Secure communication over fiber optic networks
- 1. Secure Communication Over Fiber Optic Networks Fiona Rozario D Y Patil School of Engg. & Technology M.E. (CN) – I 22nd March, 2016
- 2. Contents Optical Fiber Networks What are optical fibers? Working principle of optical fibers Types of optical fibers Fiber optic communication system Advantages of using fiber optics in communication Security issues in fiber optic networks Encryption systems What is encryption? Encryption schemes Optical cryptography Steganography
- 3. What are optical fibers? A flexible, transparent fiber made of glass or plastic Slightly thicker than human hair Its function is to guide visible and infrared light over long distances
- 4. What are optical fibers?
- 5. Working principle of optic fibers Total internal reflection
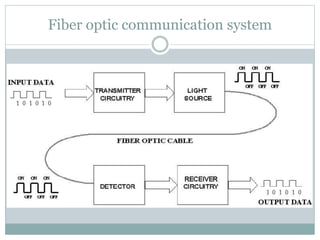
- 6. Fiber optic communication system
- 7. Advantages of fiber optics in communication networks • Longer life than copper wire • Nominal handling and installation costs • Unaffected by electromagnetic interference • Attenuation much lower than coaxial cable or twisted pair (about 0.2dB/km) • No issue of protecting against grounding and voltage problems • Higher BW offered
- 8. Security Issues Network attacks can be classified as: Service disruptions: prevents communication or degrades QoS Tapping: unauthorized access to data, compromises privacy Physical layer attacks Direct attacks: characteristics of physical elements changed Indirect attacks: introducing crosstalk
- 9. Security Issues Attacks aimed at: Network transmission – tapping, jamming
- 10. Security Issues – Direct attacks Attacks aimed at: Optical amplifiers – jamming
- 11. Security Issues – Direct attacks Attacks aimed at: Optical cross-connects – in-band and out-of-band crosstalk
- 12. Security in optical networks Security – Physical security – ensures minimum privacy of data and QoS Semantic security – protects meaning of the data even if it has already been reached by the attacker Deals with cryptopraphy
- 13. What is encryption? Mathematical altering data (plaintext) in a consistent manner to form a unintelligible ciphertext Reversible process Relies on a secret key
- 14. Encryption schemes Building blocks of all cipher algorithms: • Substitution – replace bits/characters/blocks of data with substitutes • Transposition - rearrange replace bits/characters/blocks of data
- 16. Optical encryption schemes Optical CDMA Quantum cryptography Chaos based encryptions Steganography
- 17. Optical CDMA • An optical short pulse is spread over a one-bit duration T by encoding. • The decoding time despreads the signal, reconstructing the signal if the codes between the encoder and decoder match. • The signal remains spread over T if the codes do not match.
- 18. Coherent OCDMA
- 19. Incoherent OCDMA
- 20. Elements of Quantum Cryptography Light waves are propagated as discrete quanta called photons. They are massless and have energy, momentum and angular momentum called spin. Spin carries the polarization – plane in which the electric field oscillates. Photons of different polarizations represent the different quantum states Polarization basis is the mapping we decide to use for a particular state
- 21. Quantum Cryptography Deals with secure key distribution Key transmitted at a lower rate than data but at a higher security level Key information is coded onto the quantum states of a photon
- 22. Chaos based encryption Masks the confidential data with stronger chaos Enhances robustness of data transmission
- 23. Steganography Aim – to hide the signal in the existing public channels; hacker should be unable to detect the presence of a signal
- 24. Steganography Approach 1 - temporally stretch a short optical pulse through chromatic dispersion Without the correct dispersion compensation at the receiver, signal stays buried in the noise of the public channel Attacker can use tunable dispersion compensating device to check presence of stealth signals Fine tune the device to retrieve the stealth signal
- 25. Steganography Approach 2 – Add temporal phase masks
- 26. Steganography Approach 3 - Employ ASE noise from amplifiers ASE noise from EDFA is most prevalent in optic systems ASE noise carrying stealth signal and ASE noise already existing in the system have identical spectral properties Eavesdropper cannot differentiate between the two ASE noises
- 27. Conclusion Technique Limitations Advantages OCDMA Effected by dispersions in the fiber; hence range of transmission gets limited to no longer than 100 km [3]. It is a multiple access system; plurality of codes can exist in the same channel. Confidentiality is not as strong as that provided by data encryption. Chaos based encryption Synchronization of receiver and transmitter is critical to proper functioning. It is very difficult to get lasers of the same parameters for synchronization. There is high level of robustness at high bit rates It can create jamming as well as avoid jamming to a high degree. Quantum cryptography Use of amplifiers will change the qubits. Hence the range of transmission is limited. This method can notify of interception of data [12]. It needs a dedicated channel of high quality for key exchange between every pair of sender and receiver. Hence multiplexing is not possible. Very vulnerable to jamming. Optical steganography: (a) Temporal stretching of pulse Data can be intercepted using tunable dispersion compensation devices. Simplest in implementation. (b) Temporal phase mask Robust against adversary attacks. (c) ASE noise Optical delays between receiver and transmitter must be matched exactly to get the stealth signal. Public channel does not induce any power penalty on the stealth channel and the stealth channel induces a power penalty of only 0.2- 0.3 dBm on the public channel.


























![Conclusion
Technique Limitations Advantages
OCDMA Effected by dispersions in
the fiber; hence range of
transmission gets limited to
no longer than 100 km [3].
It is a multiple access
system; plurality of codes
can exist in the same
channel.
Confidentiality is not as
strong as that provided by
data encryption.
Chaos based encryption Synchronization of receiver
and transmitter is critical to
proper functioning. It is very
difficult to get lasers of the
same parameters for
synchronization.
There is high level of
robustness at high bit rates
It can create jamming as
well as avoid jamming to a
high degree.
Quantum cryptography Use of amplifiers will
change the qubits. Hence
the range of transmission is
limited.
This method can notify of
interception of data [12].
It needs a dedicated channel
of high quality for key
exchange between every
pair of sender and receiver.
Hence multiplexing is not
possible.
Very vulnerable to
jamming.
Optical steganography:
(a) Temporal stretching of
pulse
Data can be intercepted
using tunable dispersion
compensation devices.
Simplest in implementation.
(b) Temporal phase mask Robust against adversary
attacks.
(c) ASE noise Optical delays between
receiver and transmitter
must be matched exactly to
get the stealth signal.
Public channel does not
induce any power penalty
on the stealth channel and
the stealth channel induces
a power penalty of only 0.2-
0.3 dBm on the public
channel.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar1-securecommunicationoverfiberopticnetworks-160703154858/85/Secure-communication-over-fiber-optic-networks-27-320.jpg)