Quality Risk Management
- 1. Basic Principles and Application in Product Development Ruchir Shah, FnD
- 3. Table of contents 1. Introduction 2. Principles of Quality Risk Management 3. General Quality Risk Management Process 4. Risk Management Methodology and Tools 5. Application of QRM process 6. Application in Product Development 7. Case study
- 4. 1. Introduction Quality Risk Management Quality Systems Harm Severity Stakeholder Product Life Cycle GMP Compliance Manage risk to patient, based on science
- 5. What is Risk? • ICH Q9 – Risk (R) is defined as the combination of the probability (P) of occurrence of harm and the severity (S) of that harm. • General Definition – Exposure to any kind of harm is Risk. • As a broad concept, risk inherently has many possible meanings depending on the individual or organization. The risk is mathematically expressed as: R = S x P. 1. Introduction
- 6. What is Quality Risk Management?
- 7. Advantages of quality risk management as technique · Improves decision making > Identifies what gives most benefit to the patient · Is scientific & data-driven > Reduces subjectivity · Ranks risk - allows prioritization > Better use of resources · Improves Product/Process understanding > Better Risk Mitigation Strategy · Benefits apply throughout product lifecycle
- 8. How Q9 interacts with Q8 and Q10 RiskfromManufacturingsite Product / Process Risk High Low HighLow Using Q9 Quality Risk Management principles Q10Pharm.QualitySystems Q8 Pharmaceutical Development
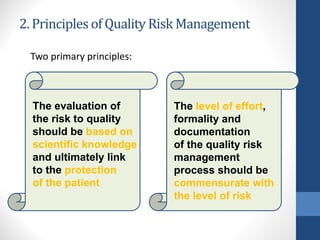
- 9. 2. Principles of Quality Risk Management Two primary principles: The evaluation of the risk to quality should be based on scientific knowledge and ultimately link to the protection of the patient The level of effort, formality and documentation of the quality risk management process should be commensurate with the level of risk
- 10. 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process Risk Review RiskCommunication Risk Assessment Risk Evaluation unacceptable Risk Control Risk Analysis Risk Reduction Risk Identification Review Events Risk Acceptance Initiate Quality Risk Management Process Output / Result of the Quality Risk Management Process RiskManagementtools 1st define a risk question i.e. Problem 2nd gather relevant information
- 11. 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process Step 1 - Risk Assessment 3 fundamental questions • Risk Identification What might go wrong? • Risk Analysis What is the likelihood (probability) it will go wrong? • Risk Evaluation What are the consequences (severity)?
- 12. 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process “What might go wrong?” • A systematic use of information to identify hazards referring to the risk question or problem • historical data • theoretical analysis • Experience Risk Assessment: Risk Identification
- 13. 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process “What is the likelihood it will go wrong?” (Probability) • The estimation (Qualitative or Quantitative) of the risk associated with the identified hazards. • Consider detectability if applicable (used in some tools) • It is data driven Risk Assessment: Risk Analysis
- 14. “What is the risk?” What are the consequences? (Severity) • Compare the Identified and Analysed risk against given risk criteria Risk Assessment: Risk Evaluation 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process
- 15. Step 2 - Risk Control: Decision-making activity · Is the risk above an acceptable level? · What can be done to reduce or eliminate risks? · What is the appropriate balance between benefits, risks and resources? · Are new risks introduced as a result of the identified risks being controlled? 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process Risk Communication – Risk acceptance or Risk Reduction Risk Review RiskCommunication Risk Assessment Risk Evaluation unacceptable Risk Control Risk Analysis Risk Reduction Risk Identification Review Events Risk Acceptance Initiate Quality Risk Management Process Output / Result of the Quality Risk Management Process RiskManagementtools
- 16. • Review the output / results of the QRM process • Take into account new knowledge and experience • Utilise planned or unplanned events • Implement a mechanism to review or monitor events • Reconsideration of risk acceptance decisions, as appropriate 3. A General Quality Risk Management Process Step 3 - Risk review: Review Events
- 17. Summary of QRM Process
- 18. Application Potentialopportunities for conducting qualityrisk management • Industry operations • Development • Facilities, equipment and utilities • Materials management • Production • Laboratory control and stability testing • Packaging and labelling · Regulatory operations > Inspection and assessment activities
- 19. Risk Management Methodology & Tools • Basic Risk Management Facilitation Method • Flow Charts • Check Sheets • Cause Effect Diagram • Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) • Break down large complex processes into manageable steps • Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) • FMEA & links severity, probability & detectability to criticality • Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) • Tree of failure modes combinations with logical operators • Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) • Systematic, proactive, and preventive method on criticality • Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP) • Brainstorming technique • Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) • Possibilities that the risk event happens • Risk ranking and filtering • Compare and prioritize risks with factors for each risk
- 20. Application In Product Development · To design a quality product and its manufacturing process > to consistently deliver the intended performance of the product (see ICH Q8) · To enhance knowledge of product performance over a wide range of > material attributes (e.g. particle size distribution, moisture content, flow properties) > processing options > process parameters
- 21. QRM as part of development · To assess the critical attributes of > Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) > Excipients > Solvents > Packaging materials · Identify critical process parameters and establish manufacturing controls · To establish appropriate specifications · To decrease variability of quality attributes: > reduce product and material defects > reduce manufacturing defects
- 22. Target Product Profile Drug substance properties; prior knowledge Proposed formulation and manufacturing process Determination of Cause – Effect relationships (Risk Identification with subsequent Risk Analysis) Risk-based classification (Risk Evaluation) Parameters to investigate (e.g. by DOE) (Risk Reduction 1. proposal; 2. verified) Product and process characteristics on the final drug product Review events Developm.Operation Research Phase 2 Phase 3 Launch Phase 1
- 23. Case Study QRM for Exhibit Bathes
- 24. QRM – Exhibit Batches • Risk question: what are the critical input and process variables that would impact drug products CQAs? • Does all relevant information/data available? • If yes then go to next step of risk assessment.
- 25. • Preliminary Risk Analysis – Empirical/Qualitative • Empirical – current practice expressed as Low, Medium, High with justification. • Qualitative – Using Suitable Tool (PHA, Risk Ranking and filtering) QRM – Exhibit Batches
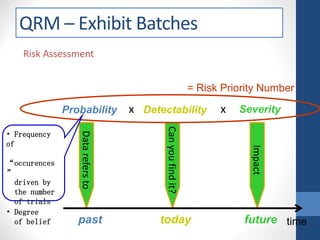
- 26. Risk Assessment Probability Detectability Severity past today future Datarefersto time Impact Canyoufindit? x x = Risk Priority Number • Frequency of “occurences ” driven by the number of trials • Degree of belief QRM – Exhibit Batches
- 27. • Identification of Tool - FMEA • Risk Scoring Scheme/Definition:- v Risk Priority No. = P x S x D QRM – Exhibit Batches
- 28. QRM – Exhibit Batches
- 29. Thank You!!!