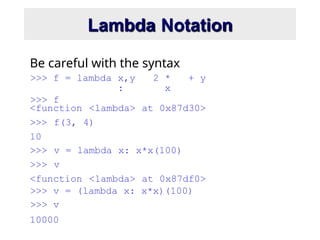
- 11. Lambda Notation >>> f = lambda x,y : 2 * x + y >>> f Be careful with the syntax <function <lambda> at 0x87d30> >>> f(3, 4) 10 >>> v = lambda x: x*x(100) >>> v <function <lambda> at 0x87df0> >>> v = (lambda x: x*x)(100) >>> v 10000
- 12. Example: composition >>> def square(x): return x*x >>> def twice(f): return lambda x: f(f(x)) >>> twice <function twice at 0x87db0> >>> quad = twice(square) >>> quad <function <lambda> at 0x87d30> >>> quad(5) 625
- 13. Example: closure >>> def counter(start=0, step=1): x = [start] def _inc(): x[0] += step return x[0] return _inc >>> >>> c1 c2 = counter() = counter(100, -10) >>> c1() 1 >>> c2() 90
- 14. map, filter, reduce >>> def add1(x): return x+1 >>> def odd(x): return x%2 == 1 >>> def add(x,y): return x + y >>> map(add1, [1,2,3,4]) [2, 3, 4, 5] >>> map(+,[1,2,3,4],[100,200,300,400]) map(+,[1,2,3,4],[100,200,300,400]) ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax >>> map(add,[1,2,3,4], [100,200,300,400]) [101, 202, 303, 404] >>> reduce(add, [1,2,3,4]) 10 >>> filter(odd, [1,2,3,4]) [1, 3]
- 16. Functions are first-class objects Functions can be used as any other datatype, eg: • Arguments to function • Return values of functions • Assigned to variables • Parts of tuples, lists, etc >>> def square(x): return x*x >>> def applier(q, x): return q(x) >>> applier(square, 7) 49
- 17. Lambda Notation Python’s lambda creates anonymous functions >>> lambda x: x + 1 <function <lambda> at 0x1004e6ed8> >>> f = lambda x: x + 1 >>> f <function <lambda> at 0x1004e6f50> >>> f(100) 101
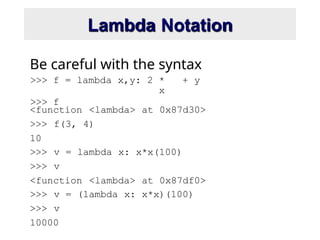
- 18. Lambda Notation >>> f = lambda x,y: 2 * x + y >>> f Be careful with the syntax <function <lambda> at 0x87d30> >>> f(3, 4) 10 >>> v = lambda x: x*x(100) >>> v <function <lambda> at 0x87df0> >>> v = (lambda x: x*x)(100) >>> v 10000
- 19. Lambda Notation Limitations Note: only one expression in the lambda body; Its value is always returned The lambda expression must fit on one line! Lambda will probably be deprecated in future versions of python Guido is not a lambda fanboy
- 20. Functional programming Python supports functional programming idioms Builtins for map, reduce, filter, closures, continuations, etc. These are often used with lambda
- 21. Example: composition >>> def square(x): return x*x >>> def twice(f): return lambda x: f(f(x)) >>> twice <function twice at 0x87db0> >>> quad = twice(square) >>> quad <function <lambda> at 0x87d30> >>> quad(5) 625
- 22. Example: closure >>> def counter(start=0, step=1): x = [start] def _inc(): x[0] += step return x[0] return _inc >>> >>> c1 c2 = counter() = counter(100, -10) >>> c1() 1 >>> c2() 90
- 23. map >>> def add1(x): return x+1 >>> map(add1, [1,2,3,4]) [2, 3, 4, 5] >>> map(lambda x: x+1, [1,2,3,4]) [2, 3, 4, 5] >>> map(+, [1,2,3,4], [100,200,300,400]) map(+,[1,2,3,4], [100,200,300,400]) ^
- 24. map + is an operator, not a function We can define a corresponding add function >>> def add(x, y): return x+y >>> map(add,[1,2,3,4], [100,200,300,400]) [101, 202, 303, 404] Or import the operator module >>> from operator import * >>> map(add, [1,2,3,4], [100,200,300,400]) [101, 202, 303, 404]
- 25. filter, reduce Python has buiting for reduce and filter >>> reduce(add, [1,2,3,4]) 10 >>> filter(odd, [1,2,3,4]) [1, 3] The map, filter and reduce functions are also at risk









![Example: closure
>>> def counter(start=0, step=1):
x = [start]
def _inc():
x[0]
+=
step
return x[0]
return _inc
>>>
>>>
c1
c2
= counter()
= counter(100, -10)
>>> c1()
1
>>> c2()
90](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction2-250724170238-8312ef57/85/Python-Introduction-2-Deep-Learning-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![map, filter, reduce
>>> def add1(x): return x+1
>>> def odd(x): return x%2 == 1
>>> def add(x,y): return x + y
>>> map(add1, [1,2,3,4])
[2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> map(+,[1,2,3,4],[100,200,300,400])
map(+,[1,2,3,4],[100,200,300,400])
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
>>> map(add,[1,2,3,4],
[100,200,300,400]) [101, 202, 303, 404]
>>> reduce(add, [1,2,3,4])
10
>>> filter(odd, [1,2,3,4])
[1, 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction2-250724170238-8312ef57/85/Python-Introduction-2-Deep-Learning-pptx-14-320.jpg)






![Example: closure
>>> def counter(start=0, step=1):
x = [start]
def _inc():
x[0]
+=
step
return x[0]
return _inc
>>>
>>>
c1
c2
= counter()
= counter(100, -10)
>>> c1()
1
>>> c2()
90](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction2-250724170238-8312ef57/85/Python-Introduction-2-Deep-Learning-pptx-22-320.jpg)
![map
>>> def add1(x): return x+1
>>> map(add1, [1,2,3,4])
[2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> map(lambda x: x+1,
[1,2,3,4]) [2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> map(+, [1,2,3,4],
[100,200,300,400])
map(+,[1,2,3,4],
[100,200,300,400])
^](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction2-250724170238-8312ef57/85/Python-Introduction-2-Deep-Learning-pptx-23-320.jpg)
![map
+ is an operator, not a function
We can define a corresponding add
function
>>> def add(x, y): return x+y
>>> map(add,[1,2,3,4],
[100,200,300,400]) [101, 202, 303, 404]
Or import the operator
module
>>> from operator import *
>>> map(add, [1,2,3,4],
[100,200,300,400])
[101, 202, 303, 404]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction2-250724170238-8312ef57/85/Python-Introduction-2-Deep-Learning-pptx-24-320.jpg)
![filter, reduce
Python has buiting for reduce and
filter
>>> reduce(add, [1,2,3,4])
10
>>> filter(odd, [1,2,3,4])
[1, 3]
The map, filter and reduce
functions are also at risk ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction2-250724170238-8312ef57/85/Python-Introduction-2-Deep-Learning-pptx-25-320.jpg)